Option A topic outline
advertisement
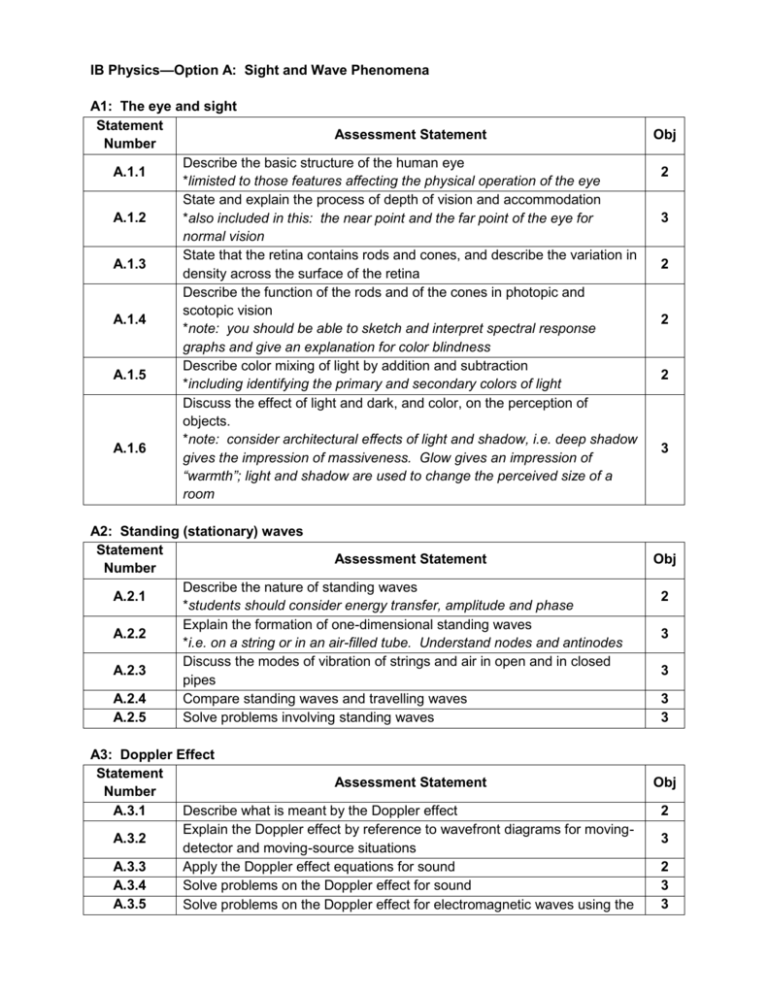
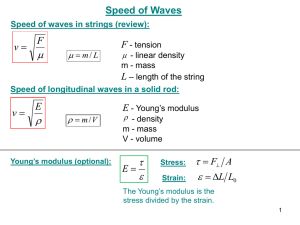
IB Physics—Option A: Sight and Wave Phenomena A1: The eye and sight Statement Assessment Statement Number Describe the basic structure of the human eye A.1.1 *limisted to those features affecting the physical operation of the eye State and explain the process of depth of vision and accommodation A.1.2 *also included in this: the near point and the far point of the eye for normal vision State that the retina contains rods and cones, and describe the variation in A.1.3 density across the surface of the retina Describe the function of the rods and of the cones in photopic and scotopic vision A.1.4 *note: you should be able to sketch and interpret spectral response graphs and give an explanation for color blindness Describe color mixing of light by addition and subtraction A.1.5 *including identifying the primary and secondary colors of light Discuss the effect of light and dark, and color, on the perception of objects. *note: consider architectural effects of light and shadow, i.e. deep shadow A.1.6 gives the impression of massiveness. Glow gives an impression of “warmth”; light and shadow are used to change the perceived size of a room A2: Standing (stationary) waves Statement Assessment Statement Number Describe the nature of standing waves A.2.1 *students should consider energy transfer, amplitude and phase Explain the formation of one-dimensional standing waves A.2.2 *i.e. on a string or in an air-filled tube. Understand nodes and antinodes Discuss the modes of vibration of strings and air in open and in closed A.2.3 pipes A.2.4 Compare standing waves and travelling waves A.2.5 Solve problems involving standing waves A3: Doppler Effect Statement Assessment Statement Number A.3.1 Describe what is meant by the Doppler effect Explain the Doppler effect by reference to wavefront diagrams for movingA.3.2 detector and moving-source situations A.3.3 Apply the Doppler effect equations for sound A.3.4 Solve problems on the Doppler effect for sound A.3.5 Solve problems on the Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves using the Obj 2 3 2 2 2 3 Obj 2 3 3 3 3 Obj 2 3 2 3 3 approximation: f A.3.6 v f c Outline an example in which the Doppler effect is used to measure speed. *i.e. blood-flow measurements; radar guns used to measure vehicle speeds A4: Diffraction Statement Assessment Statement Number Sketch the variation with angle of diffraction of the relative intensity of light A.4.1 diffracted at a single slit. A.4.2 A.4.3 Derive the formula: for the position of the first minimum of the b diffraction pattern produced at a single slit Solve problems involving single-slit diffraction 2 Obj 3 3 3 A5: Resolution Statement Assessment Statement Number Sketch the variation with angle of diffraction of the relative intensity of light A.5.1 emitted by two point sources that has been diffracted at a single slit. State the Rayleigh criterion for images of two sources to be just resolved A.5.2 *including the criterion for a circular aperture: 1.22 Obj 3 1 b A.5.3 A.5.4 Describe the significance of resolution in the development of devices such as CDs and DVDs, the electron microscope and radio telescopes Solve problems involving resolution A6: Polarization Statement Assessment Statement Number A.6.1 Describe what is meant by polarized light A.6.2 Describe polarization by reflection A.6.3 State and apply Brewster’s law A.6.4 Explain the terms polarizer and analyser Calculate the intensity of a transmitted beam of polarized light using A.6.5 Malus’ law A.6.6 Describe what is meant by an optically active substance Describe the use of polarization in the determination of the concentration A.6.7 of certain solutions A.6.8 Outline qualitatively how polarization may be used in stress analysis A.6.9 Outline qualitatively the action sof liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). A.6.10 Solve problems involving the polarization of light 2 3 Obj 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3