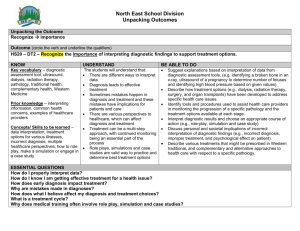
HSC10
advertisement
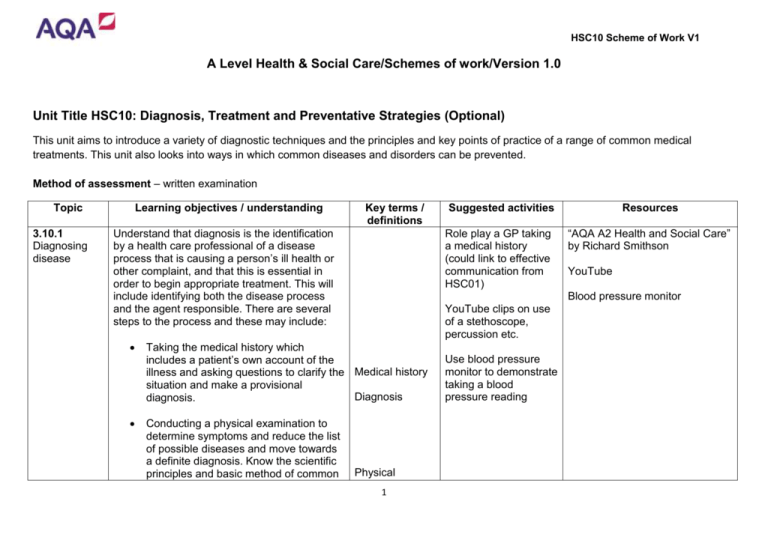
HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 A Level Health & Social Care/Schemes of work/Version 1.0 Unit Title HSC10: Diagnosis, Treatment and Preventative Strategies (Optional) This unit aims to introduce a variety of diagnostic techniques and the principles and key points of practice of a range of common medical treatments. This unit also looks into ways in which common diseases and disorders can be prevented. Method of assessment – written examination Topic 3.10.1 Diagnosing disease Learning objectives / understanding Key terms / definitions Understand that diagnosis is the identification by a health care professional of a disease process that is causing a person’s ill health or other complaint, and that this is essential in order to begin appropriate treatment. This will include identifying both the disease process and the agent responsible. There are several steps to the process and these may include: Role play a GP taking a medical history (could link to effective communication from HSC01) Resources “AQA A2 Health and Social Care” by Richard Smithson YouTube Blood pressure monitor YouTube clips on use of a stethoscope, percussion etc. Taking the medical history which includes a patient’s own account of the illness and asking questions to clarify the Medical history situation and make a provisional Diagnosis diagnosis. Conducting a physical examination to determine symptoms and reduce the list of possible diseases and move towards a definite diagnosis. Know the scientific principles and basic method of common Suggested activities Physical 1 Use blood pressure monitor to demonstrate taking a blood pressure reading HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 elements of physical examination, including visual examination, use of a stethoscope, palpation, testing reflexes, percussion, taking temperature and blood pressure. examination Stethoscope Palpation Testing reflexes Conducting special tests using diagnostic techniques to confirm the diagnosis; The use of computers to inform the medical professional of the full range of possible diagnoses for a particular set of symptoms. Percussion Temperature Blood pressure Diagnostic techniques 2 HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 3.10.2 Diagnostic techniques Know that following some screening tests further diagnostic testing may be used. Understand how dysfunctions can be tested and monitored using: YouTube clips of the different types of scanning YouTube Diagnostic imaging to include the principles of and use of x-rays, contrast x-rays, CT/PET scanning, radionuclide scanning, MRI and ultrasound scanning; X-ray Tissue biopsy, i.e. removal of a tissue or a cell sample which is then examined under a microscope and/or subjected to biochemical tests. PET scan Contrast x-ray CT scan Radionuclide scanning MRI scan Electrocardiography, including Ultrasound attachment of electrodes to the chest, wrists and ankles to display the electrical Tissue biopsy activity of the heart as a trace on a moving graph or screen; ECG Body fluid sampling to include the removal of blood samples. “AQA A2 Health and Social Care” by Richard Smithson Body fluid sampling 3 Flow charts illustrating the procedures involved in the different types of imaging HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 3.10.3 Diagnostic techniques to include screening tests Screening tests Screening Understand that early detection of a disease or disorder, often in presymptomatic stages, will allow treatment to be more effective. Screening tests may be suitable for the whole population or for specific groups of people at special risk, e.g. people over a certain age, people with a family history of a particular disorder or people employed in hazardous occupations. Presymptomatic Antenatal Genetic Down’s syndrome Know who the client group is, how each test is performed, what is being looked for and how positive or negative results are recognised. The tests to be covered are: Cystic fibrosis Antenatal screening tests: Sickle cell anaemia Amniocentesis for genetic disorder Down’s syndrome, spina bifida and sickle cell anaemia Chorionic villus sampling for genetic disorder cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy and sickle cell anaemia Blood tests for anaemia and blood groupings to include the rhesus factor. “AQA A2 Health and Social Care” by Richard Smithson www.immunisation.nhs.uk Know that there are different screening tests for Spina bifida different client groups and their importance and success rates in the UK. Sickle cell anaemia Know that following some screening, further tests may be needed to make a diagnosis. CVS YouTube clip of amniocentesis, CVS etc. being performed Muscular dystrophy Anaemia Rhesus factor PKU Caries 4 Macmillan cancer information – how to perform a personal check on breasts / testicles www.patient.co.uk HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 Snellen chart Infant and child screening tests: Blood test for phenylketonuria (PKU) Dental examination for caries Eye tests for visual defects using a Snellen chart and behavioural response test for colour blindness Hearing tests for deafness using audiograms and behavioural response tests Physical examination for hip dislocation Adult screening tests: Blood pressure for hypertension Eye tests for glaucoma using tonometry and other visual defects include shortsightedness and long-sightedness Smear test for cervical cancer Mammography for breast cancer Physical examination for testicular cancer Behavioural response test Audiogram Hip dislocation Blood pressure Hypertension Glaucoma Short-sighted Long-sighted Smear test Cervical cancer Mammography Testicular cancer 5 HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 3.10.4 Strategies to Prevent Disease: Immunisation Understand how different dangerous diseases can be avoided through immunisation, i.e. the artificial creation of immunity against infection. The difference between active and passive immunity must also be understood. Understand how immunisation works by attacking invading micro-organisms through the use of antibodies. Immunisation www.nhs.uk Active immunity www.netdoctor.co.uk Passive immunity www.rcn.org.uk Antibody Understand that infants and children are immunised against: Diphtheria Pertussis (whooping cough) Tetanus Measles, mumps, rubella (triple MMR vaccine). The following vaccinations are recommended for people of any age who travel to different countries which have specific health risks. Common examples include protection against: Cholera Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Typhoid Rabies For each of the vaccinations know about the: Disease which the vaccine protects against Causes of the disease, i.e. an organism, e.g. bacteria or virus and its name Diphtheria Whooping cough Tetanus MMR Cholera Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Typhoid Rabies Bacteria Virus Mode of transmission 6 HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 3.10.5 Treating disease Mode of transmission of the disease Symptoms and progression of the disease Risks of the disease to the person long and short term Risk of having the vaccine, side-effects. Symptom Progression Side effect Understand that many illnesses and injuries are not serious and most clear up without any treatment being necessary. Self-treatment may be required in other cases to relieve symptoms and help the person feel more comfortable. Self-treatment includes bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids and/or taking over-the-counter medications for common diseases such as coughs and colds. Understand, however, that where symptoms persist, a health care professional should be consulted and this may lead to treatments of different kinds. Self- treatment Understand the principles of home nursing for sick people and of hospital nursing including intensive care. Chemical name Drug treatment Brand name This is the use of a chemical substance that alters the function of one or more body organs or changes the process of disease. Each drug normally has three names, i.e. a detailed descriptive chemical name, a shorter generic name (official medical name) and a specific brand name chosen by the manufacturer. Genetic engineering Over-thecounter Bed rest Medication Prescription Drug Generic name Method of administration Operative 7 Examination of medication packaging to identify the three types of names “AQA A2 Health and Social Care” by Richard Smithson www.nhs.uk www.boots.com HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 Drugs are either licensed for prescription or available over-the-counter and may be from naturally occurring substances or artificially produced, sometimes by genetic engineering. surgery Know that drugs are classified, firstly according to chemical make-up, secondly to the disorder treated and thirdly by their specific effects on the body. Aseptic techniques All new drugs are tested for efficacy and safety. The different methods of administering drugs, i.e. by mouth, injection, creams, suppositories or sprays should be known, and the reasons for administration in each case. Appreciate that drugs can produce adverse side-effects and a drug is only useful if its overall benefit outweighs any risk and severity of these sideeffects. Surgical treatment as a minor or major direct physical intervention Operative surgery involves incision and the inspection and removal of diseased tissues or organs and/or replacement or redirection of body channels and/or implantation of electronic or medical devices. Understand the broad principles of transplant surgery including the need for aseptic techniques and general/local anaesthesia. The broad principles of endoscopic surgery, microsurgery and laser surgery should also be understood. Endoscopic surgery Surgical treatment Electronic/medic al devices General anaesthesia Local anaesthesia Microsurgery Laser surgery Radiotherapy Dialysis Lithotripsy 8 HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 Radiotherapy is the treatment of cancer and other diseases using ionising radiation to destroy or slow down abnormal cell growth. Understand that this is sometimes used on its own and sometimes in conjunction with surgical techniques. Radiotherapy can be administered from a machine outside the body or by introducing radioactive material into the body. Understand that the relative benefits of using this treatment must be weighed against the side-effects it produces. Other techniques Other techniques, including the broad principles of dialysis and lithotripsy in relation to the kidney. 3.10.6 Factors affecting treatment Understand that individuals may be affected differently by a particular treatment and may wish to make other choices about treatment and quality of life. Appreciate the consequences of delayed treatment and understand that ethical issues are associated with the treatment of disease and dysfunction, e.g. where lifestyle choices relating to physical exercise, diet, alcohol consumption and smoking may reduce the effectiveness of treatment. Quality of life Lifestyle factors Effectiveness Ethical issues 9 “AQA A2 Health and Social Care” by Richard Smithson HSC10 Scheme of Work V1 3.10.7 Assessment You will be assessed on your knowledge, understanding and skills relating to diagnosis and treatment through a written examination of two hours. There will be four compulsory structured questions which will include a mixture of short item and free response items. These will require you to demonstrate and apply your knowledge, understanding and skills of diagnosis and treatment. You will also be required to analyse relevant data, including numerical data, relating to diagnosis and treatment and to evaluate the evidence, make judgements and draw conclusions. The questions will be drawn from the following four areas of the unit: diagnosing disease diagnostic techniques to include screening tests strategies to prevent disease – immunisation treating disease To gain high marks in your written examination you should ensure that: your answers show a good level of detail, depth relevance and accuracy you apply knowledge, understanding and skills top the material presented in the questions successfully data analysis is thorough and produces clear, logical reasoning and judgements; suggestions and opinions are supported by the data and the material covered in all areas of the unit conclusions are consistent with the data and level of detail. 10