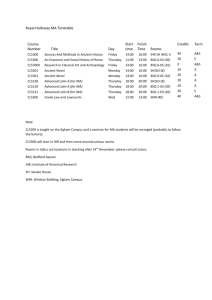
2. Laboratory of bioelectricity
advertisement
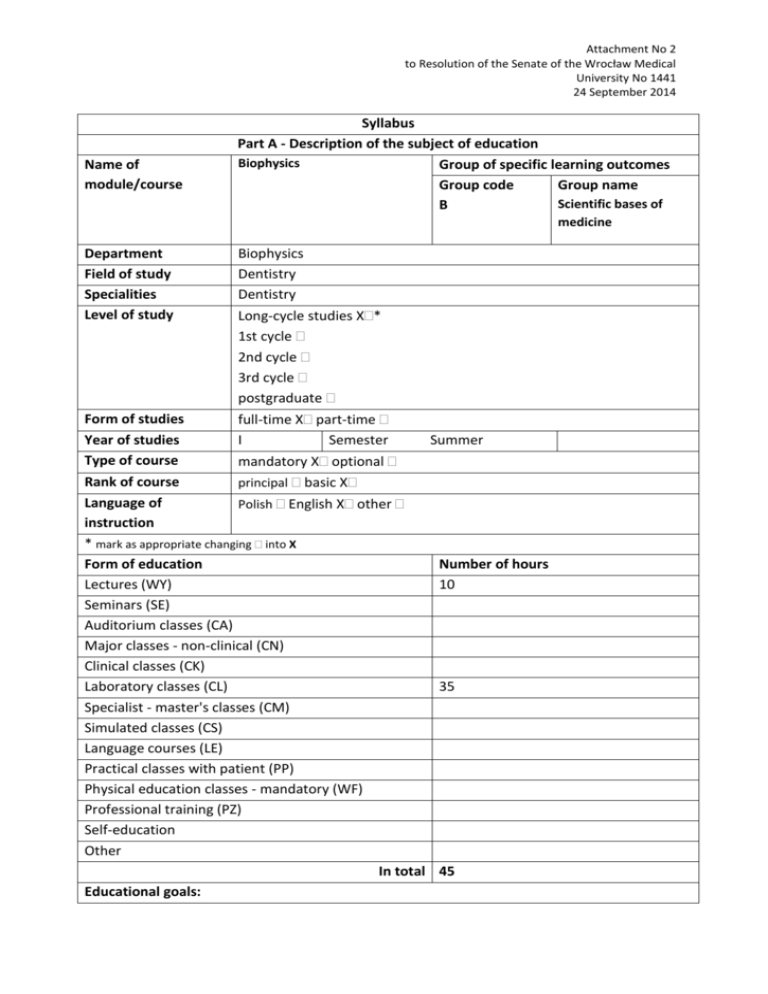
Attachment No 2 to Resolution of the Senate of the Wrocław Medical University No 1441 24 September 2014 Name of module/course Syllabus Part A - Description of the subject of education Biophysics Group of specific learning outcomes Group code Group name Scientific bases of B medicine Department Field of study Specialities Level of study Biophysics Dentistry Dentistry Long-cycle studies X* 1st cycle 2nd cycle 3rd cycle postgraduate full-time X part-time I Semester mandatory X optional principal basic X Polish English X other Form of studies Year of studies Type of course Rank of course Language of instruction * mark as appropriate changing into X Form of education Lectures (WY) Seminars (SE) Auditorium classes (CA) Major classes - non-clinical (CN) Clinical classes (CK) Laboratory classes (CL) Specialist - master's classes (CM) Simulated classes (CS) Language courses (LE) Practical classes with patient (PP) Physical education classes - mandatory (WF) Professional training (PZ) Self-education Other Summer Number of hours 10 35 In total 45 Educational goals: The aim of education in the area of biophysics is understanding physical bases of processes that occur in biological systems on the level of molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs and the whole human organism. The next educational goal is understanding physical bases of modern medical diagnostic and therapeutic methods, and some experimental methods applied in studying biological systems. During laboratory practicals students get ability to use various equipment, perform measurements applying spectroscopic, electrical, optical and other methods, use professional computer software and do analysis of obtained experimental data. Matrix of learning outcomes for module/course in relation to methods of verification of intended learning outcomes and form of classes: The number of core education outcome The number of major education outcome Student who passes the module/course has the knowledge of/knows how to/is capable of Methods of verification of intended learning outcomes achievement (forming and summary) Form of classes W 01 BW 4 1.Knowledge of structure and function of important compounds present in a human body, in particular of proteins and lipids and energy production in mitochondria. written examination L BW7 , BW8 2.Knowledge of principles of biomechanics and mechanics of the organ of mastication. colloquium, written examination L, C BW9 BW10 BW11 ** enter the symbol 3.Knowledge of physical bases of methods of imaging of tissues and organs and principles of function of diagnostic equipment used for these purposes. colloquium, written examination 4.Knowledge of principles of function of ultrasonic devices and their application in diagnostics and therapy . colloquium, written examination L, C colloquium C 5.Knowledge of principles of photometry and principles of function of waveguides and application of light sources in dentistry . L, C BW12 BW19 U 01 BU2 BU3 BU3 BU3 BU3 K 01 6.Knowledge of principles of work of lasers and their application in dentistry . 7.Knowledge of selected life functions of a human organism – physical bases of function of nerve system, circulatory system and function of selected sensory organs . 1.Ability of interpretation of physical phenomena in a human organism, in particular, in the organ of mastication . written examination L colloquium, written examination L, C 2.Ability of application of proper methods of imaging diagnostics in work of a dentist. 3.Ability of application of ultrasounds in work of a dentist. 4.Ability of application of properly-selected laser light in a clinical practice. 5.Ability of application of ionising radiation and ability of estimation of a irradiation risk in a dentical practice. Students actively participate in a team work, are creative, think logically and independently, learn to face challenges and are interested in selfeducation. **WY - lecture; SE - seminar (SE); auditorium classes - CA; CN - principal classes (non-clinical); CL - laboratory classes; CN specialist (master's) classes; CS - simulated classes; LE - language courses; PP - practical classes with patient; WF - physical education classes (mandatory); PZ - professional training; SK - self-education Put a cross on a 1 to 3 scale to mark how the above outcomes categorize your classes in terms of knowledge, skills and attitudes e.g.: Knowledge + + + Skills + ++ Attitudes +++ Student's workload (the ECTS credit balance): Form of student's workload Student's workload (h) (attendance, initiative, preparation to classes, 45 verification etc.) 1. Contact hours 5 2. Time dedicated to student's own work 40 Total student's workload 90 The ECTS credits per module/subject 5 Remarks Classes content: (please put down the classes subject matter in a concise form with the consideration of the form of classes and bearing in mind the fact that the subject matter should translate into the intended learning outcomes) Lectures 1. Physical aspects of membrane transport of substances and signal transduction. 2. Principles of electrophysiology – nerve impulse, neuromuscular transmission, muscle contraction. 3. Biophysics of systems and sensory organs. 4. Introduction in a medical physics - lasers in medicine – principles of laser action, types of lasers, waveguides, medical application. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and its application in medicine and in biomedical sciences. 5. Influence of physical factors on a human organism. 6. Principles of biomechanics. Seminars 1. 2. 3. Classes 1. Laboratory of bioacoustics and biomechanics: 1.1 Ultrasonic Doppler effect 1.2 Measurements of activation threshold of an ear 1.3 Sound spectral analysis 1.4 Determination of macromolecule’s molecular weight by colloid solution viscosity measurements 1.5 Ultrasound probe 1.6 Microcalorimetric method of investigation of phase transitions in lipids 1.7 Fundamentals of ultrasound application in medicine. 2. Laboratory of bioelectricity: 2.1 Computer simulation of action potential generation in axon 2.2 Characteristics of the Geiger-Müller counter 2.3 Estimation of the Nernst’s equilibrium potential on a ion-selective membrane 2.4 Dipolar model of a heart 2.5 Estimation of radiation attenuation coefficient 2.6 Analog model of the synaptic transmission 2.7 Nerve impulse, neuromuscular transmission, muscle contraction and its pathology 3. Laboratory of biooptics and spectroscopy: 3.1 The analysis of different emission spectra using spectroscope and monochromator. 3.2 Estimation of a colloid solution concentration using nephelometry 3.3 Fluorescence of organic dyes and its application in the quantitative luminescence analysis 3.4 Estimation of the focus length and the focus radii of the eye model 3.5 Absorption of solutions of organic dyes. Analysis of contents of a solution. 3.6 Properties of laser light and white light 3. 7 Ionising radiation and its application in medicine. Radiobiology. A physical basis of X-ray computer tomography and positron emission tomography (PET) and application of radioactive isotopes in imaging of tissues and organs. Other: 1. 2. 3. etc. Core literature: (according to relevance, no more than three titles) 1. 1. Cotterill R. Biophysics. An introduction. J. Wiley & Sons, 2004. 2. Alberts, B., Bray,D., Lewis,J., Raff.M., Roberts,K., Watson,J.D., Molecular Biology of the cell, Garland Publishing, Inc., New York, 1994. 3. Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessel, T.M. Principles of Neural Science, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1991. Supplementary literature and other aids (no more than three titles) 1. Glaser, R., Biophysics. Springer-Verlag, 2004. 2. Hille, B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, Sinauer Associates inc. Sunderland, 2004. Requirements regarding teaching aids: (e.g. laboratory, multimedia slide projector, other) Equipment setups for laboratory practicals in laboratories, multimedia projectors, computers, standard and specialist software. Initial conditions: (minimal conditions to be fulfilled be a student before signing up for the module/course) A basic knowledge in the areas of physics, biology and chemistry Terms of passing a given course: (please define the form and terms of passing given classes falling within the scope of the module/course, rules for allowing students to sit final theoretical and/or practical exam, its form and requirements that students must meet in order to pass it as well as criteria applicable to each grade) Getting a positive note from the final written examination test after having got a credit note from laboratory classes. Grade: very good (5,0) good plus (4,5) excellent (4,0) fairly good Criterion for assessment: (applies only to courses/modules ending with an exam) Giving correct answers to more than 90% of the final test questions Giving correct answers to more than 80% of the final test questions Giving correct answers to more than 70% of the final test questions Giving correct answers to more than 60% of the final test questions (3,5) satisfactory (3,0) Giving correct answers to more than 50% of the final test questions Name and address of the unit in charge of module/course, contact (phone number and email address) ……………………… Wroclaw Medical University Department of Biophysics, Ul. Chałubińskiego 10 50-368 Wrocław Tel: 71-784-14-01, e-mail: biofiz@biofiz.umed.wroc.pl A list of persons giving particular classes including: full name, degree/academic or professional title, field of science, profession, form of classes Lectures and laboratory classes are given by: dr hab. Andrzej Teisseyre – andrzej.teisseyre@umed.wroc.pl Prepared by: ………………………………………….. Revised by: ………………………………………….. Signature of the Head of unit in charge of classes …………………………………………..