Unsatisfactory - Lewiston Independent School District #1
advertisement

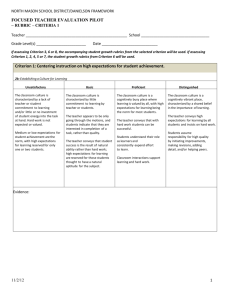
Page 1 of 5 2012 – 13 LEWISTON SCHOOL DISTRICT FRAMEWORKS REFLECTION TOOL: TEACHER NOTE: Domains 1-4 combine for 50% of the Teacher’s Ranking, Domain 5 determines the other 50% 1. PLANNING AND PREPARATION 1a. Demonstrating Knowledge of Content and Pedagogy Unsatisfactory* Teacher makes content errors or does not correct content errors students make Teacher displays little understanding of prerequisite knowledge Teacher displays little understanding of pedagogical issues 1b. Demonstrating Knowledge of Students Unsatisfactory* Teacher displays minimal knowledge of developmental characteristics of age group Teacher is unfamiliar with multiple approaches to student learning (learning styles, modalities, and different “intelligences”) Teacher does not recognize or value students’ skills, knowledge, interests, or cultural heritage 1c. Selecting Instructional Outcomes Unsatisfactory* Instructional outcomes are unsuitable for students Instructional outcomes represent trivial or low-level learning or are stated only as activities Instructional outcomes do not permit viable methods of assessment 1d. Demonstrating Knowledge of Resources Unsatisfactory* Teacher has no awareness of available resources within the school/district for teachers and/or students 1e. Designing Coherent Instruction Unsatisfactory* Learning activities are not suitable or correlated to ongoing learning, nor are they reflective of recent professional research Resources/materials do not support instructional goals or engage students in meaningful learning There is no variance in instructional groups and no correlation to instructional goals The unit or lesson has no clear structure, and time allocations are unrealistic 1f. Designing Student Assessment Unsatisfactory* Content and methods of assessment lack congruence with instructional outcomes Criteria and standards of assessment are unclear Correlation between assessment results and planning is minimal For Reference Only Basic Teacher displays basic content knowledge that is not connected with other parts of discipline(s) Teacher has some awareness of prerequisite learning (may be incomplete or inaccurate) Teacher displays basic pedagogical knowledge, but does not anticipate student misconceptions Proficient Teacher displays solid content knowledge, with connections between content and other discipline(s) Plans reflect an understanding of prerequisite relationships among topics and concepts A reflection of current best practices is evident, but teacher does not anticipate student misconceptions Distinguished Teacher displays extensive content knowledge, with evidence of continuing pursuit of such knowledge Teacher builds on knowledge of prerequisite relationships Continual search for best practices is evident, and teacher anticipates student misconceptions Basic Teachers displays general accurate knowledge of developmental characteristics Teacher displays general understanding of multiple approaches to student learning Teacher recognizes value of students’ skills, knowledge, interests, or cultural heritage for the class as a whole Proficient Teacher displays thorough understanding of developmental characteristics, including exceptions Teacher displays solid understanding of different approaches to learning exhibited by each student Teacher displays knowledge of and values students’ skills, knowledge, interests, or cultural heritage Distinguished Teacher displays knowledge of developmental characteristics and the extent to which individual students follow patterns Knowledge of students’ varied approaches to learning is reflected in instructional planning Teacher knows and values ALL students’ skills, knowledge, interests, and cultural heritage Basic Instructional outcomes are of moderate rigor and are suitable for some students Instructional outcomes consist of a combination of activities and goals, but only some permit viable assessment Instructional outcomes represent more than one type of learning but the teacher makes no attempt at coordination or integration. Proficient Instructional outcomes are stated as goals reflecting high level learning and curriculum standards. Instructional goals are suitable for most students in the class, represent different types of learning and can be assessed. The outcomes reflect opportunities for coordination. Distinguished Instructional outcomes are stated as goals that can be assessed, reflecting rigorous learning and curriculum standards Instructional outcomes represent different types of content, offer opportunities for both coordination and integration Instructional outcomes take into account the needs of individual students Basic Teacher has limited awareness of available resources within the school/district for teachers and/or students Proficient Teacher has full awareness of available resources within the school/district for teachers and/or students Distinguished The teacher seeks resources for students and to enhance instruction (such as community resources), in addition to school/district resources Basic Some learning activities are suitable, with some correlation to ongoing learning and some reflection of professional research Some resources/materials support instructional goals and engage students in meaningful learning The instructional group’s suitability to instructional goals is inconsistent, and goals have minimal variety Some structure to the lesson or unit is evident, but not consistent, and most time allocations are reasonable Proficient Most learning activities are suitable, with consistent correlation to ongoing learning, and reflect recent professional research All resources/materials support instructional goals and engage most students in meaningful learning Instructional groups are varied, as appropriate to different instructional goals The lesson or unit has clear structure, and time allocations are reasonable Distinguished Learning activities are highly relevant to students and instructional goals and reflect recent research All resources/materials support instructional goals, meaningfully engage students, and show evidence of student participation in selection and adaptation Instructional groups are varied appropriately, and students exercise choice in selection of groups The lesson’s/unit’s structure is clear, and time allocations are flexible to meet individual needs Basic There is some congruence of assessment with instructional outcomes Goals and assessments are unclear and/or are not clearly communicated to students Assessment results are used to plan for the class as a whole Proficient Assessment is aligned with instructional outcomes, but the approach is more suitable to some than others Assessment criteria and standards are clear and are clearly communicated to students There is correlation between assessments and planning for individuals and groups Distinguished Assessment is congruent with instructional outcomes Clear criteria/standards are clearly communicated to students, with evidence of students’ contribution Students are aware of how they are meeting standards and participate in planning the next steps Page 2 of 5 2. THE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT 2a. Creating an Environment of Respect and Rapport Unsatisfactory* Teacher interaction with some students is negative, demeaning, sarcastic, or inappropriate. Students exhibit disrespect for the teacher Student interactions demonstrate conflict, sarcasm, or put-downs 2b. Establishing a Culture for Learning Unsatisfactory* Teacher or students convey a negative attitude toward content, suggesting that content is not important Students demonstrate little or no pride in their work Classroom environment conveys only modest expectations for student achievement 2c. Managing Classroom Procedures Unsatisfactory* Groups of students not working with the teacher are not productively engaged in learning Classroom procedures, routines, and transitions are nonexistent or inefficient, resulting in the loss of much instructional time Paraprofessionals and volunteers have no clearly defined duties or have nothing to do 2d. Managing Student Behavior Unsatisfactory* No standards of conduct appear to have been established, or students are confused regarding expected behavior Student behavior is not monitored, and teacher is unaware of misbehavior Teacher does not respond to misbehavior, or the response is inconsistent, or teacher does not respect the student’s dignity 2e. Organizing Physical Space Unsatisfactory* The classroom is unsafe and/or furniture arrangement is not suited to the lesson’s activities Teacher uses physical resources poorly, or learning is not accessible to some students 3. INSTRUCTION AND USE OF ASSESSMENT 3a. Communicating with Students Unsatisfactory* Teacher’s directions and procedures are confusing Teacher’s spoken language is inaudible, or written language is illegible, and may contain many grammar and syntax errors. Vocabulary may be inappropriate, vague, or used incorrectly, leaving students confused For Reference Only Basic Teacher-student interactions are generally appropriate, but may reflect inconsistencies, favoritism, or disregard for students’ cultures. Students exhibit only minimal respect for the teacher Students do not behave negatively toward one another Proficient Teacher-student interactions are friendly and demonstrate warmth, caring, and respect. Students exhibit respect for the teacher Student interactions are generally respectful Distinguished Teacher demonstrates genuine caring and respect for individual students. Students exhibit respect for the teacher as an individual, beyond that for the role Students demonstrate genuine caring for one another, as individuals and as students Basic Teacher communicates importance of the work, but with minimal buy-in by the students Students invest little of their energy in the quality of the work Classroom environment conveys inconsistent expectations for student achievement Proficient Teacher conveys genuine enthusiasm for the subject, and students are consistently committed to its value Students accept teacher insistence on work of highest quality and demonstrate pride in that work Classroom environment conveys high expectations for student achievement Distinguished Students demonstrate, through their active participation, curiosity, and attention to detail, that they value the content’s importance Students take obvious pride in their work and initiate improvements in it Both students and the teacher establish a classroom of high expectations for the learning of all students Basic Tasks for group work are partially organized, resulting in some off-task behavior Classroom procedures, routines, and transitions are fairly efficient, resulting in little loss of instructional time Paraprofessionals and volunteers are productively engaged some of the time, but require frequent supervision Proficient Tasks for group work are organized, and most students are engaged at all times Classroom procedures, routines, and transitions occur smoothly, resulting in little loss of instructional time Paraprofessionals and volunteers are productively and independently engaged during the entire class Distinguished Groups working independently are productively engaged at all times, with students assuming responsibility for productivity Classroom procedures, routines, and transitions are seamless, with students assuming considerable responsibility for efficient operation Paraprofessionals and volunteers contribute substantially to the classroom environment Basic Standards of conduct appear to have been established, and most students seem to understand them Teacher is aware of student behavior, but may miss some misbehavior Teacher is inconsistent in response to misbehavior, or no serious disruptive behavior occurs Proficient Standards of conduct are clear to all students Teacher is alert to student behavior at all times Teacher’s response to misbehavior is consistent and appropriate and respects the student’s dignity, or student behavior is generally appropriate Distinguished Standards of conduct are clear to all students and have been created with student input Teacher monitors behavior in a subtle way, while students respectfully monitor their peer’s behavior Teacher’s response to misbehavior is highly effective and sensitive to students’ individual needs, or student behavior is entirely appropriate Basic The classroom is safe and furniture arrangement is adjusted for a lesson, but with limited effectiveness Teacher uses physical resources adequately, and essential learning is accessible to all students Proficient The classroom is safe, and furniture arrangement is a resource for learning activities Teacher uses physical resources skillfully, and learning is equally accessible to all students Distinguished The classroom is safe, and students adjust the furniture to benefit their own learning Teacher and students use physical resources optimally to ensure learning is equally accessible to all students Basic Teacher’s directions and procedures are clarified after initial confusion, or are excessively detailed Teacher’s spoken language is audible, written language is legible, and both are used correctly. Vocabulary is correct, but limited or not appropriate to students’ ages or backgrounds Proficient Teacher’s directions and procedures are clear and contain an appropriate level of detail Teacher’s spoken and written language is clear and correct. Vocabulary is appropriate to students’ ages or interests Distinguished Teacher’s directions and procedures are clear and anticipate possible student misunderstanding Teacher’s spoken and written language is correct and expressive, with well-chosen vocabulary that enriches the lesson Page 3 of 5 3b. Using Questioning and Discussion Techniques Unsatisfactory* Teacher’s questions are of poor quality Teacher-student interaction is predominantly recitation style, with few students participating and the teacher mediating all questions and answers Basic Teacher’s questions are a combination of high and low quality, with few inviting a response Teacher makes some attempt to engage all students in a true discussion, with limited success Proficient Teacher’s questions are mostly of high quality, and teacher gives adequate time to respond Classroom interaction engages all students in a true discussion, with teacher stepping to the side, when appropriate Distinguished Teacher’s questions are of uniformly high quality, with adequate time for students to respond. Students formulate many questions Students assume considerable responsibility for the success of the discussion, initiating topics, making unsolicited contributions, and ensuring all voices are heard 3c. Engaging Students in Learning Unsatisfactory* Representation of content is inappropriate and unclear or uses poor examples and analogies Activities and assignments are not age- and/or background- appropriate and do not mentally engage students Instructional groups are not appropriate to students or the instructional goals Instructional materials and resources are not suitable to meeting the instructional goals or do not engage students mentally The lesson has no clearly defined structure and/or the pacing is too slow or too rushed Basic Representation of content is inconsistent in quality Some activities and/or assignments are appropriate to students and engage them mentally, but others do not Instructional groups are partially appropriate to students or only moderately successful in advancing the instructional goals Instructional materials and resources are partially suitable to the instructional goals, or students’ level of mental engagement is moderate The lesson has a recognizable structure, although not uniformly maintained throughout the lesson. Pacing of the lesson is inconsistent Proficient Representation of content is appropriate and links well with students’ knowledge and experience Most activities and assignments are appropriate to students and engage them cognitively Instructional groups are productive and appropriate to students and instructional goals Instructional materials and resources are suitable to the instructional goals and engage students mentally The lesson has a clearly defined structure around which the activities are organized. Pacing of the lesson is consistent Distinguished Students contribute to representation of content, which is appropriate and links well with their knowledge and experience Students initiate or adapt activities and projects to enhance understanding, and are cognitively engaged Instructional groups are productive and appropriate to students and instructional goals. Students influence instructional groups to advance their learning Instructional materials and resources are suitable to instructional goals and fully engage students mentally. Student initiate choice, adaptation or creation of materials to enhance their own purposes The lesson’s structure allows for reflection and closure. Pacing of the lesson is appropriate for all students Basic Teacher uses targets but relies heavily on textbook or prepackaged materials. Recognizes need to relate targets to adopted curriculum and Common Core Standards. Some use of formative assessment. Tends to use the same type of assessment method. Some analysis/redesign of prepackaged assessments. Most students can demonstrate mastery of achievement standards, course objectives, curriculum standards, and/or grade level expectations. Proficient Clearly articulates targets and how they relate to adopted curriculum and Common Core Standards. Regular use of formative assessment. Uses several types of assessments. Can articulate when to use each assessment method. Involves students in assessment design. Most students can demonstrate mastery of achievement standards, course objectives, curriculum standards, and/or grade level expectations. Distinguished Designs & articulates targets to adopted curriculum and Common Core Standards. Uses formative assessment with students to increase student achievement. Uses all types of assessment methods and matches method to purpose, target and instruction. Regular involvement in assessment design and implementation. All students can demonstrate mastery of achievement standards, course objectives, curriculum standards, and/or grade level expectations. Teacher can show evidence of interventions provided to students when they are necessary. Basic Teacher attempts to adjust a lesson, with mixed results Teacher attempts to accommodate students’ questions. The effects on the coherence of a lesson are uneven Teacher accepts responsibility for the success of all students, but has only a limited repertoire of instructional strategies to use Proficient Teacher makes a minor adjustment to a lesson, and the lesson occurs smoothly Teacher successfully accommodates students’ questions Teacher persists in seeking approaches for students who have difficulty learning, possessing a moderate repertoire of strategies Distinguished Teacher successfully makes a major adjustment to a lesson Teacher seizes a major opportunity to enhance learning, building on a spontaneous event Teacher persists in seeking effective approaches for students who need help, using an extensive repertoire of strategies and soliciting additional resources from the school 3d. Using Assessment in Instruction Unsatisfactory* The teacher does not have clear learning targets nor are they aligned with the adopted curriculum and Common Core Standards. Students cannot articulate why they received their grades or self-assess. Does not use formative assessment. Only uses assessments that come with instructional materials. Few students can demonstrate mastery of achievement standards, course objectives, curriculum standards, and/or grade level expectations. 3e. Demonstrating Flexibility and Responsiveness Unsatisfactory* Teacher adheres rigidly to an instructional plan, even when a change will clearly improve a lesson Teacher ignores or brushes aside students’ questions Teacher either gives up or blames the student or the environment for student’s difficulty learning For Reference Only Page 4 of 5 4. PROFESSIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES 4a. Reflecting on Teaching Unsatisfactory* Teacher does not know if a lesson was effective or achieved its goals, or profoundly misjudges the success of a lesson Teacher has no suggestions for how a lesson may be improved another time 4b. Maintaining Accurate Records Unsatisfactory* Teacher’s system for maintaining accurate records for students’ completion of assignments, progress in learning, and non-instructional activities is nonexistent or in disarray, resulting in errors and confusion Basic Teacher has a generally accurate impression of a lesson’s effectiveness and the extent to which instructional goals were met Teacher makes general suggestions about how a lesson may be improved Proficient Teacher makes an accurate assessment of a lesson’s effectiveness and the extent to which it achieved its goals, and he/she can support the judgment Teacher makes a few specific suggestions that he/she may try another time Distinguished Teacher makes a thorough and accurate assessment of a lesson’s effectiveness and the extent to which it achieved its goals, citing specific examples Teacher offers specific alternative actions, complete with probable successes of different approaches Basic Teacher’s system for maintaining accurate records for students’ completion of assignments, progress in learning, and non-instructional activities is rudimentary and partially effective Proficient Teacher’s system for maintaining accurate records for students’ completion of assignments, progress in learning, and non-instructional activities is fully effective Distinguished Teacher’s system for maintaining accurate records for students’ completion of assignments, progress in learning, and non-instructional activities is highly effective, with students participating in the maintenance and interpretation of records Basic Teacher participates in the school’s activities and follows the required procedures for communicating to parents, but makes modest and inconsistent efforts to engage families in the instructional program Proficient Teacher provides frequent information to parents about the instructional program and individual students’ progress, and efforts to engage families are frequent and successful Distinguished Teacher provides frequent information to parents about the instructional program and student progress, and efforts to engage families are frequent and successful. Students contribute ideas for family participation Basic Teacher maintains cordial relationships with colleagues to fulfill duties required by the school or district Teacher participates in school events and/or school and district projects when specifically asked Proficient Support and cooperation characterize relationships with colleagues Teacher volunteers to participate in, and makes a substantial contribution to, school events and/or school and district projects Distinguished Support and cooperation characterize relationships with colleagues, with the teacher taking initiative in assuming leadership among the faculty Teacher volunteers to participate in, makes a substantial contribution to, and assumes a leadership role in school and/or district projects 4e. Growing and Developing Professionally Unsatisfactory* Teacher engages in no professional development activities to enhance knowledge or skill Teacher makes no effort to share knowledge with others or contribute to the profession Basic Teacher participates in professional activities to a limited extent when they are convenient Teacher finds limited ways to contribute to the profession Proficient Teacher seeks out opportunities for professional development to enhance content knowledge and pedagogical skill, Teacher actively assists other educators Distinguished Teacher seeks out opportunities for professional development and makes a systematic attempt to conduct action research in his/her classroom Teacher initiates activities to contribute to the profession, such as mentoring new teachers, writing articles for publication, and making presentations 4f. Showing Professionalism Unsatisfactory* Teacher is not alert to students’ needs Teacher contributes to school practices that result in some students being ill served by the school Teacher makes decisions based on self-serving interests Basic Teacher’s attempts to serve students are inconsistent Teacher does not knowingly contribute to some students being ill served by the school Teacher’s decisions are based on limited, though genuinely professional, considerations Proficient Teacher is moderately active in serving students Teacher works within the context of a particular team or department to ensure that all students receive a fair opportunity to succeed Teacher maintains an open mind and participates in team or departmental decision making Distinguished Teacher is highly proactive in serving students, seeking out resources when necessary Teacher makes a particular effort to advocate for all students, particularly those traditionally underserved Teacher takes a leadership role in team or department decision making, ensuring that decisions reflect the highest professional standards 4c. Communicating with Families Unsatisfactory* Teacher provides minimal information to families about the instructional program or individual students, or makes either no attempt or inappropriate attempts to engage families 4d. Participating in a Professional Learning Community Unsatisfactory* Teacher’s relationships with colleagues are negative or self-serving Teacher avoids becoming involved in school events and/or school and district projects For Reference Only Page 5 of 5 5. Student Achievement 5a. Proficiency on State Assessments Building level percent of students scoring proficient or advanced on state assessments Unsatisfactory Evidence indicates little to no student learning gains. Expectations are not met. Results are well-below expectations. Basic Expectations are nearly met. The educator may have demonstrated an impact on student learning, but overall results are below expectations. Proficient Evidence indicates significant student learning, including special populations. Meets State Goals Distinguished Evidence indicates exceptional student learning gains, including special populations. Exceeds State Expectations by 3% in at least one area (ISAT) Proficient Evidence indicates significant student learning gains, including special populations. The proficiency rate of all cohort groups (matching students) is the same as the previous year. Distinguished Evidence indicates exceptional student learning gains, including special populations. The proficiency rate of all cohort groups (matching students) exceeds the rate of the previous year. 5b. Growth on State Assessments Building level growth determined by district data Unsatisfactory Evidence indicates little to no student learning gains. Expectations are not met. Results are well-below expectations. Basic Expectations are nearly met. The educator may have demonstrated an impact on student learning, but overall results are below expectations. 5c. Grade Level or Content Area Measures Measures and targets identified at the beginning of school year. May include: essential learning, proficiency, course grades, graduation rate, end of course assessments, common assessments other measures mutually selected by the teacher and administrator. Unsatisfactory Evidence indicates little to no student learning gains. Expectations are not met. Results are well-below expectations. For Reference Only Basic Expectations are nearly met. The educator may have demonstrated an impact on student learning, but overall results are below expectations. Proficient Evidence indicates significant student learning gains, including special populations. Distinguished Evidence indicates exceptional student learning gains, including special populations.