APR 78078 Xinjiang 2013
advertisement
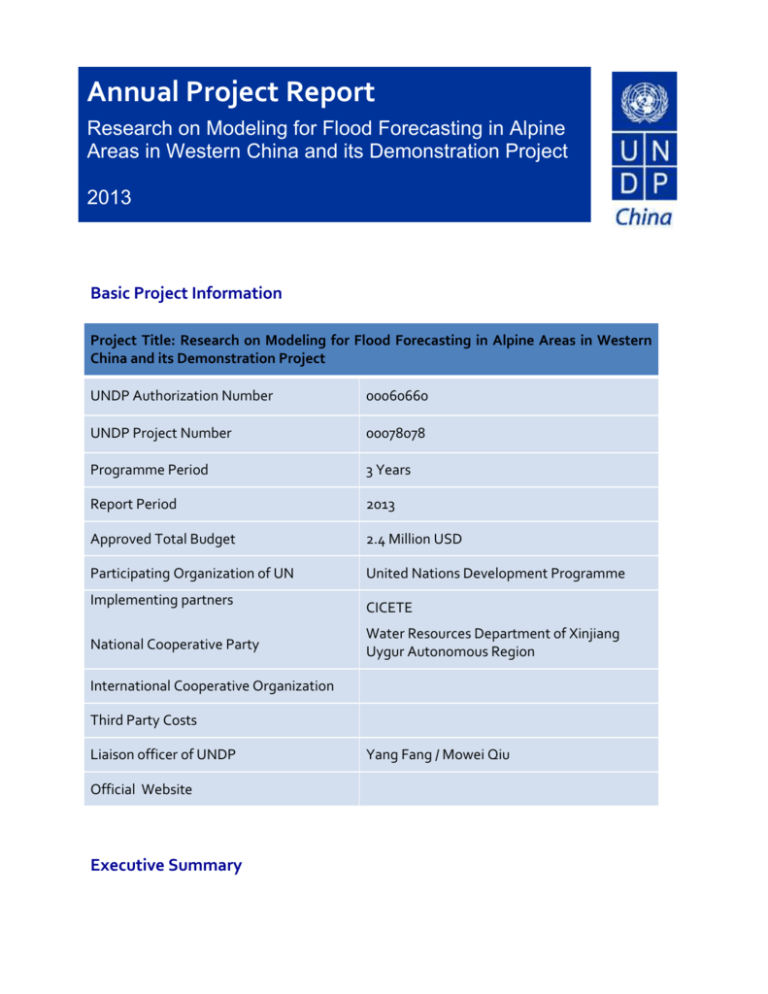
Annual Project Report Research on Modeling for Flood Forecasting in Alpine Areas in Western China and its Demonstration Project 2013 Basic Project Information Project Title: Research on Modeling for Flood Forecasting in Alpine Areas in Western China and its Demonstration Project UNDP Authorization Number 00060660 UNDP Project Number 00078078 Programme Period 3 Years Report Period 2013 Approved Total Budget 2.4 Million USD Participating Organization of UN United Nations Development Programme Implementing partners CICETE National Cooperative Party Water Resources Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region International Cooperative Organization Third Party Costs Liaison officer of UNDP Official Website Executive Summary Yang Fang / Mowei Qiu Most activities of the Subproject of Research on Modeling for Flood Forecasting in Alpine Areas in Western China and its Demonstration Project were completed in 2013. Data on water conditions and the weather for flood forecast become accessible from the constructed alpine weather stations and hydrological monitoring stations. Meanwhile, the newly developed snow remote sensing date producing system and snow remote sensing acquisition system can produce snow and ice data in a timely manner and calculate the snow coverage condition and its trends. 1. Background Development Context Flood control and disaster mitigation are important strategic issues that are tied to the development of a well-off society in every sense -- the national economy, stability and safety. Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, the largest provincial administrative unit, has long suffered from floods and droughts. As a result of climate change and the development of the society, the range, frequency and severity of the floods have been expanding annually. Restrained by traditional factors such as poor infrastructure and weak capacities for crisis management and by new challenges in the form of climate change and extreme weather, flood control and disaster mitigation mechanisms in China have not been well developed as yet, especially in the western areas. The combination of traditional and non-traditional factors has further made the task of flood control and disaster mitigation even more arduous. While the Chinese government is always mindful of floods and droughts, as can be seen from previous documents of the Central Committee, which put emphasis on investing in flood control and disaster mitigation, it must address these kinds of challenges to ensure sustainable economic development. Project Objectives and Strategy The project aims at establishing and improving the disaster prevention ability for dealing with snow-melt and ice-melt floods of the western areas by using integrated ground-space monitoring system and other technological means for flood control and disaster mitigation. Following the selection of pilot rivers, this project attempts to construct a network of monitoring stations to track meteorological, snow, hydrographic data to assist in the research of flood forecasting models, as well as to build processing stations and management systems which use remote sensing and different mechanisms for flood control. It is also planned to provide an insurance mechanism to protect human lives and properties and ensure economic development. In 2013, it focused on the enhancement of flood prevention techniques, including the the collecting and processing of the data of basic terrain and soil, snow and ice remote sensing, vegetation and land use with remote sensing method in project area. The efforts in have assisted in achieving the overall goals of the project. 2. Key Results The key achievements of 2013 include a hardware part and a software part. 1 mountain meteorological monitoring station was built in 2012, and in 2013 the focus was centred on the improvement of the station. The software part comprises the collecting and processing of the data of basic terrain and soil, snow and ice remote sensing, vegetation and land use with remote sensing method in project area. Project Outputs Output 1: Improvement of mountain meteorological monitoring station Output 2: Management Coordination Activities and Outputs The project in 2013 carried out activities, as follows: Activity 1.1 Improved the mountain meteorological monitoring station 1 mountainous meteorological station was constructed in 2012, and the mountainous weather stations’ automatic data acquisition and transmission system, as well as receiving network platform, were improved by using Beidou satellite and GSM communication. Activity 1.2 Collected and processed data of basic terrain and soil, snow and ice remote sensing, vegetation and land use with remote sensing method in project area The snow and ice remote sensing acquisition system, which covers extraction and editing of interactive information of snow and ice remote sensing, was further enhanced, and data was collected and processed for forecasting and early warning. Sustainability In 2013, the mountain meteorological monitoring station was improved. Inhabitants of China’s western regions who have long been affected by snowmelt floods directly benefit from this project. As the project progresses, the snowmelt flood forecasting models can be recommended to Central Asian countries, benefiting the people of other nations who also suffer from floods. Meanwhile this project can raise public awareness and improve local communities’ flood early warning and prevention capacities. Partnership Effectiveness As our partner, the Department of Water Resources in Xinjiang has played a critical role in the successful construction of alpine weather stations and hydrological monitoring stations, which has laid a solid foundation for later acquisition of meteorological and hydrological data. It has also actively cooperated with Aerors Inc., a private company, to develop software for this project. 3. Project Management and Oversight Implementation status The project has been implemented according to the schedule. The activities were carried out in line with our expectations and the objectives were achieved. Monitoring and Evaluation In order to guarantee the quality, progress and completeness of the project, the project executive committee has set up a comprehensive supervision system in the planning stage, and has been supervising the project from the following three aspects. Supervision on Project Scope. A Change Control Board (CCB) has been established and is responsible for verifying major changes in implementation, in order to avoid uncontrollable demand deviation and expanded scope. The CCB consists of the Project Chief Engineer, the Project Experts, and the Project Leader. Supervision on Project Schedule. During the planning stage of the project, the committee designed the work plan and appointed a person in charge for each stage. Quality management staff would check on the progress on a regular basis. In every stage, accreditations would be held to guarantee the quality as well as the schedule. Workers would not be allowed to enter the next stage unless they’ve passed the accreditation. Supervision on Project Quality. The main management measures include establishing the baseline, determining activities and tasks for every stage, determining the time frame and resources required to complete the tasks, determining the threshold conditions for activities, and designing outputs of activities and follow-up actions, as well as revising plans if necessary. All these measures aim to ensure the quality of the implementation. The supervision and evaluation system worked effectively. The project was implemented and completed as planned, and the quality of its output was in line with the expectations. The inspection work was completed successfully. Human Resource Management Staff of the PROJECT EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE has been allocated according to the requirements and responsibilities of each position. The main positions include the Project Chief Engineer, the Project Expert Team, the Planning and Scheduling Team, the System Leader, the System Design Team, the Algorithm Development Team, the Software Development Team and the System Testing Staff. The above-mentioned measures have ensured that human resource is properly allocated, which has guaranteed the project progress and quality in aspects of hardware, software, scientific research and implementation. Risk management During the implementation of the project in 2013, the PROJECT EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE managed the risks from the following four aspects. Natural Environment Risk Management. The work of 2013 includes the construction of facilities such as alpine weather stations and hydrological monitoring stations. Having taken into consideration of the climatic factors in Xinjiang, the project avoided the extreme weathers and finished the hardware construction work from May to August. Resources Risk Management. The implementing agency audited the fund utilisation, and allocated funds for procurement, research and other activities according to relevant national regulations and policies. Therefore the resource risk was efficiently managed in 2013. Personnel Risk Management. During the project planning, the PROJECT EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE carried out a capacity assessment of every staff member and assigned responsibilities accordingly. Project Management. During the project planning, the PROJECT EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE set up a complete management system to ensure the quality, progress and completeness of the project. Result of the risk management in 2013: Natural Environment Risk has NOT affected the project implementation. Resource Risk has NOT affected the project implementation due to effective management. Personnel Risk has NOT affected the project implementation. Project Management has NOT negatively affected the project implementation. The project was implemented as planned and was completed accordingly with high quality. 4. Financial Management The Finance Department of the partner organisation supervised the fund utilisation according to the rules of project management and national regulations. Source of Fund Expenditure Vs. Budget UNDP Expenditure 7,268 17,691.69 215,000 178,753.81 Approved project budget by source of funding Government Cost Sharing Third Party Cost-sharing Other (please specify) Total 222,268 196,445.50 Expenditure by Activity (US$) December 2013 Activity Cost Item Activity 1 30071 178,753.81 30071 4,761.86 30071 12,030.13 Activity 2 Expenditure Total 190,783.94 5. Management recommendations N/A 6. Conclusion The subproject of Research and Demonstration Projects of Flood Forecasting Systems of Chinese Western Alpine Areas has been successfully completed for 2013. At this point, the constructed facilities such as alpine weather stations and hydrological monitoring stations are able to provide data on water conditions and the weather for flood forecast, and the developed snow remote sensing date producing system and snow remote sensing acquisition system are able to produce snow and ice data in a timely manner, calculate the snow coverage condition and its trends. 7. Annexe/s








