Student Workbook Activity
advertisement

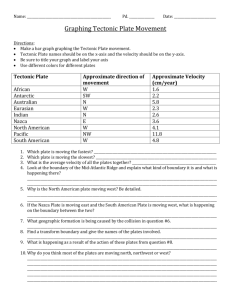
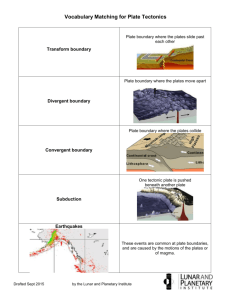
A2 TECTONICS – Holiday Work Complete the exercises then save a copy and email to me mvanston@langleyschool.co.uk I’ll mark and then print it off for your files. A. The structure of the Earth. Exercise 1: Import a diagram that shows the Earth’s structure. Annotate it to explain the characteristic features of each of the layers. (Remember to consider structure according the physical and chemical characteristics) Exercise 2: Complete the table to summarise the differences between the two types of crust. Oceanic Crust Continental Crust Age Thickness Composition Weight Why is knowledge of the crustal characteristics important to your understanding of what happens at plate boundaries? Explain. B. Continental Drift Exercise 3: Define what the theory of continental drift is and explain why the theory was not initially accepted. Exercise 4: Describe and explain the evidence for the movement of continents over time using the following 4 categories: a) Continental jigsaw puzzle b) Geological evidence c) Biological evidence d) Climatological evidence c. Theory of plate tectonics Exercise 5: What is the theory of plate tectonics? Describe and explain the key elements associated with the theory of plate tectonics. a) Define ‘Plate tectonic theory’ b) Label the major tectonic plates on the map below. c) Import a map of the world which shows a record of known earthquake and volcanic eruptions. Describe and explain the relationship between the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanoes and tectonic plate boundaries. d) Using a diagram, explain the theory behind the mechanism that causes crustal plates to move. Exercise 6: Describe and explain (using annotated diagrams) how the discovery of sea-floor spreading and Palaeomagnetism provided evidence to support the theory of continental drift, subsequently termed plate tectonics. (Hint: include a diagram showing the magnetic stripes in oceanic crust and explain how magnetism is recorded in the rocks) Exercise 7: What are the physical processes that occur at plate boundaries? a) Constructive plate boundaries i) Define the movement of plates at this boundary ii) Import and annotate a diagram to explain what happens at this boundary at a. On a landmass b. In the ocean iii) Describe and explain the processes that occur at this boundary e.g. rifting iv) Name the landforms that are produced v) Give a named example (Include the plate names) b) Destructive plate boundaries a. Define the movement of plates at this boundary b. Import and annotate a diagram to explain what happens at this boundary c. Describe and explain the processes that occur at this boundary e.g. subduction d. Name the landforms that are produced e. Give a named example (Include the plate names) c) Conservative plate boundaries a. Define the movement of plates at this boundary b. Import and annotate a diagram to explain what happens at this boundary c. Describe and explain the processes that occur at this boundary d. Name the landforms that are produced e. Give a named example (Include the plate names) d) Collision plate boundaries a. Define the movement of plates at this boundary b. Import and annotate a diagram to explain what happens at this boundary c. Describe and explain the processes that occur at this boundary e.g. rifting d. Name the landforms that are produced e. Give a named example (Include the plate names) NB: Causes of plate movement at a divergent/constructive plate boundary One possible cause of plate movement is convection in the mantle. We know that part of the mantle is ductile so it can flow slowly. Convection currents may carry the rigid plates along. There are other possible causes however. Ridge push is a mechanism in which the weight of the oceanic crust at the ridge pushes it downwards so it moves sideways. The other suggested mechanism is slab pull. The edge of the subducting plate is heavy and pulls the rest of the plate along behind it. Exercise 8: Explain the formation the of Hawaiian islands. Use a diagram to support your explanation. Exercise 9: Without looking try and complete this table to summarise your understanding of plate boundaries. Plate margin Constructive Destructive Collision Conservative Hot spots Movement of plates Tectonic features Examples Exercise 10: Vulcanicity a) Complete the table (without looking at a resource) to summarise the differences between lava at different plate boundaries: Constructive plate margin Destructive plate margin Plate margin Type of magma Lava characteristics Type of eruption Materials erupted Frequency of eruption Form of volcano b) Describe and explain the distribution of volcanoes (AQA page 11 will help) c) What is the type of magma formed at destructive (convergent) plate boundaries? d) Why is it different from the magma created at constructive (divergent) plate margins? e) Why do oceanic plates move down below continental plates? f) Volcanic activity can be classified by type of plate boundary, violence of eruption, frequency of eruption and by shape of the volcano. Research these different ways and produce a summary table for each of these. Exercise 11: Describe and explain the formation of minor extrustive landforms; solfatara, hot springs, geysers, fumaroles, boiling mud. Include diagrams and annotate their key features. Include named examples in your descriptions. Exercise 12: Intrusive landforms associate with volcanic activity a) Define the term intrusive activity b) Find a diagram which shows the features of intrusive activity e.g. it includes the following features; dykes, sills, laccoliths, batholiths. c) Describe and explain the formation and features of these intrusive landforms. Include diagrams of each with annotations to support.