Thematic plan of lectures
advertisement
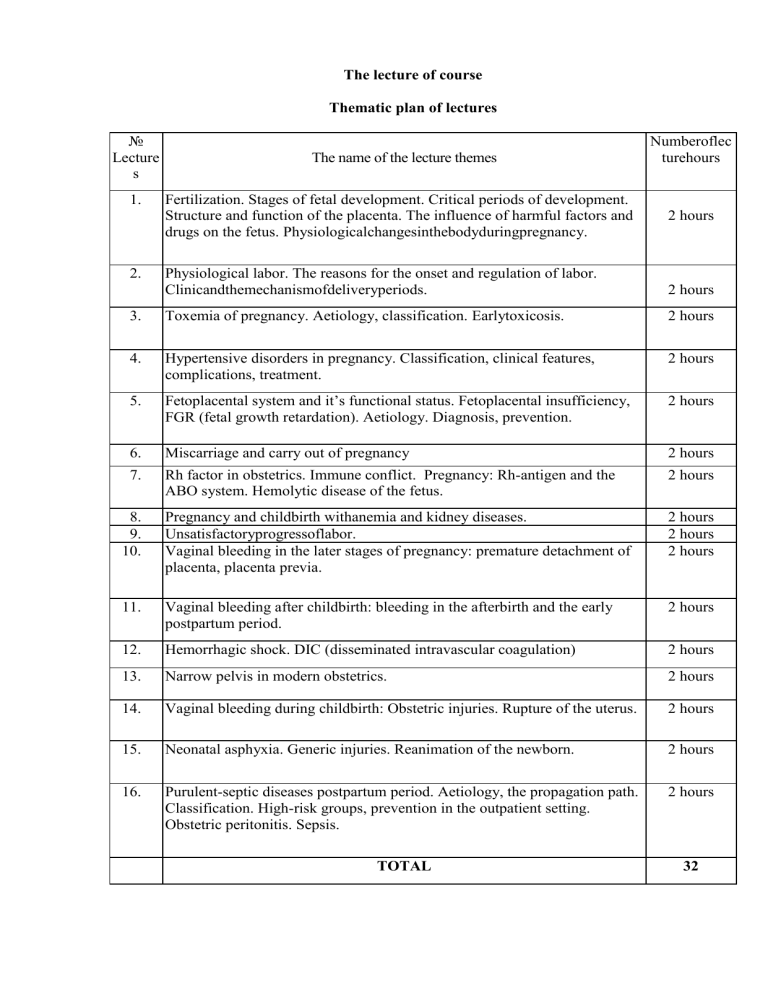
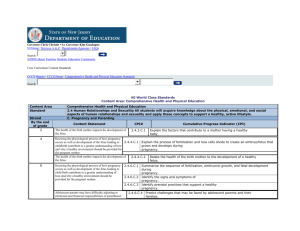
The lecture of course Thematic plan of lectures № Lecture s 1. 2. The name of the lecture themes Fertilization. Stages of fetal development. Critical periods of development. Structure and function of the placenta. The influence of harmful factors and drugs on the fetus. Physiologicalchangesinthebodyduringpregnancy. Numberoflec turehours 2 hours Physiological labor. The reasons for the onset and regulation of labor. Clinicandthemechanismofdeliveryperiods. 2 hours 3. Toxemia of pregnancy. Aetiology, classification. Earlytoxicosis. 2 hours 4. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. Classification, clinical features, complications, treatment. 2 hours 5. Fetoplacental system and it’s functional status. Fetoplacental insufficiency, FGR (fetal growth retardation). Aetiology. Diagnosis, prevention. 2 hours 6. Miscarriage and carry out of pregnancy 2 hours 7. Rh factor in obstetrics. Immune conflict. Pregnancy: Rh-antigen and the ABO system. Hemolytic disease of the fetus. 2 hours 8. 9. 10. Pregnancy and childbirth withanemia and kidney diseases. Unsatisfactoryprogressoflabor. Vaginal bleeding in the later stages of pregnancy: premature detachment of placenta, placenta previa. 2 hours 2 hours 2 hours 11. Vaginal bleeding after childbirth: bleeding in the afterbirth and the early postpartum period. 2 hours 12. Hemorrhagic shock. DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation) 2 hours 13. Narrow pelvis in modern obstetrics. 2 hours 14. Vaginal bleeding during childbirth: Obstetric injuries. Rupture of the uterus. 2 hours 15. Neonatal asphyxia. Generic injuries. Reanimation of the newborn. 2 hours 16. Purulent-septic diseases postpartum period. Aetiology, the propagation path. Classification. High-risk groups, prevention in the outpatient setting. Obstetric peritonitis. Sepsis. 2 hours TOTAL 32 Practical exercises Thematic plan of practical training № Name of the theme of practical / seminars Hours 1. The organization and structure of the obstetric and gynecologicalhospital . The principles of safe motherhood . Modern views on the prevention of nosocomial infections . Clinical anatomy of the female genital organs. The birth canal , the fetus as an object of sorts. 6 2. A. Fundamentals of perinatal care . Methods of examination of pregnant women. Diagnosis of early and late pregnancy . Assessment of the status of the fetus. The role of clinic in the prevention of obstetric complications. Preparing for the birth partner . School of motherhood. B. The physiological changes in the body of a pregnant . Methods of evaluation of the fetal heart : ultrasound, fetal biophysical profile , doplerometriya , CTG , hormonal , immunological, medical and genetic research techniques , x-ray , endoscopy ( amnioscopy , amniocentesis ) . 6 3. A. Childbirth . Periods of delivery . Affiliate birth. Keeping the partograph . Active management of the third stage of labor . Assessment of neonatal Apgar scores .Biomechanism delivery at the front as the occipital previa . Primary treatment of the newborn. B. The theory of a birth. Score maturity of the cervix. Stages of fetaldevelopment . Critical periods of ontogeny. Structureandfunctionoftheplacenta. 6 4. A. Physiological postpartum period. Rooming-in of mother and child. Care of breasts . B. During the early neonatal period . Transient state of the newborn. Physiological weight loss . Generic opuhol.Tranzitornayalihoradka.Fiziologicheskayazheltuha. Genital crises. Principles of breastfeeding , prevention of mastitis. 6 5. A. Childbirth breech .Biomechanismof birth. Admission by Lovset, by Maurice Smellie - Veit . B. Antenatal and intrapartum prepare pregnant women for delivery in breech presentation . Complications for the mother and fetus 6 6. 6 A. Premature birth . The use of tocolyticagents . Antenatal corticosteroids. Carry out of pregnancypregnancy. Induction of labor at term pregnancy . Emergency conditions and problems of the fetus. B. Signs of prematurity. Nursing of premature infants . Placental insufficiency syndrome, fetal growth retardation. 7. A.Toshnota and vomiting of pregnancy . The etiology , classification , clinical features, treatment. B.Rare forms of toxicosis of pregnancy ( ptializm, acute yellow atrophy of the liver , dermatitis, ostemalyatsiya, tetany, bronchial asthma) 6 8. A.Hypertensive condition during pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia , diagnosis , treatment and tactics . B. Eclampsia .Clinic .Diagnosis . First aid. Treatment. Methods of delivery. Complications of hypertensive states . Rehabilitation of postpartum women who have had hypertensive disorders and their complications . 6 9. The role of the Rh factor in obstetrics. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Newbornjaundice , diagnosisandtreatment. 6 10. A.Flowingpregnancy , childbirth and the postpartum period in renal disease . Asymptomatic bacteriuria . B. The course of pregnancy , childbirth and the postpartum period, with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, diseases of the liver, bronchial asthma 6 11. Flowing pregnancy , childbirth , and postpartum anemia . Intermediatecontrol . 12. Vaginal bleeding in the later stages of pregnancy : placenta previa and PDOP. 4 13. A. Vaginal bleeding after delivery : placental abnormalities , hypotension, and atony of the uterus, cervical laceration , perineum , the delay of the next . Diagnosis , tactics, preventive measures. B. Hemorrhagicshock . ICE syndrome . 14. A. Unsatisfactory progress of labor. Passive and active phase of labor .Classification . The aetiology , clinical features and diagnosis of different types of anomalies of labor. Obstetric and prevention tactics. Rodostimulation with oxytocin on the recommendations of the WHO. B. An overly strong tribal activities. Cervicaldystocia. Diskoordinativelabors. 6 15. A. Narrow pelvis ,etiology , types , classification , diagnosis . Disproportion between the fetal head and the mother's pelvis . Shoulder dystocia .Complications for the mother and fetus and their prevention . B. Clinical narrow pelvis : causes and clinical symptoms are functionally narrow pelvis .Complicatios. Tactic managements of labor. Biomechanismlabor with rare forms a narrow pelvis. 16. A. Wrongfetalposition , causes, diagnosis , tactics . B. Wrong fetal presentation: the causes, diagnosis, biomechanics birth tactics . 6 17. Vaginal bleeding during delivery: uterine rupture. Classification, aetiology and pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, principles of treatment, prevention.. 18. Surgery for delivery is: cesarean section, forceps, vacuum extraction of the fetus. 6 19. A. Transmission of HIV from mother to fetus. Integrating the prevention of HIV transmission from mother to child in an effective perinatal care. B. Prevention of postpartum complications of HIV in the workplace. Antiviral therapy Selecting the mode of delivery (elective caesarean section), safe practices of labor management. Safe infant feeding practices. 6 6 6 6 6 20. A. Infections in the postpartum period. Modern ideas. Classification, the spread of infection. B. Current concepts of infectious agents. Diagnosis . The principles of treatment .Prevention. High-riskgroups, preventionintheoutpatientsetting. 6 21. The high temperature after delivery. Obstetric peritonitis, causes, diagnosis , treatment 6 22. A. Emergency conditions and problems of the newborn. Resuscitation of the newborn. Intrauterine infection of the fetus. B. The concept of TORCH- infections. Ways of intrauterine infection. Diagnosis, treatment , obstetrical tactics for viral infections . 4