Lung Capacity
advertisement

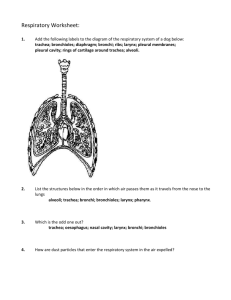
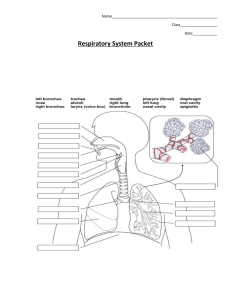
Unit 5: Human Body Systems Respiratory System: Alveoli Name _______________________________________________ Date ________________ Period _______ Assignment 7 Notes The respiratory system provides exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide Alveoli – The ___________ (2) ___________into numerous microscopic tubes called ________________, which open into ___________ of thin-walled sacs called ___________ – _______________________ where O2 & CO2 are exchanged by ______________ between air & blood Take it Farther Instructions: Use at least 1 complete sentences to answer the questions below. The respiratory system exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide. All cells require oxygen to function and must get rid of carbon dioxide. The alveoli and their capillaries are the only places where gas exchange between the lungs and the atmosphere takes place. Gas exchange in the lungs is based on three principles: Oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried by the lungs. Gas moves by diffusion—from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. The lining of the alveoli must be moist to help gases diffuse. 1. Which parts of the lungs allow gas exchange to occur? In the alveoli, the respiratory and circulatory systems come together in the process of gas exchange. The blood entering the capillaries (which surround the alveoli) contains a lower concentration of oxygen than is in the alveoli. Therefore, oxygen diffuses out of the alveoli into the blood where it binds with hemoglobin in the red blood cells. In contrast, the concentration of carbon dioxide is higher in the blood than in the alveoli, so the gas diffuses out of the blood and into the alveoli. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled from the body along with some water vapor. Gas exchange is an involuntary function regulated by the brain. When carbon dioxide levels rise and more oxygen is needed, the brain sends messages to stimulate the diaphragm and rib muscles to work harder to exhale CO2. 2. What causes oxygen to move into the blood and carbon dioxide to move into the alveoli? 3. Label the areas of high and low concentration in the picture to the right. Then draw an arrow to show the direction the particles will diffuse. Damage to the respiratory system from smoking or from various disorders makes gas exchange more difficult. Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer and also of damage to the alveoli, which can lead to a disorder called emphysema. Over time, so many alveoli are destroyed or damaged that not enough oxygen can enter the blood, and the lungs fail. Another disorder, asthma, affects the bronchioles, causing them to constrict and reduce airflow. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes the lungs to produce a thick, sticky mucus that can block the airway or lead to lung infections. 4. Why are respiratory diseases and disorders life-threatening? How do they prevent the lungs from doing their job? TedEd 1. The scientific term for the process of breathing in air is: A. Aspire B. Retire C. Inspire D. Circulate E. Ambulate 2. How do the alveoli in the lungs move oxygen and nutrients into the bloodstream? A. Gravity B. Diffusion C. Magnetic Force D. Time E. Pressure 4. What does a ‘hypoxic’ cell environment mean? A. Oxygen-poor B. High oxygen C. High pressure D. Low pressure E. Life-giving 5. Which part of the brain controls our breathing when we sleep? A. Cerebellum B. Pineal Gland C. Medulla D. Ocular nerve E. Sinuses 3. Panting breath regulates the body’s temperature by allowing it to naturally: A. Heat up B. Cool down C. Increase circulation D. Deactivate the sweat glands E. Breathe only through the nose 6. There is a lot of talk in the news about the earth’s atmosphere, and increases in carbon dioxide that may be causing global warming. How does the amount of carbon dioxide or oxygen in the air affect humans, or even animals and plants? What are the health effects of breathing polluted air, and who is most vulnerable? 7. What is yoga, and why is it so popular for people who are trying to lower their stress levels and get healthy? How do the exercises used in yoga affect both the body and mind at the same time? Why do people feel a sense of calmness when they practice breathing techniques and yoga? Graph Investigation 1. How does the lung function of a non-smoker change with age over time? 2. How does the lung function of a smoker compare to a non-smoker over time? 3. By the age of 52 how is the lung function of a smoker affected? 4. What is the average age of severe disability caused by smoking? 5. Estimate the average age of death in a smoker. 6. How does lung function change after quitting smoking? 7. Approximately how much longer might a person live if they quit smoking?