Cultural Proficiency Continuum for Closing Gaps
advertisement
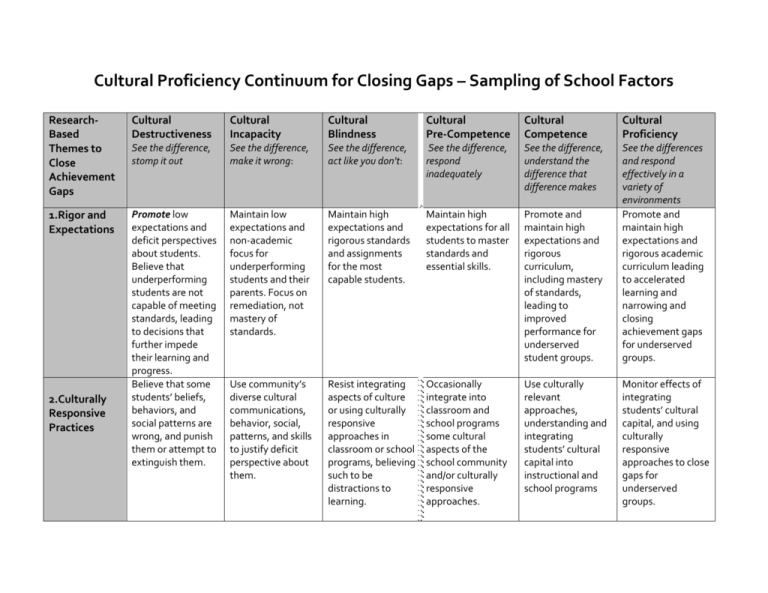
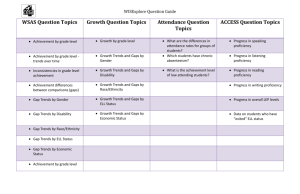
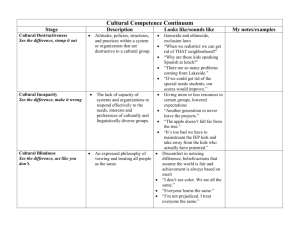
Cultural Proficiency Continuum for Closing Gaps – Sampling of School Factors ResearchBased Themes to Close Achievement Gaps Cultural Destructiveness Cultural Incapacity Cultural Blindness Cultural Pre-Competence Cultural Competence Cultural Proficiency See the difference, stomp it out See the difference, make it wrong: See the difference, act like you don't: See the difference, respond inadequately See the difference, understand the difference that difference makes 1.Rigor and Expectations Promote low expectations and deficit perspectives about students. Believe that underperforming students are not capable of meeting standards, leading to decisions that further impede their learning and progress. Believe that some students’ beliefs, behaviors, and social patterns are wrong, and punish them or attempt to extinguish them. Maintain low expectations and non-academic focus for underperforming students and their parents. Focus on remediation, not mastery of standards. Maintain high expectations and rigorous standards and assignments for the most capable students. Maintain high expectations for all students to master standards and essential skills. Promote and maintain high expectations and rigorous curriculum, including mastery of standards, leading to improved performance for underserved student groups. See the differences and respond effectively in a variety of environments Promote and maintain high expectations and rigorous academic curriculum leading to accelerated learning and narrowing and closing achievement gaps for underserved groups. Use community’s diverse cultural communications, behavior, social, patterns, and skills to justify deficit perspective about them. Resist integrating aspects of culture or using culturally responsive approaches in classroom or school programs, believing such to be distractions to learning. Occasionally integrate into classroom and school programs some cultural aspects of the school community and/or culturally responsive approaches. Use culturally relevant approaches, understanding and integrating students’ cultural capital into instructional and school programs 2.Culturally Responsive Practices Monitor effects of integrating students’ cultural capital, and using culturally responsive approaches to close gaps for underserved groups. ResearchBased Themes to Close Achievement Gaps 3. Instructional Supports Cultural Destructiveness Cultural Incapacity Cultural Blindness Cultural Pre-Competence Cultural Competence Cultural Proficiency See the difference, stomp it out See the difference, make it wrong: See the difference, act like you don't: See the difference, respond inadequately See the difference, understand the difference that difference makes Teachers believe that only some students are capable of rigorous work. They promote high expectations and rigorous work for some students while focusing on teacher-directed instruction, passive student learning, and lower level tasks for struggling students. Teachers provide all students the same opportunity to learn. They believe that all students can succeed at high levels if they try and that some are naturally inclined to succeed and others are not, regardless of the level of intervention of the teacher. This belief often leads to some students not receiving the necessary individual learning support needed to be successful. Teachers understand that some students need individual learning support . They differentiate content, resources, materials, and strategies to help students access rigorous content, inconsistently or inappropriately, which may meet the needs of some students but not others. Teachers select, use, develop, and scaffold content, resources, materials and strategies based on students’ interests and needs. They assist all students to access and navigate rigorous content leading to student engagement and success. See the differences and respond effectively in a variety of environments Teachers routinely select, use, develop, and cocreate with students content, resources, materials, and strategies that ensure that all students navigate rigorous content leading to student engagement and success. Such practices are monitored for their effectiveness in narrowing or closing gaps between student groups. ResearchBased Themes to Close Achievement Gaps Cultural Destructiveness Cultural Incapacity Cultural Blindness Cultural Pre-Competence Cultural Competence Cultural Proficiency See the difference, stomp it out See the difference, make it wrong: See the difference, act like you don't: See the difference, respond inadequately See the difference, understand the difference that difference makes 4. Use of Data Manipulate data to promote deficit perspectives about some students and to justify withholding resources Use data to sort students into tracks or to make decisions that have negative consequences for them. Resist analyzing disaggregated data believing that instructional decisions should be based what students demonstrate on assessments through item analysis. Consider disaggregated data and the needs of students groups or individual students to make decisions which may not improve student learning. Examine student learning data, demographic data, and data on instructional practices to shape effective instruction and classroom/school decision making. See the differences and respond effectively in a variety of environments Examine student learning data, demographic data, and data on instructional practices to shape effective instruction and classroom/school decision making. Decisions are monitored for their effectiveness on closing learning gaps. Adjustments are made as needed. ADAPTED From Stephanie Graham Consultant II, Equity and Student Achievement http://www.avid.org/dl/eve_natcon/nc12_creating_cultural_proficiency_handout1.pdf