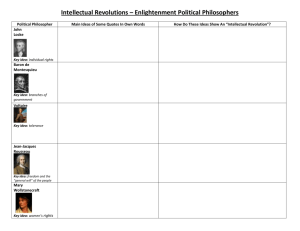
Study guide – CDA Unit 1a - Review the following The philosophers
advertisement

Study guide – CDA Unit 1a - Review the following The philosophers Locke – Life, Liberty and Property Hobbes – in the state of nature life is “nasty, short and brutish” Montesquieu – developed the 3 branches of government Social Contract Theory – idea the government is a contract between governed and the government - people have to consent –Force – fighting, so need projection in side walls -- Divine Right – rule by deity or God - Evolutionary – family unit developed into the government systems over time Magna Carta - 1st document limiting the power of government - 1215 The English Petition of Rights – established the rights of the English people – 1689 Forms of GovernmentDemocratic – ruled by the people- direct – every vote counts – indirect – republic - representatives Oligarchic – rule by the few or small group - example - Communist- China Autocratic – rule by one – absolute monarchy or dictator – example Saudi Arabia – absolute monarchy Forms of Power distribution in government – Unitary –one person or one group – all power in national or central govt. Federal – power distribution between national and states - key words divided or separated Confederation – loose voluntary alliance between states or countries for a common goal Declaration of Independence – Why was it written? To motivate American’s to free themselves from England Who was the Author? Thomas Jefferson What are the unalienable rights? Rights granted to every person by birth – life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness Study guide – CDA Unit 1a - Review the following The philosophers Locke – Life, Liberty and Property Hobbes – in the state of nature life is “nasty, short and brutish” Montesquieu – developed the 3 branches of government Social Contract Theory – idea the government is a contract between governed and the government - people have to consent –Force – fighting, so need projection in side walls -- Divine Right – rule by deity or God Evolutionary – family unit developed into the government systems over time Magna Carta - 1st document limiting the power of government - 1215 The English Petition of Rights – established the rights of the English people - 1689 Forms of GovernmentDemocratic – ruled by the people- direct – every vote counts – indirect – republic - representatives Oligarchic – rule by the few or small group - example - Communist- China Autocratic – rule by one – absolute monarchy or dictator – example Saudi Arabia – absolute monarchy Forms of Power distribution in government – Unitary –one person or one group – all power in national or central govt. Federal – power distribution between national and states - key words divided or separated Confederation – loose voluntary alliance between states or countries for a common goal Declaration of Independence – Why was it written? To motivate American’s to free themselves from England Who was the Author? Thomas Jefferson What are the unalienable rights? Rights granted to every person by birth – life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness