Respiration Student Write up
advertisement
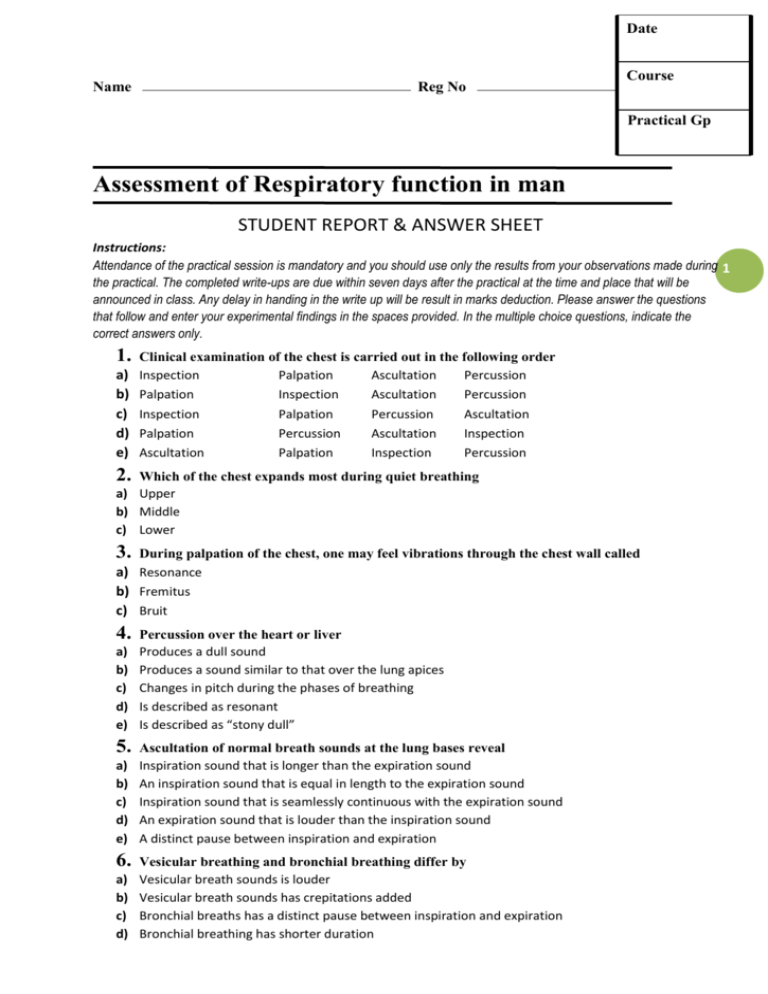
Date Name Reg No Course Practical Gp Assessment of Respiratory function in man STUDENT REPORT & ANSWER SHEET Instructions: Attendance of the practical session is mandatory and you should use only the results from your observations made during 1 the practical. The completed write-ups are due within seven days after the practical at the time and place that will be announced in class. Any delay in handing in the write up will be result in marks deduction. Please answer the questions that follow and enter your experimental findings in the spaces provided. In the multiple choice questions, indicate the correct answers only. 1. a) b) c) d) e) Clinical examination of the chest is carried out in the following order Inspection Palpation Ascultation Percussion Palpation Inspection Ascultation Percussion Inspection Palpation Percussion Ascultation Palpation Percussion Ascultation Inspection Ascultation Palpation Inspection Percussion 2. Which of the chest expands most during quiet breathing a) Upper b) Middle c) Lower 3. During palpation of the chest, one may feel vibrations through the chest wall called a) Resonance b) Fremitus c) Bruit 4. a) b) c) d) e) 5. a) b) c) d) e) 6. a) b) c) d) Percussion over the heart or liver Produces a dull sound Produces a sound similar to that over the lung apices Changes in pitch during the phases of breathing Is described as resonant Is described as “stony dull” Ascultation of normal breath sounds at the lung bases reveal Inspiration sound that is longer than the expiration sound An inspiration sound that is equal in length to the expiration sound Inspiration sound that is seamlessly continuous with the expiration sound An expiration sound that is louder than the inspiration sound A distinct pause between inspiration and expiration Vesicular breathing and bronchial breathing differ by Vesicular breath sounds is louder Vesicular breath sounds has crepitations added Bronchial breaths has a distinct pause between inspiration and expiration Bronchial breathing has shorter duration e) Bronchial breathing is normal over the lung bases 7. How does vesicular and bronchial breath sounds compare. Use the table below to describe the characteristics of vesicular and bronchial breath sounds and highlight their differences. Attribute Vesicular breathing Bronchial breathing Relative period of time heard 2 Heard throughout the mechanical chest movement Loudness Pitch Pause between inspiration and expiration phases 8. From the diagram below name the parts labelled A to D from the list provided by writing the number against the name in the appropriate 1. Filter 7 A 2. Mouth piece 3. Bell spirometer 6 B 4. Pre-amplifier 5. Respirometer pod C 1 6. Flow head 7. Plastic tubing D 2 3 9. Functions or purposes of the identified structures A B C D 10. Which respiratory volume is not measurable by spirometry Record of experimental findings Enter the values of the Respiratory parameters obtained during the experiment and their correct units in the appropriate column. Respiratory parameter Abbreviation Units Experimental & calculated value Individual Respiratory Rate f Tidal Volume VT Expired Minute volume VE Inspiratory Reserve Volume IRV Inspiratory Capacity IC Expiratory Reserve Volume ERV Expiratory Capacity EC Vital Capacity VC predicted VC measured Residual Volume RV = VC x 0.25 Total Lung Capacity TLC = VC + RV Functional Residual Capacity FRC Peak Inspiratory Flow PIF Peak Expiratory Flow PEF Forced Vital Capacity FVC Forced Expired Volume in 1 sec FEV1 FEV1/FVC (Percentage) Group average FEV1 Gp Average 4 Forced Respiration (FEV and FVC) 11. How is FEV1 and the FEV1/VC ratio affected by a. Resistance to air-flow b. Restriction of lung expansion 5 Breath holding duration during various respiratory activities. Condition Breath hold duration (sec) Following Stable normal breathing Breath hold after inhalation Breath hold after exhalation 12. Explain the differences in the duration of breath holding (after inhalation and after exhalation) and describe the physiological mechanisms involved: Condition Breath hold duration (sec) After hyperventilating for 30 seconds Breath hold after inhalation Breath hold after expiration 13. Explain the differences in the duration of breath holding (where the procedure is preceded by quiet breathing and when preceded by hyperventilation) and describe the physiological mechanisms involved: The effect of hyperventilation on breathing rate Condition Breathing rate (breaths/min) Normal breathing First minute after Hyperventilation 14. Describe and explain the changes in the rate of breathing observed. To support your answers, please attach copies of the PowerLab zoom window tracings showing: a. Lung volumes and capacities b. Flow and Volume channels during the forced breathing experiment 6