sch3u unit 3 outline – quantities in chemical reactions
advertisement
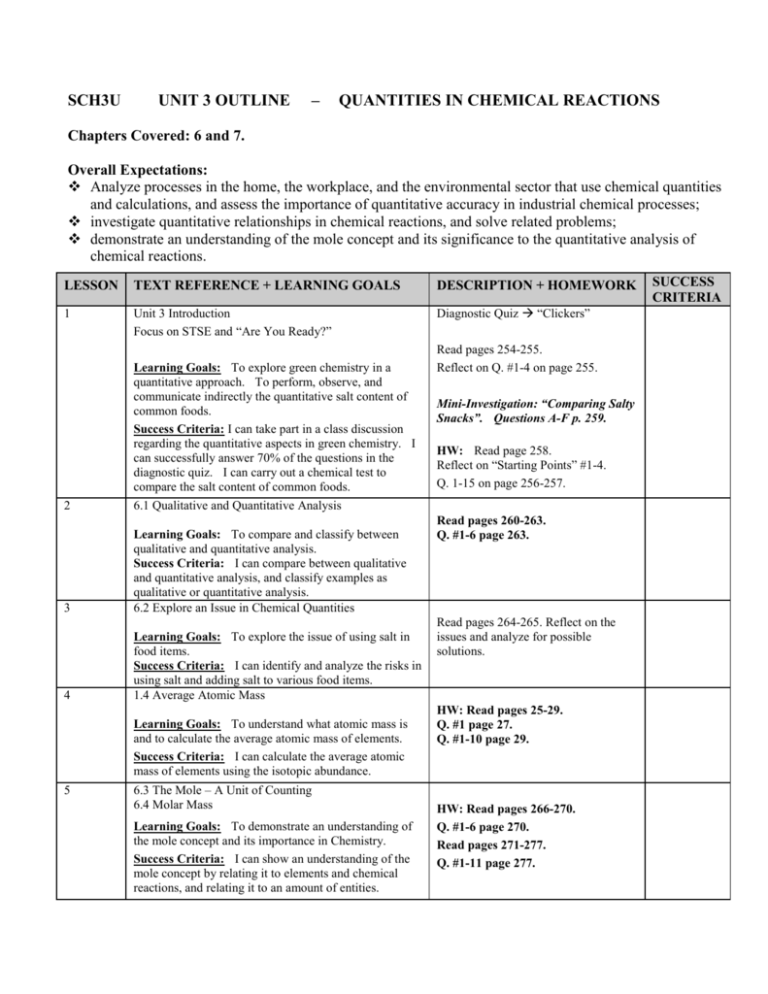
SCH3U UNIT 3 OUTLINE – QUANTITIES IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chapters Covered: 6 and 7. Overall Expectations: Analyze processes in the home, the workplace, and the environmental sector that use chemical quantities and calculations, and assess the importance of quantitative accuracy in industrial chemical processes; investigate quantitative relationships in chemical reactions, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of the mole concept and its significance to the quantitative analysis of chemical reactions. LESSON TEXT REFERENCE + LEARNING GOALS DESCRIPTION + HOMEWORK 1 Unit 3 Introduction Focus on STSE and “Are You Ready?” Diagnostic Quiz “Clickers” Learning Goals: To explore green chemistry in a quantitative approach. To perform, observe, and communicate indirectly the quantitative salt content of common foods. Success Criteria: I can take part in a class discussion regarding the quantitative aspects in green chemistry. I can successfully answer 70% of the questions in the diagnostic quiz. I can carry out a chemical test to compare the salt content of common foods. 2 6.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis 3 Learning Goals: To compare and classify between qualitative and quantitative analysis. Success Criteria: I can compare between qualitative and quantitative analysis, and classify examples as qualitative or quantitative analysis. 6.2 Explore an Issue in Chemical Quantities 4 Learning Goals: To explore the issue of using salt in food items. Success Criteria: I can identify and analyze the risks in using salt and adding salt to various food items. 1.4 Average Atomic Mass Learning Goals: To understand what atomic mass is and to calculate the average atomic mass of elements. Success Criteria: I can calculate the average atomic mass of elements using the isotopic abundance. 5 6.3 The Mole – A Unit of Counting 6.4 Molar Mass Learning Goals: To demonstrate an understanding of the mole concept and its importance in Chemistry. Success Criteria: I can show an understanding of the mole concept by relating it to elements and chemical reactions, and relating it to an amount of entities. Read pages 254-255. Reflect on Q. #1-4 on page 255. Mini-Investigation: “Comparing Salty Snacks”. Questions A-F p. 259. HW: Read page 258. Reflect on “Starting Points” #1-4. Q. 1-15 on page 256-257. Read pages 260-263. Q. #1-6 page 263. Read pages 264-265. Reflect on the issues and analyze for possible solutions. HW: Read pages 25-29. Q. #1 page 27. Q. #1-10 page 29. HW: Read pages 266-270. Q. #1-6 page 270. Read pages 271-277. Q. #1-11 page 277. SUCCESS CRITERIA LESSON TEXT REFERENCE + LEARNING GOALS 6 6.5 Mass and Number of Entities 7 Learning Goals: To calculate quantities of entities using the unit “mole”. Success Criteria: I can use Avogadro’s Constant and the unit “mole” to calculate quantities of atoms, ions, molecules, and other items. 6.6 The Composition of Unknown Compounds 8 Learning Goals: To calculate the percentage composition of substances by using lab data and chemical formula. Success Criteria: I can calculate the percentage composition of substances using lab data and/or chemical formula. 6.7 Empirical Formulas 6.9 Molecular Formulas Learning Goals: To determine the chemical composition (empirical and molecular formulas) of substances using percentage composition. Success Criteria: I can use calculations to determine the empirical and molecular formulas of different substances using percentage composition. 9 10 11 6.8 Chemistry JOURNAL Learning Goals: To read a Chemistry Journal on “Drug Contaminated Currency”, and to gain more knowledge on Mass Spectroscopy. Success Criteria: I have (more) knowledge about how chemistry is used in the real world and how Mass Spectroscopy is used to determine for an unknown substance. Hydrates Learning Goals: To learn nomenclature of hydrates and to calculate for the chemical formula of hydrates. Success Criteria: I can name and write chemical formulas of hydrates. I can also calculate for the chemical formula of an unknown hydrate from lab data. HW: Read pages 278-283. Q. #1-9 page 283. Investigation 6.6.1: “Popping Percentage Composition” HW: Read pages 284-288. Q. #1-8 page 288. HW: Read pages 289-293. Q. #1-10 page 293. HW: Read pages 296-300. Q. #1-9 page 300. HW: Read pages 294-295. Q. #1-6 page 295. LAB HANDOUT! REFERENCE: Investigation 6.9.1 “Determining the Formula of a Hydrate” page 304-305. 7.1 Stoichiometry: Mole Ratios in Chemical Equations Learning Goals: To review balancing equations. To make the connection between the coefficient in a balanced chemical equation and The Law of Conservation of Mass (LCM) as mole ratios. Success Criteria: I can balance chemical equations more efficiently. I can use the coefficients in the balanced equation to verify the LCM, and to relate the coefficients as mole ratios between substances in the chemical equation. 12 DESCRIPTION + HOMEWORK 7.2 Mass Relationships in Chemical Equations (ie. HW: Read pages 314-320 Q. #1-9 page 320. SUCCESS CRITERIA LESSON TEXT REFERENCE + LEARNING GOALS DESCRIPTION + HOMEWORK Mass-to-Mass Problems) Learning Goals: To use Stoichiometry to calculate for the mass of another substance in a balanced chemical equation given the mass of one of the substances. Success Criteria: I can calculate the mass of any substance given the mass of another substance in a balanced chemical equation using Stoichiometry. 13 7.3 Which Reagent Runs Out First? 7.4 Calculations Involving Limiting Reagents Learning Goals: To understand what a limiting reagent is and to determine the limiting reagent in a chemical reaction. To calculate the mass of a product using information of the limiting reagent. Success Criteria: I can define and identify the limiting reagent in a chemical reaction, and I can calculate the mass of product from the limiting reagent using Stoichiometry. 14 HW: Read pages 321- 324. Q. #1-10 page 325. HW: Read pages 326-329. Q. #1-7 page 330. HW: Read pages 331-334. Q. #1-11 page 335. 7.5 Percentage Yield Lab Handout: “Percentage Yield” Learning Goals: To define and identify between theoretical yield, experimental yield, and percentage yield. As well, to calculate for the various yields in a chemical reaction. Success Criteria: I can differentiate between theoretical yield, experimental yield, and percentage yield. I can carry out Stoichiometric calculations to determine for theoretical, experimental, and percentage yields in a chemical reaction. I can also carry out an experiment to determine the Percentage Yield of a chemical reaction. 15 p. 307-312 p345-351 p. 354-362 16 HW: Read pages 336-338. Q. #1-14 page 339. Chapter 6 Self-Quiz Questions + Review Questions Chapter 7 Self-Quiz Questions + Review Questions ** REVIEW Unit 3 ** *** TEST: UNIT 3 *** SUCCESS CRITERIA








