Fall Physics Review 2015_ANSWERS
advertisement

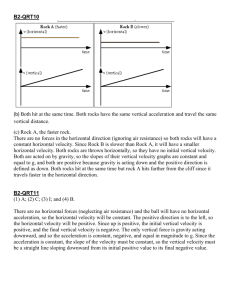
Fall Physics Review VECTORS 1. What is the resultant net force of adding together vectors F1 and F2? 21.2 N northeast 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. F1 = 15 N North F2 = 15 N East A student is traveling up a river in a motorboat at a velocity of 40 km/hr[E] relative to the bank. The student throws a ball to the back of the boat at a velocity of 20 km/hr[W] relative to the boat. What is the velocity of the ball relative to the bank? 20 km/h E An airplane has a velocity of 350 km/hr[S] relative to the air. A 60 km/hr wind is blowing towards the east. What is the velocity of the airplane relative to the ground? 355 km/hr SE List examples of scalar quantities distance, speed, mass, power List examples of vector quantities displacement, velocity, work A student walks 50 meters along a hallway that heads due north, then turns and walks 20 meters along another hallway that heads due east. What is the magnitude of the student’s resultant displacement? 53.85 m Under what circumstance would both the horizontal and vertical components be the same in magnitude? The vector is directed at a 45° angle to a horizontal line. MOTION 1. List facts about the movement of an object with zero acceleration. constant velocity, stationary 2. When velocity is negative and acceleration is negative, what happens to the object’s motion? The object speeds up 3. A bicycle travels 15 km in 45 min. Its average velocity is 0.33 km/min 4. An airplane requires 15 s and 300 m of runway to become airborne, starting from rest. Its velocity when it leaves the ground is 40 m/s 5. A softball fast-pitch flies at 40 meters per second. If the batter is 15 meters from the pitcher, approximately how much time does it take for the ball to reach the batter? 0.38 s 6. A car has an initial velocity of 15 m/s and an acceleration of 1.0 m/s 2. In the first 10 s after acceleration begins, the car travels how far? 200 m 7. A race car traveling at 10 m/s accelerates at the rate of 1.5 m/s2 while traveling a distance of 600 m. The final velocity of the race car is approximately 44 m/s 8. How long does a car with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 take to go from 10 m/s to 30 m/s? 10 s 9. What is acceleration? Rate of change in velocity (rate of change of speed in a particular direction, rate of change in the rate of motion in a particular direction) 10. A 1000 kg car traveling with a velocity of 20 m/s decelerates uniformly at -5.0 m/s until it comes to rest. a. What is the total distance the car travels as it decelerates to rest? 40 m b. What is the time that it takes for the car to come to rest? 2 s 11. Describe the motion in each section on the velocity-time below. Constant acceleration, constant velocity/zero accel, constant deceleration, constant acceleration 2 FREE FALL & PROJECTILE MOTION 1. A stone is thrown downward from a roof at the same time as an identical stone is dropped from there. Describe the relationship between the two stone’s time they hit the ground thrown downward hits first, their velocities stone thrown downward is going faster hits ground, and their accelerations BOTH have the same acceleration because gravity is providing the acceleration (9.8 m/s2). 2. A rock flies horizontally off the edge of the cliff at a velocity of 35 m/s. If the canyon below is 90 m deep, how far from the edge of the cliff does the rock land? 150.15 m 3. A ball thrown vertically upward at 35 m/s continues to rise for how long? 3.57 s 4. When there is no air resistance, objects of different masses fall with equal/different accelerations with similar/different displacements. 5. A basketball is dropped from a balcony 1.5m high. What is the ball’s velocity as it hits the ground? 5.42 m/s 6. What is the relationship between launch angle and the time of flight? The larger the angle, the more time it stays in the air 7. If a projectile is launched horizontally from two different heights, what factors change? Remain the same? Different: final velocity, horizontal distance, vertical distance, time / Same: acceleration FORCES 1. A hockey stick hits a puck on the ice. Identify an action-reaction pair, and compare the forces exerted by each object. Stick exerts force on puck and puck exerts force on stick 2. A stationary object remains stationary and a moving object continues to move because of inertia (Newton’s 1st law) 3. Definition of inertia an object with no net force acting on it remains at rest or in motion with a constant velocity. 4. Newton’s first law of motion law of inertia (see above def) 5. Newton’s second law of motion Force is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration of the object (1 force & 1 object) 6. Newton’s third law of motion for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction (2 forces & two objects) 7. What is the relationship between mass and acceleration when the force is held constant? They are inversely proportional If the mass is doubled, what happens to the acceleration? halved 8. When a bird hits the windshield of a moving car, the force acting on the bird is equal to the car. 9. The mass of a sack of potatoes whose weight is 200 N is 20.41 kg 10. A stone is dropped from a cliff. After it has fallen 25 m, what is its velocity? 22.14 m/s 11. If the force of gravity on a balloon is 4500 N, and the upward lift force provided by the atmosphere is 3300 N, in which direction is the net force acting? down 12. A 5 N force is required to keep a 40 N object moving at a constant velocity over a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the object and the surface is 0.125 13. An object with a mass of 5 kg is accelerated at 3 m/s2. The net force on the object is 15 N 14. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on a 3.0 x 103 kg car as it accelerates from rest to a speed of 20 m/s in 6.0 s? 10,000 N 15. A book rests on a table. Describe the forces involved. FN is up, Fg is down 16. A 600 N person is standing in an elevator. If the upward force by the elevator on the person is 400 N, the person is moving in which direction? down 17. Which of these objects has the greatest inertia? D 18. Two forces are applied to a 2.0 kg block on a frictionless, horizontal surface, as shown in the diagram to the right. What is the acceleration of the block? 3 m/s2 to right 19. A horizontal force is used to pull a 5.0 kg cart at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s across the floor, as shown in the diagram below. If the force of friction between the cart and the floor is 10 N, the magnitude of the horizontal force along the handle of the cart is 10 N 20. Draw a free body diagram of a 45kg object that is moving at a constant velocity with a frictional force of 30N and an applied force of 30N. FN Ff = 30 N 45 kg Fapp = 30 N Fg = 441 N a. What is the magnitude normal force? 441 N 21. If an object is moving horizontally at a constant speed, what is true about the horizontal and vertical forces acting on the object? All forces are balanced. All horizontal forces are the same and all vertical forces are the same. 22. How do you calculate the normal force acting on an object on an incline? FN = FgcosΘ On a horizontal surface? FN = Fg 23. Which string has more tension force? 1 24. What is the tension in each string if the mass is 10 kg? 69.3 N CIRCULAR MOTION & GRAVITY 1. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between an electron (mass of electron = 9.11 x 10 -31 kg) and a proton (mass of proton = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) separated by a distance of 2.0 x 10-9 m? 2.54 x 10-50 N 2. What is the weakest force in nature? Gravitational 3. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the force of attraction between any two masses is directly related to the product of the two masses 4. A tornado is whirling debris around its outer edge in a horizontal circle. If the debris are seen to move at 40 m/s and have a centripetal acceleration of 20 m/s2, what is the radius of the tornado at the level where the debris are whirling? 80 m 5. The diagram to the right shows an object traveling clockwise in a horizontal, circular path at constant speed. Draw an arrow to show the direction of the centripetal acceleration acting on the object. 6. What is the relationship between force of attraction (gravitational force) between two masses and the distance between them? Inversely proportional: cut distance in half, the force will multiply by four because distance is squared and in the denominator. 7. What is the gravitational force between two motorcycles, each with a mass of 200 kg that are 3 meters apart? 2.96 x 10-7 N 8. There are two tracks with two cars of the same mass. Car A is on the outside track while car B is on the inside track. a. Which car has greater angular velocity? same b. If both have the same tangential velocity, which car has the greater centripetal force? B c. If both complete the lap in the same amount of time, which car must have the greater tangential velocity? A