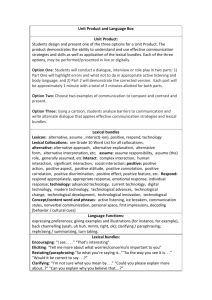
KNOW UNDERSTAND DO
advertisement
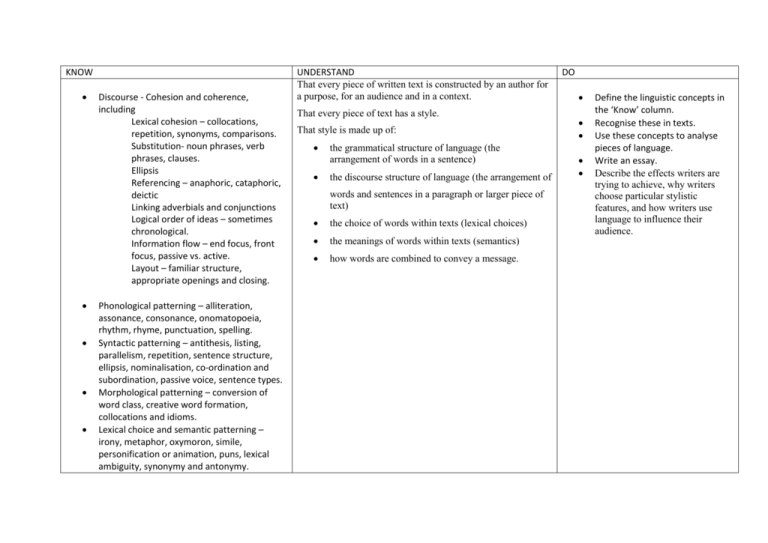
KNOW Discourse - Cohesion and coherence, including Lexical cohesion – collocations, repetition, synonyms, comparisons. Substitution- noun phrases, verb phrases, clauses. Ellipsis Referencing – anaphoric, cataphoric, deictic Linking adverbials and conjunctions Logical order of ideas – sometimes chronological. Information flow – end focus, front focus, passive vs. active. Layout – familiar structure, appropriate openings and closing. Phonological patterning – alliteration, assonance, consonance, onomatopoeia, rhythm, rhyme, punctuation, spelling. Syntactic patterning – antithesis, listing, parallelism, repetition, sentence structure, ellipsis, nominalisation, co-ordination and subordination, passive voice, sentence types. Morphological patterning – conversion of word class, creative word formation, collocations and idioms. Lexical choice and semantic patterning – irony, metaphor, oxymoron, simile, personification or animation, puns, lexical ambiguity, synonymy and antonymy. UNDERSTAND That every piece of written text is constructed by an author for a purpose, for an audience and in a context. That every piece of text has a style. That style is made up of: the grammatical structure of language (the arrangement of words in a sentence) the discourse structure of language (the arrangement of words and sentences in a paragraph or larger piece of text) the choice of words within texts (lexical choices) the meanings of words within texts (semantics) how words are combined to convey a message. DO Define the linguistic concepts in the ‘Know’ column. Recognise these in texts. Use these concepts to analyse pieces of language. Write an essay. Describe the effects writers are trying to achieve, why writers choose particular stylistic features, and how writers use language to influence their audience.