Cellular Respiration
advertisement

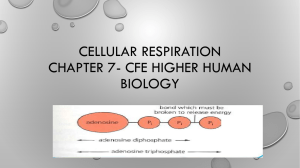
Cellular Respiration Respiration is a series of chemical reactions that converts glucose or other food molecules into stored energy in the form of the chemical ATP. Respiration is usually divided into three stages: Glycolysis, Krebs’ cycle and the electron transport chain. A) Web site name: University of Cincinnati, Clermont College Web URL: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cellresp.htm Read “Cellular Respiration and Fermentation” 1) What is glycolysis? _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2) Does glycolysis need oxygen as part of any of its chemical reactions?______ 3) What color are the Nitrogen (N) atoms in the diagram? _________________ 4) What is the connection between yogurt and sore muscles? ____________________________________________________________ 5) Which long protein molecule in bread traps the CO2 so that the bread rises? _____________________________________________________________ B) Web site name: Indiana University Biotech Web URL: http://biotech.icmb.utexas.edu/glycolysis/glycohome.html 6) What is glucose converted into during glycolysis? ____________________ 7) What is the connection between glycolysis and beer? __________________ _____________________________________________________________ Click on Pathway 8) How many carbon atoms are there in fructose? ____________________ 9) What is the difference in chemical structure between Dihydroxyacetone phosphate and Glyceraldehyde phosphate ? _________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 10) Which enzyme (ending is –ase) breaks Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into two 3carbon molecules ? __________________________ C) Web site name: University of California Muscle Physiology Lab Web URL: http://muscle.ucsd.edu/musintro/glucose.shtml Read “Aerobic metabolism” 11) What 2-carbon molecule is pyruvate oxidized to? _____________________ 12) What 6-carbon molecule is shown on the top right of the cycle? _____________________________________________________________ 13) How many NADH molecules are produced for every pyruvate that enters the Krebs cycle? __________________ Click on NADHs 14) How many ATPs are actually formed from each NADH ? _______________ 15) Which cells have creatine phosphate in them ? ________________________ D) Web site name: University of California Muscle Physiology Lab Web URL: http://muscle.ucsd.edu/musintro/creatine.shtml 16) What is the normal turnover rate of creatine? _________________________ 17) If you eat (ingest) more creatine what happens to the amount synthesized by your body? ____________________________________________________ Many companies sell creatine as a “nutritional supplement”. One example is: E) Web site name: Absolute Creatine Web URL: http://www.absolute-creatine.com/1.htm 18) How much creatine was sold in 1998? ____________________________ 19) What claims does this company make for creatine? ____________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 20) Why may some people “not be a responder to creatine”? _____________________________________________________________ 21) Read the fine print at the bottom of the screen. Do you think that the Food and Drug Administration should investigate statements made by these companies ? ______________ Why ? ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ The reactions of the Krebs cycle and Electron Transport Chain occur inside the mitochondria. This next web site shows the structure of mitochondria: F) Web site name: Rice University, Texas Web URL: http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~bioslabs/studies/mitochondria/mitotheory.html 22) Mitochondria are ___________-sized organelles, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. 23) What is one of the richest sources of mitochondria known? _____________________________________________________________ 24) What is the function of “porins”? __________________________________ 25) Where is the electron transport chain located? ________________________ 26) Why can photos make it appear that there is more than one mitochondrion? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ G) Web site name: Florida State College at Jacksonville Web URL: http://web.fscj.edu/David.Byres/etchain.html Read “The Electron Transport Chain” 27) The proteins of the inner membrane collect electrons from which two chemicals? ______________________________________________ 28) What is the purpose of oxygen in the electron transport chain? ___________ _____________________________________________________________ 29) How many ATP molecules are made from each FADH2 ? _______________ One way of increasing respiration ( and “burning” food ) is to exercise. H) Web site name: Federal Citizen Information Center Web URL: http://www.pueblo.gsa.gov/cic_text/health/exercise-heart/page3.htm Look at the table of “Activity” and “Calories Burned”. 30) Which activity listed here uses the fewest calories? ____________________ 31) How many calories are used when you run at 10mph? __________________ 32) How many more calories are used by jogging at 7 mph compared to 51/2 mph? ___________________________ 33) How many calories are burned by swimming at 50 yds/min? ____________ 34) A Big Mac cheeseburger (without fries) has 704 calories. Roughly how many hours would you have to walk at 2 mph to burn these calories? ____________________