Study Guide Fall Semester
advertisement

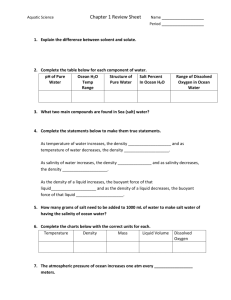
Marine Biology Fall Study Guide 1. What happens to sea water as it cools? 2. The attractions between liquid water molecules are called____________. How strong are these bonds? 3. What is the name of a. The amount of heat required to melt a substance? b. the amount of heat needed to raise a substance’s temperature by a given amount? c. The amount of heat required to evaporate a substance? d. What is so special about water in regards to these amounts? 4. What is water good at dissolving (a general class of molecules)? What happens to salt when it is placed in water? What is the process called when salt dissolves in water? 5. What are processes that contribute to materials that are dissolved in sea water? What is salinity? What are the two units that are used to express salinity? 6. What is the average salinity of the ocean? What two factors contribute to slight variations in the average salinity of the water? 7. Describe the relationship between salinity, temperature, and density? What is a profile? What devices are used to measure salinity, temperature, and density ( give acronym and full name)? 8. What are the three most important gasses in the ocean? What is the process that occurs between the ocean and atmosphere called? 9. Give the equation for i. Photosynthesis ii. Respiration 10. Sketch the diagram of colors of light penetrating to different depths in the ocean. What color would be found at 164ft? What is the first color to disappear? At around what depth? And a depth of 3300ft what color would the surrounding water be? 11. How much pressure are animal on land under? In water how much depth ( ft and meter) equals 1 atmosphere? 12. The stability of water depends on? What does stratified mean? What makes the water column harder to mix vertically? 13. What is the process of downwelling known as? What form of circulation is driven by density changes? 14. What are the three main layer of the ocean? Sudden drops in temperature over a small depth interval are called? What is the main thermocline? What is the mix layer and where is it found? 15. What are the effects of the Coriolis effect( North and South)? 16. Pretend that you are performing an experiment to see which of two identical kelp fronds (Kelp types A and B) will grow into a taller frond. You put Kelp A and B in separate aquaria that are identical. The aquaria receive the same sediment, saltwater, sunlight, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. However, you put nitrogen fertilizer in Kelp B’s aquaria, but not in Kelp A’s aquaria. After two weeks you measure the mean height of all kelp fronds. a) identify the control group b) identify the experimental group c) identify the independent variable d) identify the dependent variable e) identify the constants f) form a sensible hypothesis for this experiment g) if after 2 weeks of running the experiment, the control group has bigger kelp fronds compared to the experimental group, list several potential sources of error (i.e., confounding variables) that could explain what happened. h) identify the variable that goes on the Y-axis i) identify the variable that goes on the x-axis j) now pretend that the mean frond height after two weeks is bigger for the control group, however, the error bars about the mean overlap. What do you conclude? 17. If you have high accuracy in darts, then your precision is ______. 18. What questions do you ask yourself when trying to identify the independent and dependent variables? Name at least 3 for each one. 19. Which do scientists use when reporting their findings, subjective or objective statements? 20. “The coral reefs at the study site were bleached white and there were very few fish inhabiting the reef structure.” Is this statement qualitative or quantitative? 21. What group of plankton a) is at the very bottom of the food web? b) is in the Kingdom Protista? c) is in the Kingdom Animalia? d) composes the singled celled algae? e) forms red tides and HABs? f) eats phytoplankton? g) performs photosynthesis? h) has larval crabs and shrimp in it? i) produces the air we breathe? j) has pigments like chlorophyll? k) is detectable using satellites? l) has representatives called Diatoms and Dinoflagellates? m) forms the primary producers? n) forms the primary consumers? o) is heterotrophic? p) is autotrophic? q) has the highest total amount of energy? r) has a lower number of individuals and biomass? 22. Site 8 lines of evidence supporting the theory of Plate Tectonics. 23. Draw a picture of the ocean floor and label all of the different parts. Where is most sea life located, and why? 24. Compare and contrast the processes that occur at mid-ocean ridges and subduction zones? 25. Compare and contrast 5 characteristics of continental and oceanic crusts, and explain why each crust type has those characteristics. 26. Where are hydrothermal vents located and how do organisms survive there? 27. Where do earthquakes and volcanoes tend to occur/form? Why is this? 28. Give two examples of how plate tectonics has affected our present day biogeography. 29.. Explain what a magnetic anomaly is and how it is formed. 30. Why do Iceland and the Azores exist? 31. Two examples of Mid-ocean ridges are___________ and ____________. 32. Draw the different layers of the Earth. Which layer is the thickest? Densest? 33. 3 types of plate boundaries include__________, __________, & _________. 34. 3 types of plates include ____________, ______________, &____________. 35. What are 4 possible scenarios involving plate collision/separation (continental crust collides with oceanic crust, etc), and explain the physical consequences of each scenario. 36. 3 kinds of mammals are _________, __________, &_________. 37. Know the difference between and be able to draw/label a hydrogen bond, an ionic bond, a covalent bond, and a polar covalent bond. Which bond forms between water molecules? Which bond is present within a water molecule? 38. Be able to draw a salt water solution. 39. Be able to explain why water is polar, and why polarity makes water a good solvent. 40. Write down everything you know about density in regards to the demos from class. What is the equation, and how does the equation change when you, say, increase/decrease temperature and salinity. What are 3 factors that affect the density of ocean water at the surface (pg 51)? How does density relate to downwelling and thermohaline circulation? 41. Define the terms evaporation, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, surface runoff, water table, ground water, root uptake (absorption), catchment, & watershed. 42. 43. Why do we have seasons on Planet Earth? Similarly, why is it winter in Australia when it is summer in the United States? 44. Know how upwelling along California’s Coast is a result of the wind direction working in combination with the Coriolis Effect. 45. What major systems are affected by the Coriolis Effect? What direction do the major ocean gyres rotate in the Northern versus Southern Hemispheres? 46.the deepest, and why (see Fig. 3.11 and text on pg 48)? 47. Pressure: If you’re 100m below the ocean surface, how much pressure are you under? 48. Compare the relative percentages of the major gases in the atmosphere and the ocean. 49. Salinity: What are the units? If the salinity of the ocean is 40 ppt, what percentage of your solution is salt? 50. What process is the opposite of photosynthesis? 51. I can identify which prokaryote is more related to a eukaryotic cell and why. 52. I can explain what pseudopodia are and identify which groups possess them. 53. I can explain five major ecological roles of cyanobacteria. 54.works. 55. I can identify the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and can place the eight organism groups learned in class into the correct domain. 56. I can explain the main objective of chemosynthesis and photosynthesis. 57. I can differentiate the three groups of phytoplankton/microalgae based on where they are most commonly found. 58. I can differentiate the following: Lorica, Frustule, Theca Plate, Coccolith 59. For the items in #11 above, I know the chemical compounds of each one. 60. I can identify two groups that possess a silica dioxide outer layer. 61. I can list the steps of asexual and sexual reproduction in diatoms while explaining what happens to the frustule during the entire cycle. 62. I can identify three diatom examples, two cyanobacteria, and five dinoflagellates by scientific name or just genus. 63. I can state the main difference and main similarity between protozoans and microalgae. 64. I can recite the relevant taxonomy (D, K, P, C – where applicable) on the flow chart for each of the eight organism groups. 65. I can explain the important roles of decay bacteria. 66. In the mutualistic relationship between corals and “zoocs”, I know several ways each organism benefits. 67. I can recite which organism group has which pigment types for cyanobacteria, diatoms, and dinoflagellates. 68. I can name the different oozes created by different Protist groups and identify the chemical compounds in each kind. 69. I can identify two properties of diatoms that aid in floatation. 70. On the back of this paper, draw a sketch of the different layers of the Earth. For each layer, indicate whether it is liquid or solid. 71. Compare and contrast the continental and oceanic crusts in terms of color, density, age, floatation in the mantle. 72. What is the mid-ocean ridge system analogous to? 73. At or near the ridge there is _____ sediments which are geologically ____ in age. 74. Examine Fig. 2.5. What Ocean has the most trenches? 75. Examin Fig. 2.6. What do you notice about the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes? 76. Explain what a magnetic reversal is, and sketch a picture of a magnetic anomaly on the back of this paper. 77. At mid-ocean ridges _____ forms which allows the process of _________________ to occur. 78. As new plate material forms, somewhere else other plate material is destroyed at a _____ in a process known as ____________. 79. Sediments of the ocean are either __________ or ___________, which means they are derived from either ____________________________ or ___________________. 80. During _______periods the water is warmer and higher. During _______ the water is colder or frozen and the sea level is _________. 81. Sketch the bottom of the ocean floor and label the different parts.