3.1 Permutations With Non
advertisement

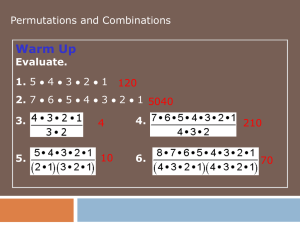
3.1 Permutations With Non-Ordered Elements Learning Goals I am learning to Recognize the advantages of different counting techniques Make connections between situations that involve permutations and combinations Investigate Permutations With Identical Elements 1. List all the permutations of coloured blocks with the following conditions: a) Two of one colour, two of different colours b) Two of one colour, two of another colour c) Two of one colour, three of another colour 2. Raj counted all of the permutations of 3 red, 2 blue, and 2 yellow blocks and found there were 210 possible arrangements. Explain how the number of arrangements relates to the types of blocks in the set. 3. Assume you know the number of arrangements of n objects when p, q, r, … of them are alike. Make a hypothesis of what you would multiply by to get the total number of arrangements if the objects were all different. Test your hypothesis. Example 1 Permutations With Like Elements Compare the number of arrangements of the sets of letters AaBC and AABC. Permutations With Like Objects In example 1, we could multiply the number of arrangements of AABC by 2! To determine the number of arrangements of AaBC. You can also divide the number of arrangements of AaBC by 2! To determine the number of arrangements of AABC. The number of permutations of 𝑛 elements, when 𝑝 of one type are identical, 𝑞 of another type are identical, 𝑟 of another type are identical and so on, is 𝑛(𝐴) = 𝑛! . 𝑝!𝑞!𝑟!… Example 2 Permutations With Several Identical Elements During a lunch rush the customers at a chip truck order 14 poutine, 6 hamburgers and 2 hot dogs. In how many ways could these outcomes have happened? Example 3 Arrangements of the Letters in Gana’s Name How many arrangements are there in Gana’s surname (EASWARASUBRAMANIAM)? Example 4 Distinct Objects in a Fixed Order How many ways are there to arrange the letters in the word NUMBER if the consonants must remain in the original order? Reflect R1. Explain why there are not 9! Arrangements of the letters in the word LAKESHORE R2. Which has a greater number of permutations: two blue blocks and four red blocks or two math textbooks and four science textbooks? Explain. Success Criteria I will know I'm successful when I can • • • • • write a permutation to express the number of possible arrangements of a set of unique objects write a permutation to express the number of possible arrangements of a set of objects of which some are identical. use permutations to determine the number of arrangements of distinct objects in a fixed order. recognize situations that use permutations. solve problems involving permutations with distinct and identical objects. Homework p. 108 #1 – 5, 7 – 16, 19