File - Kelsey`s E
advertisement

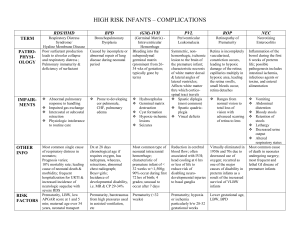
Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY Effects of Prematurity throughout the Lifespan Kelsey Opfar-Neuman Salt Lake Community College PSY-1100 July 28, 2015 Author’s Note: This assignment was chosen because too few many people would choose not to talk about this issue. All sources used were credited on the reference page. 1 Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY 2 Premature Birth through Life Introduction Most people know someone who was born premature or have at least heard a little about what prematurity is. Usually people don’t know much about it and they at least come to the conclusion that it is a bad thing. Well they’re right about that! Being premature can have devastating risks and can even last throughout the child’s whole life. It is true that some babies who were born premature are close to perfectly healthy and outgrow most of their health problems. But overall, it is a scary time for parents if their babies are born premature. What it Means to be a Preemie Well first off, what does it mean when a baby is premature? There are different stages of prematurity and they all effect the time the baby has to develop in the womb. In the womb, this is the most critical time for normal brain development. They range from late preterm which the baby is born between 34 to 36 weeks of pregnancy to extremely preterm which the baby is born at or before 25 weeks of pregnancy. A full term pregnancy usually lasts about 40 weeks so for the extremely preterm baby that would be a very uneasy time. So when a baby is born premature, what symptoms could they have? Well depending on how early the baby was born, they could include; the baby being small size with a larger head, the baby could have more defined features, almost as if the baby was skinny, respiratory distress, difficulty with eating due to the lack of ability to suck or swallow, etc. So to show the severity of the issue with prematurity, let’s say there was a baby boy who was born at 24 weeks gestation, he would only weigh about 1 lb. and 6.9 oz. Then if there was a baby girl who was also born at 24 weeks gestation, she would only Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY 3 weigh about 1 lb. 5.2 oz. If a baby is born at 24-25 weeks they could face health issues that are lifelong like developmental delays, blindness, lung disease (chronic), cerebral palsy, etc. After Effects of Being a Preemie in Childhood So let’s say that the baby survives being born premature, what would happen later in a child’s life once they reached to let’s say 7 to 13 years old? Compared to children who were born full term, premature children had more difficulties with visuospatial reasoning (The inability to comprehend and conceptualize visual representations and spatial relationships in learning and doing a task), visual memory, slower processing skills with a lack of processing speed (the ability to automatically perform a simple task quickly). Children who have a lack of processing speed may need more time than others in the classroom to complete tasks. Typically preterm children are found to have less cerebral white matter, cerebral white matter is critical in communication between nerve cells and smaller thalami (a region in the brain which involves motor and sensor signaling, hence developmental delays). Preterm children also have been found to have more problems including hyperactivity, attention deficit disorder, opposition and aggression versus children who were born full term. After Effects of Being a Preemie in Young Adulthood So let’s say the baby continues to grow till they are about to the age of 17 (young adulthood), are the effects of prematurity still relatively noticeable? Some of the most notable findings are that the preterm baby was born with neurological effects at birth, that by time they were to young adulthood they would be at a greater risk of asthma, vision problems and trouble with fine motor skills (precise coordinated movements with activities like writing, cutting, tracing or visual tracking) and hand-eye coordination. Preterm children were also less likely to Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY 4 complete High School. If the preterm baby was born under 3 lbs. that by the time of young adulthood, they would have a greater risk of pulmonary issues and would have higher blood pressure than those who were born over 3 lbs. If boys especially were born low weight then they were found to have difficulty breathing. Overall, babies born premature were more likely to be in poor health, growth and have worse neurological outcomes versus those who were full term. After Effects of Being a Preemie in Adulthood Impairments that premature babies are born with can remain well into adulthood, around the time when a person reaches the ages of 25 to 65 years. People who were born premature were at a higher risk of not being able to bear children later in life. A small percentage of both genders were able to have children, 14% of men and 25% of women. Later effects of prematurity into adulthood also showed the higher risk of death from respiratory disorders, diabetes, heart disease, etc. If the preterm baby reaches their 60’s then they are more likely to have neurocognitive impairments such as word list recognition, constructional praxis/recall, clock drawing, mini-mental state examination and memory total. After Effects of Being a Preemie in Old Age You can’t find too many issues of prematurity when someone reaches the old age of 66 or older. It all just depends on what issues the baby was born with and if those issues progressed through their lifespan or if they had resolved on their own. Short-term complications can include; lung problems, heart problems (the most common heart problem for a premature baby is a Patent Ductus Arteriosus which often closes on its own but if left untreated it can cause too much blood flow to the heart which could cause heart failure. Other treatments for low blood pressure may require intravenous fluids, medications and sometimes even blood transfusions), brain problems Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY 5 (the earlier the prematurity, the higher risk of intraventricular hemorrhage. Most hemorrhages are small and will resolve on their own), gastrointestinal problems (they are more likely to develop necrotizing enterocolitis), metabolism problems (they could develop low blood sugar) and they can even have immune system problems (they could have underdeveloped immune systems which often leads to infections). Conclusion Overall, premature birth is something that shouldn’t be taken lightly. Many premature babies will continue to suffer with the health issues after birth and throughout their entire lives. Many doctors plead for families to research and understand the risk factors of having a premature baby. If the baby is lucky then they will live through their first couple months of life, others aren’t as fortunate. But even after the first couple months, it is continues to be a never ending uphill battle. Luckily for parents who have premature babies, technology has come a long way and there are now fewer amounts of preemies. Most of the illnesses that premature babies have can be accommodated with medications, special medical supplies or some happen to go away on their own. It is still a scary thought to have a preemie but one need not worry too much about it. Running Head: EFFECTS OF PREMATURITY References American Academy of Pediatrics. (2015, March 2). Late preterm birth and neurocognitive performance in late adulthood: a birth cohort study. Beamish, R. (n.d.). Preterm Birth and Adult Illness. Behrman, R., & Butler, A. (n.d.). Neurodevelopmental, Health, and Family Outcomes for Infants Born Preterm. Mayo Clinic Staff. (2014, November 27). Premature Birth Complications. Pediatric Academic Societies. (2014, May 5). Being Born 4-6 weeks Premature Can Affect Brain Structure, Function. Randerson, J. (2008, March 25). Premature birth has long-term effects. Riley, L. (n.d.). Preterm Labor and Delivery. Rochman, B. (2011, August 1). How Long Do the Effects of Being Born Premature Last? Until Adulthood. Sifferlin, A. (2013, August 27). Lasting Effects of Being Born Too Early. 6