Lecture 9 - Biosbcc.net
advertisement

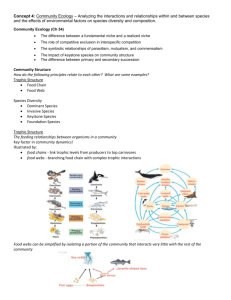
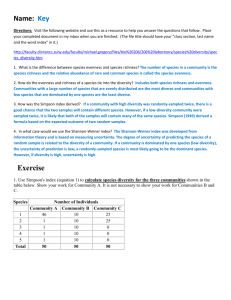
Bio122 Ecology F15 Lecture #9 (10/22/15): Mutualism (Ch15); Communities (Ch 16) I. Mutualism (Ch 15) A. Defined (+/+) B. Types 1. Trophic 2. Habitat 3. Service C. Costs & Benefits D. Ecological Consequences 1. Abundance 2. Distribution 3. Diversity 4. Species Interactions II. Communities (Ch 16) A. Defined B. Categorizing communities 1. Particular area 2. Taxonomic group 3. Guild 4. Functional group C. Community structure 1. Trophic relationships 2. Species diversity a. Diversity indices b. Rank abundance curves c. Species accumulation curves D. Processes that shape community structure: Interactions 1. Types of indirect effects 2. Interaction strength 3. Dominant species 4. Ecosystem engineers 5. Keystone species ***** Study Questons 1. Is the net effect in a mutualism positive, negative, or neutral for each member of the relationship? 2. List each of the 3 types of mutualism and provide an example for each. 3. Provide an example of a situation in which a mutualism is no longer beneficial for one of the members and so the relationship is constrained or terminated. 4. Briefly discuss how mutualism can impact each of the following: abundance of a species, geographic distribution, diversity, species interaction. 5. Define community. 6. What makes a community more than the sum of its parts? 1 Bio122 Ecology F15 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Lecture #9 (10/22/15): Mutualism (Ch15); Communities (Ch 16) 2 List & briefly describe 4 different approaches to characterizing a community. What is the difference between species richness, species evenness, and species diversity? What is a species accumulation curve and why would you use one? Describe a rank-abundance curve, noting what is plotted along each axis. How would the curves differ for communities with relatively higher vs. lower species richness and for higher vs. lower species evenness? What 2 pieces of information are used in calculating species diversity (such as the Shannon index)? What would cause a community with low species richness have a higher species diversity than another community with higher species richness? Define trophic cascade. Provide an example. Define: direct interaction, indirect interaction, foundation species, ecosystem engineers, and keystone species. Provide an example for each.