File
advertisement
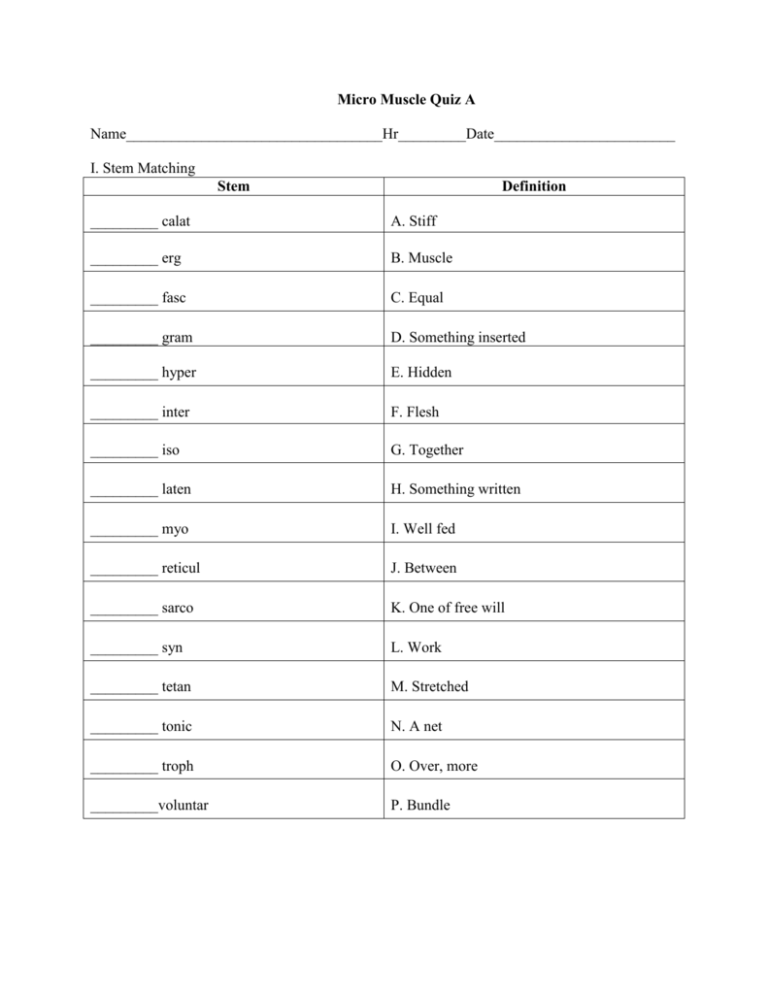
Micro Muscle Quiz A Name__________________________________Hr_________Date________________________ I. Stem Matching Stem Definition _________ calat A. Stiff _________ erg B. Muscle _________ fasc C. Equal _________ gram D. Something inserted _________ hyper E. Hidden _________ inter F. Flesh _________ iso G. Together _________ laten H. Something written _________ myo I. Well fed _________ reticul J. Between _________ sarco K. One of free will _________ syn L. Work _________ tetan M. Stretched _________ tonic N. A net _________ troph O. Over, more _________voluntar P. Bundle II. Vocab Matching Word Definition A. A narrow extracellular space between presynaptic and post synaptic neuron ___________ Acetylcholinesterase B. Impulse propagated along the sarcolemma into the transverse tubules ___________ Cisternae C. Contractile fibers in muscle cells ___________ Motor end plate D. Enlarged portion of the sarcoplasmic reticulum near the actin and myosin filaments of a muscle fiber ___________ Motor neuron E. Specialized part of a muscle fiber membrane at a neuromuscular junction ___________ Muscle impulse ___________ Myofibrils F. Muscle contract when the thin (actin) and thick (myosin) filaments move past each other, shortening the skeletal muscle cells G. Protein that attaches myosin filaments to the z lines in muscles ___________ Myosin H. Enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine ___________ Neurotransmitters ___________ Sarcomeres I. Membranous network of channels and tubules in a muscle fiber, corresponding to the endoplasmic reticulum of the other cells J. Structural and functional unit of the myofibril ___________ Sarcoplasmic Reticulum K. Neuron that transmits impulses from the central nervous system to an effector ___________ Sliding Filament Model ___________ Synaptic Cleft L. Chemicals that an axon end secretes that stimulates a muscle fiber to contract or a neuron to fire an impulse M. Protein that functions with tropomyosin to block muscle contraction until calcium ions are present ___________ Titin N. Protein that, with actin, contracts and relaxes muscle fibers. ___________ Troponin . III. Multiple choice. Write the correct letter on the blank to the left of the question. 1. __________ Muscle fibers contract when they receive signals from the ___________ system. A. Skeletal B. Respiratory C. Nervous D. Digestive 2.__________Which of the following proteins is not part of the thin filament A. Tropomysosin B. Titin C. Actin D. Troponin 3. _________ 80% of a muscle fiber’s volume is made of A. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum B. Fascicles C. Myofibrils D. Perimysium 4._________ The neurotransmitter used to stimulate muscle contraction is called A. Dopamine B. Epinephrine C. Serotonin D. Acetylcholine 5._________ The ___________ runs through the middle of the I band A. Z-disk B. H-Zone C. Synapse D. T-Tubule 6.________ Skeletal muscle contraction is called: A. Peristalsis B. a twitch C. a beat D. a pull 7.________ A forceful, sustained contraction is called a _____________ contraction. A. latent B. tetanic C. summation D. threshold 8. _______ The spot where T-tubules and terminal cisternae meet is called A. triad B. synaptic cleft C. vesicle D. motor plate end 9. ________ The ions that bind to troponin are made of this element A. Sodium B. Carbon C. Magnesium D. Calcium 10.________The conductive cell membrane the covers the muscle fiber is called the A. Sarcolemma B. Epimysium C. Sarcoplasmic reticulum D. Troponin 11.________ The space in the middle of the A band is called the A. Z- disk B. H-zone C. Fascicle D. Synapse IV. Diagram Identify the following structures Word bank 3 (Not all words will be used) A. Fascicle 2 1._________ B. Endomysium C. Osteomysium 1 2._________ D. Perimysium 4 3._________ 5 E. Eccomysium F. Muscle fiber G. Sarcomere 4._________ H. Epimysium I. Trabeculae 5._________ V. Ordering. List the order of actions (1-4) that occur in the sliding filament model. Start with myosin binding to the thin filament. _________ Myosin pulls the thin filament to the center of the sarcomere _________ Myosin binds to actin _________ Myosin uses ATP to restore its head to the “cocked” position _________ ATP binds to myosin causing it to release from the thin filament ***Extra Credit*** (2 pts each) What is one advantage of fast twitch muscles and one advantage of slow twitch muscles? Name and describe one muscle disorder. Include how it is treated