Mechanisms for Evolution Test Review with answers
advertisement
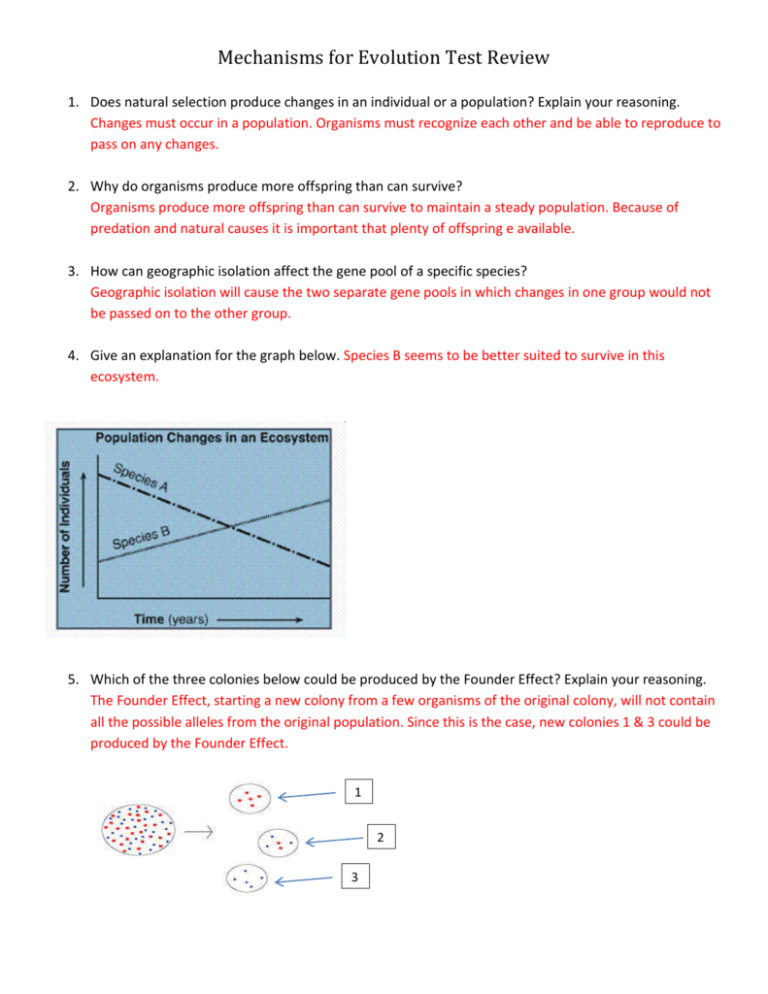
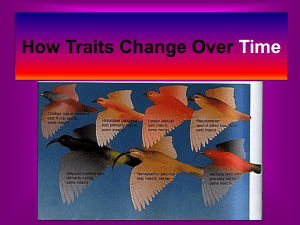
Mechanisms for Evolution Test Review 1. Does natural selection produce changes in an individual or a population? Explain your reasoning. Changes must occur in a population. Organisms must recognize each other and be able to reproduce to pass on any changes. 2. Why do organisms produce more offspring than can survive? Organisms produce more offspring than can survive to maintain a steady population. Because of predation and natural causes it is important that plenty of offspring e available. 3. How can geographic isolation affect the gene pool of a specific species? Geographic isolation will cause the two separate gene pools in which changes in one group would not be passed on to the other group. 4. Give an explanation for the graph below. Species B seems to be better suited to survive in this ecosystem. 5. Which of the three colonies below could be produced by the Founder Effect? Explain your reasoning. The Founder Effect, starting a new colony from a few organisms of the original colony, will not contain all the possible alleles from the original population. Since this is the case, new colonies 1 & 3 could be produced by the Founder Effect. 1 2 3 Mechanisms for Evolution Test Review 6. When organisms pass on their beneficial genes to offspring, does it increase the frequency of genes in an individual organism or in the population of the organisms? This is an example of natural selection in which the passing on of genes will affect the frequency of genes in a population. 7. Define genetic flow. Give an example. Immigration and emigration, the moving of organisms into and out of populations, causes genes to move into and out of the population. This movement increases genetic variation. 8. What is mimicry and how is it beneficial to an organism? Give an example. Mimicry is when one organism has an adaptation that allows it to look like another organism or another object. This adaptation protects the organism from predation. The insect called a walking stick looks like a stick. 9. List the 5 conditions that must be met for the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem. If these conditions are not met it will most likely cause a change in the gene frequency of the population. a. Population must be large b. No mutations c. Random mating d. No migration e. No natural selection 10. Define “Survival of the Fittest”. What does “fitness” refer to? Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce, passing on the genes that help the organism to survivie. 11. Define speciation. Speciation is the formation of new species as a result of geographic, physiological, anatomical, or behavioral factors that prevent previously interbreeding populations from breeding with each other. 12. Explain how the Founders Effect could cause speciation. The Founder Effect causes geographic isolation and the separation of genes. 13. How would a high mutation rate in a changing environment affect natural selection? High mutations and a changing environment would cause a higher rate of natural selection 14. Why do antibiotics and pesticides work at first, but later are ineffective? Antibiotics and pesticides can cause mutations that eventually cause organisms to become resistant. Mechanisms for Evolution Test Review 15. How come acquired characteristics (such as cutting off a dog’s tail) can’t be passed to offspring? Only changes that occur in the gametes of the organisms can be passed on to their offspring. 16. Is getting a tan in the summer (environmental factor) considered natural selection? Why or why not? No, because the tan cannot be passed on to the offspring. 17. Define natural selection. Natural selection is the process by which forms of life having traits that better enable them to adapt to specific environmental pressures, as predators, changes in climate, or competition for food or mates, will tend to survive and reproduce in greater numbers than others of their kind, thus ensuring the perpetuation of those favorable traits in succeeding generations. 18. Why do similarities in protein sequences of different species mean they are closely related? Amino acids all have specific codes which can be seen as organisms are compared. 19. Explain the 3 types of selection modes: stabilizing, directional, and disruptive. a. Stabilizing selection – selection pressure is on both of the extremes keeping allele frequency stable b. Directional selection – selection pressure is on one extreme or the other causing a swing in allele frequency c. Disruptive selection – selection pressure is on the average individual which can possibly cause speciation to occur 20. Identify the three selection modes below: a. Directional b. Disruptive c. Stabilizing Mechanisms for Evolution Test Review 21. What does the following table show us about beak adaptations of Darwin’s finches? The diversity of the adaptations found in the beaks of the finches is caused by food and habitat availability.