Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 Points, Lines, and Planes Lesson
advertisement
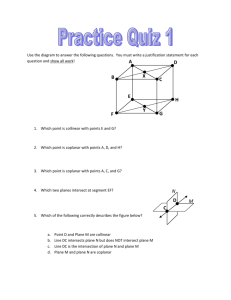
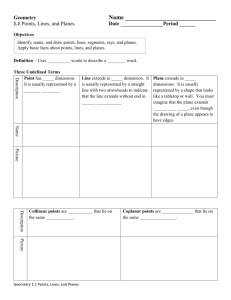
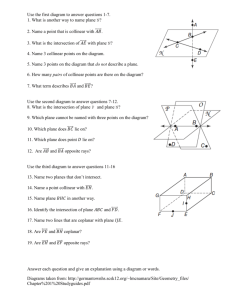
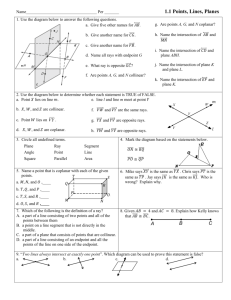
Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 Points, Lines, and Planes Lesson Objectives: In this lesson, we will be learning about the fundamental building blocks of all geometric figures as well as building a foundation for our geometric library. You should be able to do the following: Understand and use basic geometric vocabulary Understand and apply the four basic postulates of geometry Undefined Terms: Undefined terms are the basic terms you can use to build the definitions of all other figures in geometry. Although you cannot define undefined terms (hence the name “undefined”), it is important to have a general description of their meanings. Undefined Terms Term Description Point: Indicates an exact location and has no size. Line: Is represented by a straight path that extends in two opposite directions without end and has no thickness. A line contains infinitely many points. Plane: Is represented by a flat surface that extends without end and has no thickness. A plane contains infinitely many lines. How to Name It Diagram Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 Collinear Points: Points that lie in the same line are collinear. Coplanar: Points and lines that lie in the same plane are coplanar. 1. Are all points on a line coplanar? Are the terms point, line and plane defined or undefined? Why or why not? Can you use undefined terms to define other terms? Use the diagram below to complete the following problems. 2. Name three collinear points:________________ 3. Name three points that are not collinear:______________ 4. Name four coplanar points:_____________________ 5. Name four points that are not coplanar:_____________________ 6. What are two other ways to name RS : ___________________ 7. What are two more ways to name Plane P: _______________ Segments, Rays, and Opposite Rays Term Definition Segment: a part of a line consisting of two endpoints and all points between them. Ray: a part of a line consisting of one endpoint and all points of the line on one side of the endpoint. Opposite Rays: are two rays that share an endpoint and form a line. Diagram How to Name It Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 Use the diagram at the right to answer the following. 8. Name two rays that have B as an endpoint:_______________ 9. Name two segments that have C as an endpoint:______________ 10. Name a pair of opposite rays:____________________ 11. Is DB the same ray as CB ? 12. Are CA and CB opposite rays? 13. Are EC and CE opposite rays? Refer to the diagram at the right. 14. Can you find two points that are not collinear? Explain. 15. Can you find three points that are not coplanar? Explain. Postulates Postulate: A postulate (or axiom) is an accepted statement of fact. Postulates, like undefined terms, are basic building blocks of the logical system of geometry. Postulates will be used to prove other facts in geometry. When you have two or more geometric figures, their intersection is the set of points the figure have in common. Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 There is a similar postulate about the intersection of planes. Example: Each surface of the box at the right represents part of a plane. What is the intersection of plane ADE and EFG? 16. What is the intersection of plane BCG and plane DHC? 17. Which two planes intersect in EF ? When you name a plane from a figure like the box in the above example, list the corner points in consecutive order. For example, plane ABCD and plane ADCB are also names for the top plane. Plane ACBD is not. Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 Use the figures at the right. 18. What plane contains points E, F, and G? Shade the plane. 19. What plane contains points A, B, and H? Shade the plane. 20. What is the name of a line that is coplanar with EF and EH ? Assignment 1A Points, Lines, and Planes (1–2) At the end of this assignment, you should be able to do the following: Understand and use basic geometric vocabulary Understand and apply the four basic postulates of geometry Part I: Practice 1. Use the figure at the right to answer the following questions. a. What are two other ways to name EF ? _______________ b. What are two other ways to name plane C? _____________ c. Name three collinear points. __________________ d. Name four coplanar points. __________________ 2. Use the figure at the right to complete the following exercises. a. Name the segments in the figure. __________________________________ b. Name the rays in the figure. ___________________________________ c. Name the pair of opposite rays with endpoint T. ___________________ d. Name another pair of opposite rays. _____________________ Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 3. Use the figure at the right to complete the following exercises. a. Name the intersection of planes QRS and RSW. _____________ b. Name the intersection of planes TXW and TQU. _____________ c. Name two planes that intersect in line QU ._____________________ d. Name two planes that intersect in line TS . _____________________ Part II: Application and Problem Solving 4. Postulate 1-4 states that any three non-collinear points lie in exactly one plane. Find the plane that contains the first three points listed. Then determine whether the fourth point is in that plane. Write coplanar or non-coplanar to describe the points. a. X, Y, Z, U b. X, S, V, U ___________________ ___________________ c. X, Z, S, V d. S, V, C, Y ___________________ ___________________ 5. Open-Ended Draw a figure with points B, C, E, F, and G that shows CD , BG , and EF , with one of the points on all three lines. 6. Your friend drew the diagram at the right to prove to you that two planes can intersect in exactly one point. Describe your friend’s error. Geometry (H) Lesson 1.2 7. Determine whether the following statements are always, sometimes, or never true. a. TQ and QT are the same line. ______________________ b. Intersecting lines are coplanar. ______________________ c. Four points are coplanar. _______________________ d. A plane containing two points of a line contains the entire line. ____________ e. Two distinct lines intersect in more than one point.______________________ 8. If one ray contains another ray, are they the same ray? Explain. 9. Telecommunications A cell phone tower at point A receives a cell phone signal from the southeast. A cell phone tower at point B receives a signal from the same cell phone from due west. Trace the diagram at the right and fine the location of the cell phone. Describe how Postulates 1-1 and 1-2 help you locate the phone. 10. How many planes contain the same three collinear points? Explain. 11a. Suppose two points are in plane P. Explain why the line containing the points is also in plane P. 11b. Reasoning Suppose two lines intersect. How many planes do you think contain both lines? Use the diagram at the right and your answer to part (a) to explain your answer.