Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri
advertisement

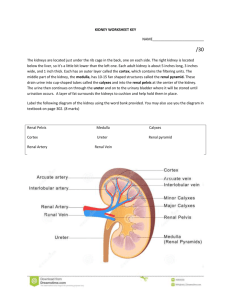
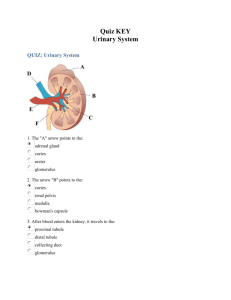
Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri Self test questions 1. Given below is a list of substances—select the ones that need to be got rid off from the body. Glucose, excess water, amino acid, urea, carbon dioxide, excess common salt, glycogen, uric acid. Ans: excess common salts, excess water, urea, carbon dioxide, uric acid. 2. Undigested and unabsorbed food which passes out is termed as excreta in popular language. Is it a kind of excretion? Ans: No! all the undigested food are not directly involved in the cellular metabolism, excretion refers to the all the activities that are taking place in the cellular metabolism. All wastes that has been produced from the each cells are collected by the circulatory system and majors separation happens in the kidney and others surfaces of the body. Name the following: i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi) The tube arising from the notch of the kidney on the median side and connecting behind with the urinary bladder. Ans: ureter The tube that passess the urine to the outside of the body. Ans: Urethra The inner lighter coloured region of the kidney. Medulla Knot-like mass of blood capillary inside Bowmann’s capsule. Ans: Glomerulus The structural and functional unit of kidney Ans:Nephron/uriniferous tubule State if the following statements are true or false. i) The blood flows through glomerulus under great pressure Ans: True ii) Glomerulus filtrate consists of many substances such as water, salts, glucose and white blood corpuscles Ans: True iii) Sodium Chloride contained in glomerulus filtrate is fully reabsorbed in the renal tubule Ans: False Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri iv) Besides the normal constituents, the urine may pass out excess vitamins but not the antibodies Ans: False v) Excessive uric acid and urine may produce Kidney stones [Ans: True] Review questions: 1. Select the correct answer out of the four available choices given under each. a) Excretion primarily involves i. Removal of all byproducts during catabolism ii. Removal of by products during anabolism iii. Removal of nitrogenous wastes iv. Throwing out excess water. Ans: Removal of nitrogenous wastes b) Maximum amount of water from the glomerulus filtrate is absorbed in i. Proximal convoluted tubule ii. Descending limbs of loop of Henle iii. Ascending limb of loop of Henle iv. Distal convoluted tubule Ans: proximal convoluted tubule c) Sodium reabsorption occurs in kidney tubules under the influences of i. Amount of sodium in the blood ii. Amount of sodium in the urine iii. The hormone rennin iv. ADH Ans: ADH d) Which one of the following is not an excretory activity? i. Removal of carbon dioxide ii. Removal of faecal matter iii. Removal of sweat due to perspiration iv. Removal of urea v. Ans: Removal of faecal matter e) In Human urea is formed in i. Body tissue ii. Liver iii. Spleen iv. Kidney Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri Ans: Liver 2. Name the following: a. The organ which produces urea [ liver] b. The outer part of kidney containing the Bowmann’s Capsule [ Malphigian capsule] c. The tuft of capillaries in a nephron [ Glomerulus] d. The part where the term urine is first use for the fluid in it. [Ureter] e. The vein in which urea concentration is maximum [ Renal vein] Define the following terms: a. Ultrafiltration The blood flows through the glomerulus under great pressure which is much greater than in the capillaries elsewhere. The reason for this greater pressure is that the efferent arteriole is narrower than the afferent incoming arteriole. This high pressure hydrostatic pressure causes the liquid parts of the blood to filter out form the glomerulus into the renal tubule. This filtration under extraordinary force is called ultrafiltration. b. Micturition urine is expelled from urinary bladder through urethra by relaxation of urinary bladder into urinary bladder into urethra under impulse form the nervous system. Such a process is called micturition. c. Renal pelvix the front end of the ureter is somewhat expanded into the kidney and is called pelvis. d. Urea urea is highly poisonous nitrogenous wastes produced as results of the metabolites waste from the cells. If allowed to accumulate in the blood to a certain level it causes death. e. Osmoregulation the kidney while removing wastes like urea from the blood also regulates its composition. i.e. the percentage of water and salts. This function is called osmoregulation. 3. Look at the figure given below. It is a section of Human Kidney as seen from the front. Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri a. Is it the left kidney or the right one? Give reason for your answer. Ans: It is right kidney b. Is it longitudinal section or a cross section? Ans: it is longitudinal section c. Name the part numbered 1-6 1 Pelvis 2Renal Artery 3Ureter 4 cortex 5 Papilla 6 Pyramid 4. a) b) c) d) e) 5. Write down the functional activity of the given organs. Glomerulus ultrafiltration Henle’s loop selection reabsorption Ureter collect the urine and transfer to urinary bladder Renal artery carries impure blood for filtration Urethra excrete out the wastes as urine Given below are two sets of five terms. Rewrite the terms in correct order to be in logical sequences. a) Afferent arteriole, renal vein, capillary network, glomerulus, efferent arteriole. Ans: Afferent arteriole, capillary network, glomerulus, efferent arteriole, renal vein b) Renal artery, urethra, ureter, kidney, urinary bladder Ans: Renal artery, kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra. 6. Why is excretion necessary? Name the common excretory substances in our body. Ans: A large number of waste products are formed during the metabolic activities in the body. These products become toxic or harmful if retained inside. Large amounts of carbond dioxide and water are produced by metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein. Nitrogenous wastes such as ammonia, urea, uric acid etc.. Are formed protein and other complex nitrogenous compound. The wastes are carbon dioxide, water and nitrogenous waste. 7. What is uriniferous tubule? How does it function? Ans: The kidney is composed of an enormous number of minute tubules called uriniferous tubules; these are the structural as well as functional units of the kidney. The blood flows through the glomerulus under great pressure which is much greater than in Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri the capillaries elsewhere, this high pressure causes the liquid part of the blood to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal tubule. This filtration under force is ultrafiltration. During ultrafiltration almost all the liquid part of the blood comes out the glomerulus and passes into the funnel-shaped cavity of the Bowmann’s capsule, the fluid entering the renal tubule is called the glomerulus filtrate consist of water, urea, salts, glucose and other plasma. Thus blood proceeding away from the glomerulus is relatively thick. The glomerular filtrate entering the renal tubule is not urine. It is an extremely dilute solution containing a lot of usable materials including glucose and some salts such as those of sodium. As the filtrate passes down the tubule, much of the water is reabsorption is only to the extent of that the normal concentration of the blood is not disturbed. This is called selective absorption. Certain substance like K+ions in the normal course, and large number of foreign chemicals including drug like penicillin are passed into the forming urine in the distal convoluted tubule. This passage involves the activity of the cells of the tubular wall, and hence it is called tubular secretion. 8. Why is it necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood? Ans: The kidney while removing wastes like urea from the blood also regulates its composition, i.e. the percentage of water and salts. This function is osmoregulation and its implies the regulation of osmotic pressure of the blood. 9. If you donate one kidney to a needy patient, would it cause any harm to you? Give reason. Ans: if one kidney is donated for the needy patient, another kidney is sufficient for excretory needs and the person can lead a normal life. There is no harm in donating a single kidney, however, both malfunctioning kidney may lead to the death. 10. In summer the urine is slightly thicker than in winter. Explain why? Ans: we urinated fewer times in summer tank in winter and the urine passed is generally thicker, the reason is obvious, we lose a considerable part of water through perspiration and the kidneys have to reabsorb more water from the ureine making it more concentrated. 11. Differentiate between the following pairs of terms: a. Bowman’s Capsule and Malpighian capsule b. Renal cortex and renal Medulla c. Renal Pelvis and Renal medulla d. Renal pelvis and papilla e. Urea and urine Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri Bowman’s capsule It is thin-walled cup, something like a hollow ball pressed deep on one side. Its hollow internal space continuous into the tubule. Renal cortex Malpighian Capsule The Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus together are called Malpighian capsule or just renal capsule Renal Medulla It is outer region of LS of kidney with dark cortex. Inner lighter region of LS of Kidney which is composed of a finely striped substance arranged in several pyramid. Renal Pelvis The front end of the ureter is somewhat expanded into the kidney is called Pelvis Renal medulla Inner lighter region of LS of Kidney which is composed of a finely striped substance arranged in several pyramid. Renal pelvis The front end of the ureter is somewhat expanded into the kidney is called Pelvis Papilla The apex of each pyramid prject into the Pelvis of the Kidney Urea It is chief nitrogenous that our body needs to be got rid off. Urine It is ultimate products of urine containing some salts and all metabolic wates 12 . What is dialysis? Under what condition is it carried out? Ans: If therer is failure of both the kidneys would lead to death. Artificial Kidney is a dialysis Machine. The patient’s blood is led from the radial artery in his arm through the machine where the urea and excess salts are removed and the purified blood is returned to a vein in the same arm. In cases of permanent damge to the kidney dialysis is to be repeated for about twelves hours twice a week. 13. Name the main nitrogenous metabolic waste excreted out by mammals. Ans: these include urea, uric acid, Ammonia. Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri 14. Given alongside is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the question that follow; a. Name all the organ system shown completely or Partially Ans: Excretory system and circulatory system b. Name the parts numbered 1-6 Ans: 1Glomerulus 2Proximal convoluted tubule 3Henle’s loop 4 Bowman’s Capsule 5 Distal convoluted tubule 6 Ureter c. Name the structural and functional unit of the part marked ‘1’ Ans: uriniferous tubule d. Name the two main organic constituent of the fluid that flows down the part labelled ‘3’ Ans: Glucose & Vitamin e. Name the two major steps involved in the formation of the fluid that passes down the the part labelled ‘3’ Ans: Tubular secretion & Selective Reabsorption. 15. Fill in the blanks in the following passages to make a meaningful description In a Nephron, the ………blood …………flows through the…Glomerulus………under great pressure. The reason for this great pressure is Excretory system- Shankarlal Chhetri that the…………efferent arteriole……(outgoing)…….is narrower than the ……………afferent arteriole……(incoming). This high pressure causes the Liquid………….part of the blood to filter out from the ……Glomerulus….into the………Renal…....Capsule 16. The following diagram represented a mammalian kidney tubule and its blood supply. Parts indicated by the guidelines 1-8 are as follows Math the items in Column I with those in Column II i) Bowman’s Capsule a. Renal artery ii) Contains more CO2 and less Urea b. Regulates amount of water excreted iii) Antidiuretic Hormone c. Renal vein iv) Contains more urea d. Glomerulus Ans: Bowman’s capsule Glomerulus Contains more CO2 and less Urea Renal Vein Antidiuretic Hormone Regulates amount of water excreted Contains more urea Renal Artery.