P1 The Earth and the Universe
advertisement

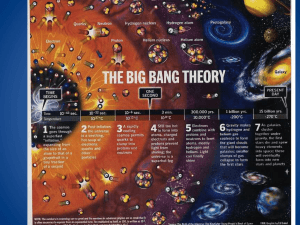
P1 The Earth and the UniverseAnswers P1.1 What do we know about the earth and space 1. Rocks provide evidence for changes in the Earth in the form of erosion and sedimentation, fossils, folding, radioactive dating, craters. 2. Continents would be worn down to sea level, if mountains were not being continuously formed. 3. Rock processes seen today can account for past changes. 4. The Earth must be older than its oldest rocks, which are about 4 thousand million years old; 5. 6. The solar system was formed over very long periods from clouds of gases and dust in space, about 5 thousand million years ago. 7. A comet is a rocky lump, held together by frozen gases and water that orbits the Sun. An asteroid is a dwarf rocky planet, generally orbiting the Sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. 8. Fusion of hydrogen nuclei is the source of the Sun’s energy; 9. All chemical elements larger than helium were made in earlier stars. 10. light travels at a high but finite speed; 300 000 km/s. 11. Due to the finite speed of light, and the distance stars are away from us, the light that is reaching us is anywhere from 4 years to 10 billion years old. Page 1 P1 The Earth and the Universe Answers 12. 13. 14. 15. A light-year is a unit of distance. A light-year is the distance travelled by light in a year. From oldest the youngest: the Universe; the Sun; the Earth. From smallest to largest, the relative diameters are: the Earth, the Sun and the Milky Way; P1.2 How have the Earth’s continents moved, and with what consequences? 1. Some of the evidence for Wegener’s theory of continental drift: geometric fit of continents and their matching fossils; mountain chains; rocks. 2. Collisions between tectonic plates cause mountains to be formed. There are three ways that this can happen: a. Where an ocean plate dives back down into the Earth, volcanic peaks may form at the surface b. The pushing movement at destructive margins can also cause rocks to buckle and fold, forming a mountain chain. c. Sometimes an ocean closes completely and two continents collide in slow motion. The edges of the continents crumble together and pile up, making mountain chains. This is happening today, in the Himalayas and Tibet. 3. Some of the reasons for the rejection of Wegener’s theory by geologists of his time: movement of continents not detectable; Wegener an outsider to the community of geologists; too big an idea from limited evidence; simpler explanations of the same evidence. 4. Seafloor spreading is a consequence of movement of the solid mantle, as two tectonic plates are driven apart by hot molten rock rising and cooling, then being forced out the way by new molten rock. 5. Seafloors spread by about 10 cm a year; 6. When rock is molten, it has the ability to change its magnetic alignment, which is then fixed as it cools. The Earth’s magnetic field flips direction every now and again, for reasons that scientists do not fully understand. This results in rocks on the ocean floors having differing magnetic alignments. 7. Earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain building generally occur at the edges of tectonic plates. Page 2 P1 The Earth and the Universe Answers 8. The movement of tectonic plates causes earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building and contributes to the rock cycle. P1.3 What is known about stars and galaxies? 1. We know about distant stars and galaxies comes only from the radiation astronomers can detect using telescopes: telescopes can be used to collect radiation across the whole electromagnetic spectrum. 2. The distance to stars can be measured using the relative brightness of stars or parallax. 3. understand that light pollution interferes with observations of the night sky; 4. The Sun is a star. 5. The Sun is in the Milky Way Galaxy. 6. Each galaxy may contain thousands of millions of stars. 7. There are thousands of millions of galaxies. 8. No: all stars have a life cycle. 9. Yes: astronomers have detected planets around some nearby stars. Page 3 P1 The Earth and the Universe Answers 10. Yes: if even a small proportion of stars have planets, many scientists think that it is likely that life exists elsewhere in the Universe; 11. No: no evidence of alien life (at present or in the past) has so far been detected. 12. Distant galaxies are moving away from us. 13. The further away a galaxy is from ours, the faster it appears to be receding (moving away). This is due to Hubble’s law. 14. The motions of galaxies suggest that Space itself is expanding. 15. Scientists believe the Universe began with a ‘big bang’ about 14 thousand million years ago. 16. The ultimate fate of the Universe is difficult to predict because the evidence is so uncertain. This has resulted in several competing theories of the ultimate fate of the Universe. P1.4 How do scientists develop explanations of the Earth and Space? 1. a. Observation b. Explanation c. Peer review 2. There are many possible answers. One example is: ‘What will the ultimate fate of the Universe be?’ The ultimate fate of the Universe is difficult to predict because the evidence is so uncertain. This has resulted in several competing theories of the ultimate fate of the Universe. Page 4