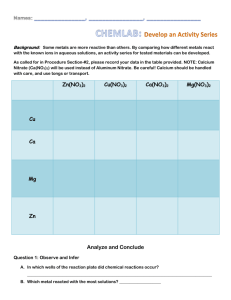
New words - Всероссийская информационно
advertisement

МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ РЕСПУБЛИКИ МОРДОВИЯ Государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение Республики Мордовия среднего профессионального образования (среднее специальное учебное заведение) «Торбеевский колледж мясной и молочной промышленности» Рабочая тетрадь по учебной дисциплине ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык для студентов, обучающихся по специальности 230401 «Информационные системы» (по отраслям) 2014 год Рассмотрено на заседании предметной (цикловой) комиссии общих гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин ________________Н.И. Пониматкина/ «______» ___________________ 2014г. Составлено в соответствии с ФГОС-3 на основании рабочей программы по дисциплине ОГСЭ.03 «Английский язык» _______________/Н.И. Годяева/ «______» _______________2014г. Рабочая тетрадь рекомендована к применению. Заместитель директора по НМР: _________________ /Н.Н. Байшева/ «______» ________________ 2014г. Автор: Пониматкина Н.И., преподаватель дисциплины «Английский язык» ГБОУ РМ СПО (ССУЗ «ТКММП». Рецензенты: Половникова Е.И., директор МБУ «ЦИМ и ТОМБУО» Сиркина Л.И., преподаватель ГБОУ РМ СПО (ССУЗ) «ТКММП» Рабочая тетрадь составлена в соответствии с Федеральным государственным образовательным стандартом среднего профессионального образования основной профессиональной образовательной программы и рабочей программой учебной дисциплины ОГСЭ.03 Английский язык для студентов 4 курса специальности 230401 Информационные системы (по отраслям). В рабочей тетради содержится множество заданий, которые позволяют обучающимся проверить и закрепить свои знания по английскому языку, степень сформированных общих и профессиональных компетенций. Пояснительная записка Данная рабочая тетрадь предназначена для студентов средних специальных учебных заведений по специальности 230401 Информационные системы (по отраслям). Цель: ознакомление с информационной терминологией на английском языке и ее усвоение, выработка и развитие навыка чтения, различных видов устной и письменной речи на практических занятиях. Содержание занятий вполне доступное для студентов, задания направлены на расширение активного словаря, развитие языковой догадки, повторение грамматического материала. Тематика текстов профессиональной направленности способствует развитию у студентов – программистов навыков сравнительно-информационного толкования. Рабочая тетрадь представляет собой упражнения и задания для студентов 4 курса. Планирование носит примерный характер. Преподаватель по своему усмотрению может, в зависимости от уровня знаний студентов, уменьшить или увеличить изучаемый материал. Автор старалась использовать разнообразные приемы работы над текстом, лексическим и грамматическим материалом. Поэтому в каждой теме приемы разные. Автор специально включила в рабочую тетрадь избыточное количество упражнений, предоставив преподавателю право выбирать наиболее необходимые для своих студентов. Там, где, по мнению автора, недостаточно теоретического материала, перед выполнением упражнений предлагается недостающий материал для изучения. Упражнения намеренно не снабжены ключами, что дает возможность преподавателю проверить реальные знания студентов. Автор надеется, что данное издание станет надежным помощником преподавателю и студентам в работе по совершенствованию умений и навыков в английском языке. Рецензия на рабочую тетрадь по дисциплине ОГСЭ.03 «Английский язык», составленную преподавателем ГБОУ РМ СПО (ССУЗ) «ТКММП» Пониматкиной Ниной Ивановной Рабочая тетрадь соответствует Федеральному государственному образовательному стандарту среднего профессионального образования, требованиям программы по иностранным языкам и тематическому планированию по дисциплине «Английский язык» по специальности 230401 Информационные системы (по отраслям). Материал рабочей тетради подобран не только с учетом профессиональных интересов студентов, но и с точки зрения его новизны и актуальности, что способствует мотивации студентов и стимулирует их к работе над иностранным языком. Тексты аутентичны. В них представлена профессиональная лексика, знание которой необходимо студентам для формирования навыка чтения специальной литературы. Данная рабочая тетрадь построена на принципе взаимосвязанного обучения всем видам речевой деятельности на профессионально – ориентированном материале (чтение, перевод, устная монологическая и диалогическая и письменная речь). Система упражнений направлена на закрепление лексического, грамматического, фразеологического минимума и обеспечивает практику устной речи по теме. В результате работы с тетрадью студенты получают возможность расширить словарный запас профессиональной лексики, освоить нормы и особенности делового общения, научиться читать и переводить тексты по специальности, правильно оформлять деловые письма, а также работать со справочной литературой и словарем. Рабочая тетрадь рекомендуется к практическому применению на занятиях по дисциплине «Английский язык» для студентов IV курса по специальности 230401 Информационные системы (по отраслям) в ГБОУ РМ СПО (ССУЗ) «ТКММП». Рецензент: ___________ /Е.И. Половникова, директор МБУО «ЦИМ и ТОМБУО»/ Рецензия на рабочую тетрадь по дисциплине ОГСЭ.03 «Английский язык», составленное преподавателем ГБОУ РМ СПО «ССУЗ) «ТКММП» Пониматкиной Ниной Ивановной. Рабочая тетрадь по дисциплине «Английский язык» предназначена для студентов средних специальных учебных заведений по специальности 230401 «Информационные системы» (по отраслям) в ходе выполнения аудиторной работы и составлена в соответствии с Федеральным государственным образовательным стандартом среднего профессионального образования III поколения. Она построена на коммуникативно-функциональном принципе и предусматривает развитие всех видов речевой деятельности в рамках учебной программы по английскому языку. Данная рабочая тетрадь отражает терминологию основных направлений информационной и управленческой деятельности, включая основные аспекты деловой этики. Материал рабочей тетради отражает современные тенденции и требования к обучению и практическому владению иностранным языком в повседневном общении и профессиональной деятельности, направлено на повышение общей и коммуникативной культуры специалистов, совершенствование коммуникативных умений и навыков, повышение качества профессионального образования, интеллектуализации и мобильности специалистов. Рабочая тетрадь имеет практическую направленность и ориентирована на активные методы обучения иностранным языкам. Рецензент: ____________________ /Сиркина Л.И., преподаватель ГБОУ РМ СПО (ССУЗ) «ТКММП»»/ В результате освоения учебной дисциплины обучающийся должен уметь: - общаться (устно и письменно) на иностранном языке на профессиональные и повседневные темы; - переводить (со словарем) иностранные тексты профессиональной направленности; - самостоятельно совершенствовать устную и письменную речь, пополнять словарный запас. В результате освоения учебной дисциплины обучающийся должен знать: - лексический (1200 – 1400 лексических единиц) и грамматический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода (со словарем) иностранных текстов профессиональной направленности. Кроме знаний и умений студент должен развивать общие компетенции: ОК 1. Понимать сущность и социальную значимость своей будущей профессии, проявлять к ней устойчивый интерес. ОК 2. Организовывать собственную деятельность, определять методы и способы выполнения профессиональных задач, оценивать их эффективность и качество. ОК 3. Решать проблемы, оценивать риски и принимать решения в нестандартных ситуациях. ОК 4. Осуществлять поиск, анализ оценку информации, необходимой для постановки и решения профессиональных задач, профессионального и личностного развития. ОК 5. Использовать информационно-коммуникативные технологии для совершенствования профессиональной деятельности. ОК 6. Работать в коллективе и команде, обеспечивать ее сплочение, эффективно общаться с коллегами. ОК 7. Ставить цели, мотивировать деятельность подчиненных, организовывать и контролировать их работу с принятием на себя ответственности за результат выполнения заданий. ОК 8. Самостоятельно определять задачи профессионального и личностного развития, заниматься самообразованием, осознанно планировать повышение квалификации. ОК 9. Быть готовым к смене технологий в профессиональной деятельности. ОК 10. Исполнять воинскую обязанность, в том числе с применением полученных профессиональных знаний (для юношей). Желаю Вам успехов в учебе и интересной работы! РАЗДЕЛ 3. ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНО-ОРИЕНТИРОВАННЫЙ КУРС ТЕМА 3.1. МАТЕРИАЛЫ И ТЕХНОЛОГИИ. Практическое занятие № 1 Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Электротехника и электроника) This is the widest field of engineering, concerned with systems and devices that use electric power and signals. Among the most important subjects in the field are electric power and machinery, electronic circuits, control systems, computer design, superconductors, solid-state electronics, and fibre optics. Electrical engineering can be divided into four main branches: electric power and machinery, electronics, communications and control, and computers. Electronic Engineering (Электроника) Electronic engineering deals with the research, design and application of circuits and devices used in the transmission and processing of information. The revolution in electronics is the trend towards integrating electronic devices on a single tiny chip of silicon or some other semi conductive material. Much of the research in electronics is directed towards creating even smaller chips, faster switching of components, and three-dimensional integrated circuits. New words: electrical engineer – инженер - электротехник systems engineer – системный программист integrated circuit – интегральная микросхема structural design – проектирование конструкций to shield – заслонять, защищать fibre optics – волоконная оптика copper wire (cable) – медный провод alteration – изменение, переделка to safeguard – охранять, защищать VLST – очень широкомасштабная интеграция Answer the questions: 1. Is engineering a science? ____________________________________________________________ 2. How can we translate the word “engineering”? ____________________________________________________________ 3. What are the Russian equivalents for this term? ____________________________________________________________ 4. What do mechanical engineers deal with? ____________________________________________________________ 5. What knowledge is necessary for a mechanical engineer? ____________________________________________________________ 6. What is the task of a mechanical engineer? ____________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 2 Technological Processes Drawing consists of pulling metal through a die. An example of drawing is wire drawing. The diameter reduction that can be achieved in one die is limited, but several dies in series can be used to get the desired reduction. Sheet metal forming is widely used when parts of certain shape and size are needed. It includes forging, bending and shearing. One characteristic of sheet metal forming is that the thickness of the sheet changes little in processing. The metal is stretched just beyond its yield point (2 to 4 percent strain) in order to retain the new shape. Bending can be done by pressing two dies. Shearing is a cutting operation similar to that used for cloth. Forging is the shaping of a piece of metal by pushing with open or closed dies. It is usually done hot in order to reduce the required force and increase the metal’s plasticity. Open-die forging is usually done by hammering a part between two flat faces. It is used to make parts that are too big to be formed in a closed die or in cases where only a few parts are to be made. Closed-die forging is the shaping of hot metal within the walls of two dies that come together to enclose the workpiece on all sides. Two closed-die forging operations are given special names. They are upsetting and coining. Coining takes its name from the final stage of forming metal coins, where the desired imprint is formed on a metal disk that is pressed in a closed die. New words: to pull – тянуть in series – серия, последовательно yield point – точка текучести металла shearing – обрезка, отрезание lower die – нижний штамп upper die – верхний штамп forming operation – операция штампования open-die forging - ковка в открытом штампе (подкладном) required – необходимый hammering – ковка within – внутри, в пределах to enclose – заключать upsetting – высадка, выдавливание coining – чеканка imprint – отпечаток Answer the questions: 1. How can the reduction of diameter in wire drawing be achieved? ____________________________________________________________ 2. What is sheet metal forming and where it can be used? ____________________________________________________________ 3. What is close-die forging? ____________________________________________________________ 4. What is forging? ____________________________________________________________ 5. What are the types of forging? ____________________________________________________________ 6. What types of hammers are used now? ____________________________________________________________ 7. Where are coining and upsetting used? ____________________________________________________________ 8. What process is used in wire production? ____________________________________________________________ Find the following word combinations in the text: 1. протягивание металла через фильеру _________________________________________________________ 2. волочение проволоки _________________________________________________________ 3. уменьшение диаметра _________________________________________________________ 4. толщина листа _________________________________________________________ 5. растягивать выше точки текучести _________________________________________________________ 6. сохранять новую форму _________________________________________________________ 7. края отрезаются _________________________________________________________ 8. конечные размеры _________________________________________________________ 9. уменьшить необходимое усилие _________________________________________________________ 10.увеличить пластичность металла _________________________________________________________ Translate into English: 1. При волочении проволоки диаметр отверстия волочильной доски каждый раз уменьшается. ___________________________________________________________________ 2. Штамповка листового металла включает в себя ковку, изгиб и обрезку. ____________________________________________________________________ 3. Небольшая деформация листа при растяжении помогает сохранять новую форму детали. ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Изменение формы при штамповке производится путем сжатия между двумя штампами. ____________________________________________________________________ 5. Края листа при штамповке отрезаются для получения конечных размеров. ____________________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 3 Automation Automation is performing certain tasks, previously done by people, by machines only. The sequences of operations are controlled automatically. The most familiar example of a highly automated system is an assembly plant for automobiles or other complex products. The term automation is also used to describe nonmanufacturing systems in which automatic devices can operate independently of human control. Such devices as automatic pilots, automatic telephone equipment and automated control systems are used to perform various operations much faster and better than could be done by people. Automated manufacturing had several steps in its development. Mechanization was the first step necessary in the development of automation. The simplification of work made it possible to design and build machines that resembled the motions of the worker. These specialized machines were motorized and they had better production efficiency. Industrial robots, originally designed only to perform simple tasks in environments dangerous to human workers, are now widely used to transfer, manipulate, and position both light and heavy workpiece performing all the functions of a transfer machine. Using feedback devices, machines can start, stop, speed up, slow down, count, inspect, test, compare and measure. These operations are commonly applied to a wide variety of production operations. Computers gave rise to the development of numerically controlled machines. The motions of these machines are controlled by punched paper or magnetic tapes. Automation has also had an influence on the areas of the economy other than manufacturing. Найдите в правой колонке перевод английских слов: 1. aid A. автоматизация 2. automation B. датчик 3. handling C. заменять 4. previously D. контролировать 5. sensor E. обработка 6. sequence F. помощь 7. simplification G. последовательность 8. to monitor H. ранее 9. to substitute I. упрощение _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________ Дополнительный словарь: assembly plant – сборочный завод nonmanufacturing – непроизводственный efficiency – эффективность steam engine – паровоз facilitate – способствовать punched – перфорированный Answer the questions: 1. How is the term automation defined in the text? 2. What is the most “familiar example” of automation given in the text? 3. What was the first step in the development of automation? 4. What were the first robots originally designed for? 5. What is feedback principle? 6. What industries use automation technologies? Find the following words and word combinations in the text: 1. автоматические устройства __________________________________________________________________ 2. автоматизированное производство __________________________________________________________________ 3. выполнять простые задачи __________________________________________________________________ 4. как легкие, так и тяжелые детали __________________________________________________________________ 5. интегрированная система производства __________________________________________________________________ 6. принцип обратной связи __________________________________________________________________ 7. механизм может разгоняться и тормозить __________________________________________________________________ 8. компьютер автоматически посылает команды __________________________________________________________________ 9. высокоавтоматизированная система __________________________________________________________________ 10. непроизводственная система __________________________________________________________________ Find Russian equivalents to the following: system of manufacture ____________________________________________ certain tasks _____________________________________________________ sequences of operations ____________________________________________ assembly plant ___________________________________________________ highly automated system ___________________________________________ automatic devices ________________________________________________ automated control systems _________________________________________ perform various operations _________________________________________ simplification of work _____________________________________________ motions of the worker _____________________________________________ dangerous environments ___________________________________________ numerically controlled machines ____________________________________ reprogramming of the equipment ____________________________________ Практическое занятие № 4 Types of Automation Manufacturing is one of the most important application fields for automation technology. There are several types of automation in manufacturing. 1. Fixed automation, sometimes called “hard automation” refers to automated machines in which the equipment configuration allows fixed sequence of processing operations. These machines are programmed by their design to make only certain processing operations. They are not easily changed over from one product to another. 2. Programmable automation is a form of automation fro producing products in large quantities, ranging from several dozen to several thousand units at a time. For each new product the production equipment must be reprogrammed and changed over. The program is coded in computer memory for each different product style and the machine-tool is controlled by the computer program. 3. Flexible automation is a kind of programmable automation. Programmable automation requires time to reprogram and change over the production equipment for each series of new product. This is lost production time, which is expensive. In flexible automation the number of products is limited so that the changeover of the equipment can be done very quickly and automatically. The reprogramming of the equipment in flexible automation is done at a computer terminal without using the production equipment itself. Flexible automation allows a mixture of different products to be produced one right after another. New words: investment – инвестиция, вклад rate – скорость, темп assembly machines – сборочные машины non-productive – непроизводительный changeover – переход, переналажка Answer the questions: 1. What is the most important application of automation? ____________________________________________________________ 2. What types of automation are used in manufacturing? ____________________________________________________________ 3. What is fixed automation? ____________________________________________________________ 4. What are the limitations of hard automation? ____________________________________________________________ 5. What is the best example of programmable automation? ____________________________________________________________ 6. What are the limitations of programmable automation? ____________________________________________________________ 7. What are the advantages of flexible automation? ____________________________________________________________ 8. Is it possible to produce different products one after another using automation technology? ____________________________________________________________ Find English equivalents in the text: 1. сфера применения ___________________________________________ 2. фиксированная последовательность операций ____________________________________________________________ 3. автоматические сборочные машины ____________________________ 4. определенные химические процессы ____________________________ 5. станок с числовым программным управлением ____________________________________________________________ 6. потерянное производственное время ____________________________ 7. разнообразная продукция _____________________________________ Explain in English what does the following mean: 1. automation technology ______________________________________ 2. fixed automation ___________________________________________ 3. assembly machines _________________________________________ 4. non-productive time ________________________________________ 5. programmable automation ___________________________________ 6. computer terminal __________________________________________ 7. numerical-control machine-tool _______________________________ Практическое занятие № 5 Engineering Materials Engineers have to know the best and most economical materials to use. Engineers must also understand the properties of these materials and how they can be worked. There are two kinds of materials used in engineering – metals and non-metals. We can divide metals into ferrous and non-ferrous. The former contain iron and the latter do not contain iron. Cast iron and steel, which are both alloys, and mixtures of iron and carbon, are the two most important ferrous metals. Steel contains a smaller proportion of carbon than cast iron. Certain elements can improve the properties of steel and are therefore added to it. For example, chromium may be included to resist corrosion and tungsten to increase hardness. Aluminum, copper, and the alloys (bronze and brass) are common non-ferrous metals. Plastics and ceramics are non-metals; however, plastics may be machined like metals. Plastics are classified into two types – thermoplastics and thermo sets. Thermoplastics can be shaped and reshaped by heat and pressure but thermo sets cannot be reshaped because they undergo chemical changes as they harden. Ceramics are often employed by engineers when materials which can withstand high temperatures are needed. Active vocabulary: Область приме- Существительные Глаголы, нения и сочетания с су- глагольные соче- ществительными тания 1.Виды инженер- cast iron ных материалов steel Коннекторы alloy ferrous metal non-ferrous metal tungsten copper bras thermo sets thermoplastics however 2.Характеристики corrosion to resist / to with- therefore материалов stand corrosion because hardness to improve the properties to undergo changes 3.Классификация to classify объектов to divide into 4.Виды взаимо- to shape действия на ма- to add elements териалы Answer the questions: 1. What kinds of materials are used in engineering? ___________________________________________________________________ 2. How are metals classified? ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between ferrous and non-ferrous metals? ___________________________________________________________________ 4. For what purpose are some elements added to steel? ___________________________________________________________________ 5. What kinds of non-metals do you know? ___________________________________________________________________ 6. What can you say about classification and properties of plastics? ___________________________________________________________________ 7. In what cases are ceramics used? ___________________________________________________________________ Пользуясь информацией текста, дополните схему. Classification of Engineering Materials Engineering materials Metals Ferrous metals Copper Steel Thermoplastics Найдите в тексте предложения, в которых говорится о классификации материалов, и переведите их на русский язык. Пользуйтесь таблицей. Classification There are Materials two types are of three kinds fall into several sorts many classes of materials varieties We can classify materials into several classes divide categories split groups according to … types Engineering materials consist of metals and non-metals include Пользуясь таблицей, произведите классификацию различных материалов. Практическое занятие № 6 Plastics Plastics are a large and varied group of materials consisting of combinations of carbon and oxygen, hydrogen, and other organic and inorganic elements. While solid in its finished state, a plastic is at some stage in its manufacture, liquid and capable of being formed into various shapes. Forming is most usually done through the application, either singly or together, of heat and pressure. There are over 40 different families of plastics in commercial use today, and each may have dozens of subtypes and variations. A successful design in plastics is always a compromise among highest performance, attractive appearance, efficient production, and lowest cost. Achieving the best compromise requires satisfying the mechanical requirements of the part, utilizing the most economical resin or compound that will perform satisfactorily, and choosing a manufacturing process compatible with the part design and material choice. Most people have now outgrown the impression that plastics are low-cost substitute materials. Those that still view plastics as cheap and unreliable have not kept up with developments in polymer technology for the past ten years. Many plastics did indeed evolve as replacements for natural products as rubber, ivory, silk or wool, which became unavailable or on short supply. But the new materials did not successfully replace the older ones permanently nor made them obsolete. In many cases, they met an increased demand that could not be met by the natural product alone. Today’s engineering resins and compounds serve in the most demanding environments. Their toughness, lightness, strength, and corrosion resistance have won many significant applications for these materials in transportation, industrial and consumer products. The engineering plastics are now challenging the domains traditionally held by metals: truly load-bearing, structural parts. Заполните пропуски в логической схеме текста предложениями из текста. Понятие «пластмассы» Способы изготовления пластмасс Применение пластмасс Требования к пластмассам Способы удовлетворения требованиям в настоящем в прошлом Перескажите текст, используя схему как план для пересказа. Используйте активный словарь. Область приме- Существительные нения и сочетания с существительными Виды элементов carbon материалов oxygen hydrogen nitrogen organic element inorganic element plastics Свойства матери- corrosion resistance алов strength lightness toughness Условия и спосо- forming бы изготовления heat Глаголы Прилагательные пластмасс pressure Прогресс в разви- to achieve тии материалов to satisfy requirements to meet demands to keep up to outgrow to win Физическое со- solid стояние веществ; liquid преимущества attractive одного материала reliable перед другим cheap available economical Определите, какие из высказываний соответствуют содержанию текста. 1. A) Plastics evolved as replacements for natural products. B) Plastics have evolved as replacements for natural products. 2. A) Those people who considered plastics unreliable did not keep up with the developments in polymer technology in the past. B) Those people who consider plastics unreliable have not kept up with the developments in polymer technology for the past ten years. 3. A) Plastics properties won many applications for these materials in the past. B) Plastics properties have won many applications for these materials in the past. Практическое занятие № 7 Fibers Fibers are probably the oldest engineering materials used by man. Jute, flax, and hemp have been used for “engineered” products such as rope, cordage, nets, water hose, and containers since antiquity. Other plant and animal fibers have been used for felts, paper, brushes, and heavy structural cloth. The fiber industry is clearly divided between natural fibers (from plant, animal, or mineral sources) and synthetic fibers. Many synthetic fibers have been developed specifically to replace natural fibers, because synthetics often behave more predictably and are usually more uniform in size. For engineering purposes, glass, metallic, and organically derived synthetic fibers are most significant. Nylon, for example, is used for belting, nets, hose, rope, parachutes, webbing, ballistic cloths, and as reinforcement in tyros. Metal fibers are used in high-strength, high temperature, light-weight composite materials for aerospace applications. Fiber composites improve the strength-to-weight ratio of base materials such as titanium and aluminum. Metal-fiber composites are used in turbine compressor blades, heavy-duty bearings, and pressure vessels and spacecraft reentry shields. Boron, carbon, graphite, and refractory oxide fibers are common materials used in high-strength fiber composites. Glass fibers are probably the most common of all synthetic engineering fibers. These fibers are the finest of all fibers, typically one to four microns in diameter. Glass fibers are used for heat, sound, and electrical insulation; filters; reinforcements for thermoplastics and thermo set resins and for rubber (such as in tyros); fabrics, and fiber optics. Изучите схемы и скажите, какая из них точнее передает логику текста. вступление вступление Классификация волокна Классификация волокна Заполните таблицу. Вид волокна Metal fiber Glass fiber Свойства fine тонкий Применение space стекловолокно ТЕМА 3.2. МЕТАЛЛЫ И РАБОТА С МЕТАЛЛАМИ. Практическое занятие № 8 Metals Metals are materials most widely used in industry because of their properties. The study of the production and properties of metals is known as metallurgy. The separation between the atoms in metals is small, so most metals are dense. The atoms are arranged regularly and can slide over each other. That is why metals are malleable (can be deformed and bent without fracture) and ductile (can be drawn into wire). Metals vary greatly in their properties. For example, lead is so soft and can be bent by hand, while iron can only be worked by hammering at red heat. The regular arrangement of atoms in metals gives them a crystalline structure. Irregular crystals are called grains. The properties of the metals depend on the size, shape, orientation, and composition of these grains. In general, a metal with small grains will be harder and stronger than one with coarse grains. Heat treatment controls the nature of the grains and their size in the metal. Small amounts of other metals (less than 1 per cent) are often added to a pure metal. This is called alloying (легирование) and it changes the grain structure and properties of metals. All metals can be formed by drawing, rolling, hammering and extrusion, but some require hot-working. Metals are subject to metal fatigue and to creep (the slow increase in length under stress) causing deformation and failure. Both effects are taken into account by engineers when designing, for example, airplanes, gas- turbines, and pressure vessels for high-temperature chemical processes. Metals can be worked using machine-tools. The ways of working a metal depends on its properties. Many metals can be melted and cast in moulds, but special conditions are required for metals that react with air. New words: arrangement - расположение coarse – грубый, крупный to draw – волочить, тянуть wire – проволока lead – свинец composition - состав to hammer – ковать rolling – прокатка metal fatigue - усталость металла to slide – скользить to cast – отливать mould – форма для отливки Find the following words and word combinations in the text: свойства металлов, расстояние между атомами, сильно отличаются по своим свойствам, кристаллическая структура, размер зерен, форма зерен, волочение, прокатка, ковка, структура и свойства зерна, горячая обработка, усталость металла, ползучесть металла, плавка и отливка в формы, способы обработки металлов. ______________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 9 Steel The most important metal in industry is iron and its alloy – steel. Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It is strong but corrodes easily through rusting, although stainless and other special steels resist corrosion. The amount of carbon in steel influences its properties considerably. Steels of low carbon content (mild steels) are quite ductile and are used in the manufacture of sheet iron, wire and pipes. Medium-carbon steels containing from 0, 2 to 0, 4 per cent carbon are tougher and stronger and are used as structural steels. Both mild and medium-carbon steels are suitable for forging and welding. High-carbon steels contain from 0, 4 to 1,5 per cent carbon, are hard and brittle and are used in cutting tools, surgical instruments, razor blades and springs. Tool steel, also called silver steel, contains about 1 per cent carbon and is strengthened and toughened by quenching and tempering. The inclusion of other elements affects the properties of the steel. Manganese gives extra strength and toughness. Steel containing 4 per cent silicon is used for transformer cores or electromagnets because it has large grains acting like small magnets. The addition of chromium gives extra strength and corrosion resistance, so we can get rust-proof steels. Heating in the presence of carbon or nitrogen-rich materials is used to form a hard surface on steel (case-hardening). High-speed steels, which are extremely important in machine-tools, contain chromium and tungsten plus smaller amounts of vanadium, molybdenum and other metals. New words: carbon - углерод to corrode – разъедать, ржаветь rusting – ржавление stainless – нержавеющий to resist – сопротивляться considerably – значительно, гораздо tough – крепкий, прочный forging – ковка welding – сварка cutting tools – режущие инструменты core – сердцевина blade – лезвие spring – пружина inclusion – включение manganese – марганец silicon – кремний rust-proof – нержавеющий case-hardening – упрочнение цементацией nitrogen – азот tungsten – вольфрам Answer the questions: 1. What is steel? ________________________________________________ 2. What are the main properties of steel? ____________________________________________________________ 3. What are drawbacks of steel? ____________________________________________________________ 4. What kinds of steel do you know? ____________________________________________________________ 5. Where are they used? ____________________________________________________________ 6. What gives the addition of manganese, silicon and chromium to steel? ____________________________________________________________ 7. What can be made of mild steels (medium-carbon steels, high-carbon steels)?______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 8. What kind of steels can be forged and welded? ____________________________________________________________ 9. How can we get rust-proof (stainless) steel? ____________________________________________________________ 10.What is used to form a hard surface on steel? ____________________________________________________________ 11.What are high-speed steels alloyed with? ____________________________________________________________ Find the following words and word combinations in the text: 1. сплав железа и углерода ______________________________________ 2. прочный и жесткий __________________________________________ 3. легко коррозирует ___________________________________________ 4. нержавеющая сталь __________________________________________ 5. низкое содержание углерода ___________________________________ 6. ковкость ___________________________________________________ 7. листовое железо, проволока, трубы _____________________________ 8. конструкционные стали _______________________________________ 9. пригодны для ковки и сварки __________________________________ 10.твердый и хрупкий ___________________________________________ 11.режущие инструменты ________________________________________ 12.инструментальная сталь ______________________________________ 13.упрочнять __________________________________________________ 14.добавление марганца (кремния, хрома, вольфрама, молибдена, ванадия)________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 10 Methods of Steel Heat Treatment Quenching is a heat treatment when metal at a high temperature is rapidly cooled by immersion in water or oil. Quenching makes steel harder and more brittle, with small structure. Tempering is a heat treatment applied to steel and certain alloys. Hardened steel after quenching from a high temperature is too hard and brittle for many applications and is also brittle. Tempering, that is re-heating to an intermediate temperature and cooling slowly, reduces this hardness and brittleness. Tempering temperatures depend on the composition of the steel but are frequently between 100 and 650 degrees C. Higher temperatures usually give a softer, tougher product. The color of the oxide film produced on the surface of the heated metal often serves as the indicator of its temperature. Annealing is a heat treatment in which a material at high temperature is cooled slowly. After cooling the metal again becomes malleable and ductile (capable of being bent many times without cracking). All these methods of steel heat treatment are used to obtain steels with certain mechanical properties for certain needs. to immerse – погружать intermediate – промежуточный oxide film – оксидная пленка annealing – отжиг, отпуск quenching – закалка охлаждением tempering - отпуск после закалки, нормализация Answer the questions: 1. What can be done to obtain harder steel? __________________________________________________________________ 2. What makes steel more soft and tough? __________________________________________________________________ 3. What makes steel more malleable and ductile? __________________________________________________________________ 4. What can serve as the indicator of metal temperature while heating it? __________________________________________________________________ 5. What temperature range is used for tempering? __________________________________________________________________ 6. What are the methods of steel treatment used for? __________________________________________________________________ Translate into English: температура нормализации _______________________________________ мелкозернистая структура ________________________________________ быстрое охлаждение _____________________________________________ закаленная сталь ________________________________________________ состав стали ____________________________________________________ окисная пленка __________________________________________________ индикатор температуры __________________________________________ медленное охлаждение ___________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 11 Hot Working of Steel An important feature of hot working is that it provides the improvement of mechanical properties of metals. Hot-working (hot-rolling or hot-forging) eliminates porosity, directionality, and segregation that are usually present in metals. Hot-worked products have better ductility and toughness than the unworked casting. During the forging of a bar, the grains of the metal become greatly elongated in the direction of flow. As a result, the toughness of the metal is greatly improved in this direction and weakened in directions transverse to the flow. Good forging makes the flow lines in the finished part oriented so as to lie in the direction of maximum stress when the part is placed in service. The ability of a metal to resist thinning and fracture during cold-working operations plays an important role in alloy selection. In operations that involve stretching, the best alloys are those which grow stronger with strain (are strain hardening) – for example, the copper-zinc alloy, brass, used for cartridges and the aluminum-magnesium alloys in beverage cans, which exhibit greater strain hardening. Fracture of the work piece during forming can result from inner flaws in the metal. These flaws often consist of nonmetallic inclusions such as oxides or sulfides that are trapped in the metal during refining. Such inclusions can be avoided by proper manufacturing procedures. The ability of different metals to undergo strain varies. The change of the shape after one forming operation is often limited by the tensile ductility of the metal. Metals such as copper and aluminum are more ductile in such operations than other metals. New words: feature – черта, особенность to provide – обеспечивать improvement – улучшение porosity – пористость directional – направленный to segregate – разделять casting – отливка elongated – удлиненный to weaken – ослабевать, ослаблять transverse – поперечный flow – течение, поток finished – отделанный thinning – утончение strain hardening -деформационное упрочнение brass – латунь beverage – напиток can – консервная банка inner – внутренний to exhibit – проявлять inclusion – включение trapped – заключенный refining – очищать, очистка tensile ductility – пластичность при растяжении Answer the questions: 1. What process improves the mechanical properties of metals? ____________________________________________________________ 2. What new properties have hot-worked products? ____________________________________________________________ 3. How does the forging of a bar affect the grains of the metal? What is the result of this? ____________________________________________________________ 4. How are the flow lines in the forged metal oriented and how does it affect the strength of the forged part? ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 5. What are the best strain-hardening alloys? Where can we use them? ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 6. What are the inner flaws in the metal? ____________________________________________________________ 7. Can a metal fracture because of the inner flaw? ____________________________________________________________ 8. What limits the change of the shape during forming operations? ____________________________________________________________ Find the following in the text: 1. важная особенность горячей обработки _________________________________________________________ 2. улучшение механических свойств металла _________________________________________________________ 3. необработанная отливка ____________________________________ 4. направление максимального напряжения _________________________________________________________ 5. способность сопротивляться утончению и разрушению _________________________________________________________ 6. проявлять большее деформационное упрочнение _________________________________________________________ 7. разрушение детали при штамповке _________________________________________________________ 8. внутренние дефекты в металле _________________________________________________________ 9. неметаллические включения _________________________________________________________ 10.способность металлов подвергаться деформации _________________________________________________________ 11.ограничивается пластичностью металла при растяжении _________________________________________________________ ТЕМА 3.4. ДЕТАЛИ И МЕХАНИЗМЫ. Практическое занятие № 12 Machine – Tools Machine-tools are used to shape metals and other materials. The material to be shaped is called the workpiece. Most machine-tools are now electrically driven. Machine-tools with electrical drive are faster and more accurate than hand tools: they were an important element in the development of mass-production processes, as they allowed individual parts to be made in large numbers so as to be interchangeable. All machine-tools have facilities for holding both the workpiece and the tool, and for accurately controlling the movement of the cutting tool relatively to the workpiece. Most machining operations generate large amounts of heat, and cooling fluids (usually a mixture of water and oils) must be used for cooling and lubrication. Machine-tools usually work materials mechanically but other machining methods have been developed lately. They include chemical machining, spark erosion to machine very hard materials to any shape by means of a continuous highvoltage spark (discharge) between an electrode and a workpiece. Other machining methods include drilling using ultrasound, and cutting by means of a laser beam. Numerical control of machine-tools and flexible manufacturing systems have made it possible for complete systems of machine-tools to be used flexibly for the manufacture of a range of products. New words: machine-tools – станки electrically driven – с электроприводом fluid – жидкость spark erosion – электроискровая обработка by means of – посредством drilling – сверление Найдите в правой колонке перевод английских слов: 1. facility а. винт 2. feed б. внутри 3. flexible в. гибкий 4. friction г. диапазон 5. inside д. допуск 6. outside е. закреплять 7. range ж. колесо 8. screw з. обрабатываемая деталь 9. sharp и. острый 10.thread к. подача 11.to allow л. позволять 12.to lubricate м. приспособление 13.to mount н. резьба 14.to remove о. смазывать 15.to require п. снаружи 16.tolerance р. требовать 17.wheel с. трение 18.workpiece т. удалять ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Give a short summary of the text. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 13 Robots in Industry Today most robots are used in manufacturing operations. The applications of robots can be divided into three categories: 1. material handling 2. processing operations 3. assembly and inspection Material handling is the transfer of material and loading and unloading of machines. Material - transfer applications require the robot to move materials or work parts from one to another. Many of these tasks are relatively simple: robots pick up parts from one conveyor and place them on another. Other transfer operations are more complex, such as placing parts in an arrangement that can be calculated by the robot. The processing operations robot manipulates a tool to perform a process on the work part. Examples of such applications include spot welding, continuous arc welding and spray painting. Spot welding of automobile bodies is one of the most common applications of industrial robots. The robot positions a spot welder against the automobile panels and frames to join them. Arc welding is a continuous process in which robot moves the welding rod along the welding seam. Spray painting is the manipulation of a spray-painting gun over the surface of the object to be coated. The third application area of industrial robots is assembly and inspection. The use of robots in assembly is expected to increase because of the high cost of manual labour. But the design of the product is an important aspect of robotic assembly. Inspection is another area of factory operations in which the utilization of robots is growing. It is a typical inspection job. There are certain characteristics of industrial jobs performed by humans that can be done by robots: 1. the operation is repetitive, involving the same basic work motions every cycle; 2. the operation is hazardous or uncomfortable for the human worker (for example: spray painting, spot welding, arc welding, and certain machine loading and unloading tasks); 3. the workpiece or tool are too heavy and difficult to handle; 4. the operation allows the robot to be used on two or three shifts. New words: transfer – передача, перенос location – местонахождение arrangement – расположение to utilize – утилизировать, находить применение frame – рама spot welding – точечная сварка continuous – непрерывный spray painting – окраска распылением spray-painting gun – распылитель краски manual – ручной labour – труд shift – смена Answer the questions: 1. How are robots used in manufacturing? ____________________________________________________________ 2. What is “material handling”? ____________________________________________________________ 3. What does a robot need to be equipped with to do loading and unloading operations? ____________________________________________________________ 4. What does robot manipulate in robotic processing operation? ____________________________________________________________ 5. What is the most common application of robots in automobile manufacturing?________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 6. What operations could be done by robot in car manufacturing industry? ____________________________________________________________ 7. What are the main reasons to use robots in production? ____________________________________________________________ 8. What operations could be done by robots in hazardous or uncomfortable for the human workers conditions ________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Translate into English: 1. Существует несколько различных сфер использования автоматизации в производстве. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 2. Для использования жесткой автоматизации необходимы большие инвестиции. ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 3. Жесткая автоматизация широко используется в химической промышленности. ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 4. Гибкая автоматизация делает возможным перепрограммирование оборудования. ______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 5. Время простоя оборудования оборачивается большими убытками. ____________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 14 Machines and Work Defined in the simplest terms a machine is a device that uses force to accomplish something. More technically, it is s device that transmits and changes force or motion to work. This definition implies that a machine must have moving parts. A machine can be very simple, like a block and tackle to raise a heavy weight, or very complex, like a railroad locomotive or the mechanical systems used for industrial processes. A machine receives input from an energy source and transforms it into output in the form of mechanical or electrical energy. Machines whose input is a natural source of energy are called prime movers. Natural sources of energy include wind, water, steam, and petroleum. Windmills and waterwheels are prime movers; so are the great turbines driven by water or steam that turn the generators that produce electricity. Electric motors are not prime movers, since an alternating current of electricity which supplies most electrical energy does not exist in nature. Terms like work, force, and power are frequently used in mechanical engineering, so it is necessary to define them precisely. Force is an effort that results in motion or physical change. If you use your muscles to lift a box you are exerting force on that box. The water which strikes the blades of a turbine is exerting force on those blades, thereby setting them in motion. In a technical sense work is the combination of the force and the distance through which it is exerted. To produce work, a force must act through a distance. If you stand and hold a twenty-pound weight for any length of time, you may get very tired, but you are not doing work in an engineering sense because the force you exerted to hold up the weight was not acting through a distance. However, if you raised the weight, you would be doing work. Power is another term used in a special technical sense in speaking of machines. It is the rate at which work is performed. The rate of doing work is sometimes given in terms of horsepower, often abbreviated hp. This expression resulted from the desire of the inventor James Watt to describe the work his steam engines performed in terms that his customers could easily understand. After much experimentation, he settled on a rate of 33,000 foot-pounds per minute as one horsepower. In the metric system power is measured in terms of watts and kilowatts. The kilowatt, a more widely used term, equals a thousand watts or approximately 1,1/3 horsepower in the English system. Соедините термин с соответствующим ему определением. Machine the rate at which work is performed. Prime mov- a device that uses force to accomplish something. is er Force an effort that results in motion or physical change. Work a machine whose input is a natural source of energy. Power a combination of force and the distance through which it is exerted. __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Заполните следующую таблицу. Термин Класс Характеристика prime mover internal combustion engine turbine Как следует из содержания текста, все абзацы включают в себя определение какого-нибудь понятия, разъяснение этого понятия, пример. Например, первый абзац можно представить в виде следующей схемы: 1 абзац Определение понятия Дополнительные разъ- Примеры различных «машина» яснения машин Постройте структурную схему каждого абзаца. 2 абзац Дополнительное Определение понятия разъяснение по- «_________________» нятия «машина» 3 абзац Вводное предложение Определение понятия «_____" 4 абзац Определение понятия Сделайте краткое сообщение на тему “Machine, Work, Power”. При подготовке используйте активный словарь. Область применения Существительные и сочетания с существительными Глагольные сочетания 1.Машины и механизмы prime mover windmill turbine generator steam engine internal combustion engine electric motor 2.Источники энергии wind water steam petroleum 3.Общие понятия физи- electricity to produce electricity ки и механики effort to exert effort motion to set in motion distance to result in motion rate to hold up a weight weight to exert force horsepower to produce work watt to perform work kilowatt to result from force work _____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 15 Melting Furnaces The metals used in various kinds of castings are melted in several types of furnaces. They are cupolas, electric furnaces, open-hearth furnaces, crucible furnaces and some others. A cupola furnace is a vertical type, cylindrical or shaft furnace designed to melt ferrous metals in the production of cast iron castings. The cupola consists of a refractorylined steel stack testing on a cast iron base plate which is supported by four steel legs. The bottom of the cupola consists of two doors which are supported in closed position by a centre prop. Iron, coke and flux are charged onto a coke bed and are held above the tuyere openings where the maximum temperature is maintained. Molten metal is tapped through a tap hole at the base of the cupola. Although the first cupola was built about 1720 cupola melting is still recognized as the most economical melting process and most of the grey cast iron produced is melted by this method. Electric furnaces are used for producing high quality castings. The principle of the electric furnace operation is based on the heating effect obtainable from the passing of electricity. There are three general types: arc, induction and resistance. Arc furnaces are used for melting or refining ferrous metals. Two types of arc furnaces are in use: direct-arc and indirect-arc. In the direct-arc furnace the arc comes in direct contact with the metal charge. Indirectarc furnaces are the type in which the arc is maintained between two electrodes above the charge. In the induction furnace electric current are induced in the charge and their circulation through the charge produces heat. This type of furnace is used for producing exact alloys. In the resistance furnace the electrodes are placed in the charge and the flow of electric current through the charge produces heat. These furnaces are generally used for nonferrous metals production. New words: cupola – вагранка refractory-lined stack –шахта, облицованная огнеупорным материалом to rest – опираться prop – подпорка tuyere opening – фурменное отверстие (для подачи в печь воздуха) to maintain – поддерживать to tap metal – выпускать металл arc furnace – электродуговая печь direct-arc furnace – электродуговая печь прямого нагрева indirect-arc furnace – электродуговая печь непрямого нагрева resistance furnace – печь сопротивления metal charge – металлическая шихта Скажите, какие из данных утверждений соответствуют содержанию текста. 1. The cupola is designed to melt non-ferrous metals. 2. Cupola melting is the most economical melting process. 3. The cupola is a horizontal type furnace. 4. Iron, coke and flux are charged onto a coke bed at the bottom of the furnace. 5. The maximum temperature is maintained under the tuyere openings. 6. Molten metal is tapped through a tap hole. Завершите предложения, выбрав соответствующие окончания в правом столбце. 1.Electric furnaces are used for a) comes in direct contact with the metal charge. 2. There are three general types of electric furnaces b) direct-arc and indirect-arc. 3.Two types of arc furnaces are in use c) produces heat. 4.In the direct-arc furnace the arc d) production of high-quality castings. 5.In the indirect-arc furnace the arc e) for non-ferrous metals production. 6.In the induction furnace current circu- f) arc, induction and resistance furnaces. lation through the charge 7.The resistance furnace is generally g) is maintained between two electrodes used for above the charge. _____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ТЕМА 3.4. ИКТ В ЖИЗНИ СОВРЕМЕННОГО СПЕЦИАЛИСТА. Практическое занятие № 16 Computer One of the most important developments of the 20th century is the computer. As a consequence, there is now at the service of a man an inanimate power of over 200 billion calculating operations per second, supplementing the thinking and the memory of man. Computers are used nowadays for many different kinds of work, e.g. in offices, banks, factories, hospitals, universities and educational establishments. Their use is becoming more widespread as cheaper and smaller computers become available. People can now buy small personal computers. What are computers? And what can they be used for? Computers are electronic systems. They are used for handling, or processing, facts and figures. The facts and figures processed by a computer are usually known as data. Computers can process large amounts of data very quickly. The data fed, or put, into a computer is input data. Input data is processed according to a set of instructions called a program. Both input data and programs are needed for processing. The results of processing are output data. Very often, the output data is new and useful information. “Information” here means output data useful for making decisions. Input data COMPUTER Output data Program A computer can be used to process many different types of data. For example, a scientist can use a computer to do numerical calculations. A businessman can use a computer to analyze a list of customers or stock (stores held by the business). An engineer can use a computer to produce diagrams or plans. A student can use a computer to do research or to prepare for lectures. Выпишите информацию о классе и характеристике приведенных терминов. Term Class A computer Characteristics electronic machine that processes data Data Program Information Input data Output data Изучив схемы, скажите, какая из них точнее отражает логику всего текста. 1. Вводный абзац 1 Определение понятий компьютер и информация 2 Определение понятий программа, входные и выходные данные 3 Применение компьютеров 4 Иллюстрация положений 4 абзаца 5 2. 1 2 3 4 5 Расскажите об основных узлах компьютера, их назначения, применении компьютеров в различных сферах деятельности. Область Существительные Глаголы и гла- применения и сочетания с ни- гольные сочета- ми ния 1.Понятия, data to process связанные с input data to handle работой ком- output data to put into пьютера program Прилагательные Коннекторы information instruction 2.Сфера ис- to do calculations пользования to analyze a list of quence компьютера to produce dia- for example grams to control measurements numerical as a conse- Практическое занятие № 17 Internet Millions of people around the world use the Internet to search for and retrieve information on all sorts of topics in a wide variety of areas including the arts, business, government, humanities, news, politics and recreation. People communicate through electronic mail (e-mail), discussion groups, chat channels and other means of informational exchange. They share information and make commercial and business transactions. All this activity is possible because tens of thousands of networks are connected to the Internet and exchange information in the same basic ways. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a part of the Internet. But it’s not a collection of networks. Rather, it is information that is connected or linked together like a web. You access this information through one interface or tool called a Web browser. The number of resources and services that are part of the WWW is growing extremely fast. In 1996 there were more than 20 million users of the WWW, and more than half the information that is transferred across the Internet is accessed through the WWW. By using a computer terminal (hardware) connected to a network that is a part of the Internet, and by using a program (software) to browse or retrieve information that is a part of the World Wide Web, the people connected to the Internet and WWW through the local providers have access to a variety of information. Each browser provides a graphical interface. You move from place to place, from site to site on the Web by using a mouse to click on a portion of text, icon or region of a map. These items are called hyperlinks or links. Each link you select represents a document, an image, a video clip or an audio file somewhere on the Internet. The user doesn’t need to know where it is, the browser follows the link. All sorts of things are available on the WWW. One can use Internet for recreational purposes. Many TV and radio stations broadcast live on the WWW. Essentially, if something can be put into digital format and stored in a computer, then it’s available on the WWW. You can even visit museums, gardens and cities throughout the world, learn foreign languages and meet new friends. And, of course, you can play computer games through WWW, competing with partners from other countries and continents. Just a little bit of exploring the World Wide Web will show you what a lot of use and fun it is. New words: World Wide Web – «Всемирная Паутина» variety – разнообразие, спектр network – сеть recreation – развлечение humanities – гуманитарные науки business transactions – коммерческие операции access – доступ to browse – рассматривать, разглядывать browser – браузер (программа поиска информации) to provide – обеспечивать broadcast live – передавать в прямом эфире to link – соединять hyperlink – гиперссылка to compete – соревноваться Ответьте на вопросы: 1. What is internet used for? ___________________________________________________________________ 2. Why so many activities are possible through the Internet? ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What is World Wide Web? ___________________________________________________________________ 4. What is Web browser? ___________________________________________________________________ 5. What does a user need to have an access to the WWW? ___________________________________________________________________ 6. What are hyperlinks? _________________________________________________ 7. What resources are available on the WWW? ___________________________________________________________________ 8. What are the basic recreational applications of WWW? ___________________________________________________________________ Which of the listed below statements are true or false? Specify your answer using the text. 1. There are still not so many users of the Internet. 2. There is information on all sorts of topics on the Internet, including education and weather forecasts. 3. People can communicate through e-mail and chat programs only. 4. Internet is tens of thousands of networks which exchange the information in the same basic way. 5. You can access information available on the World Wide Web through the Web browser. 6. You need a computer (hardware) and a special program (software) to be a WWW user. 7. You may from site to site by clicking on a portion of text only. Define the following: 1) Internet _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2) World Wide Web _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3) Web browser ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4) Internet provider _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5) Hyperlinks____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Find the equivalents in the text: 1. Объем ресурсов и услуг, которые являются частью WWW, растет чрезвычайно быстро. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. Каждая ссылка, выбранная вами, представляет собой документ, графическое изображение, видеоклип или аудио файл где-то в Интернете. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. Интернет может быть также использован для целей развлечения. _____________________________________________________________ 4. Вы получаете доступ к ресурсам Интернет через интерфейс или инструмент, который называется браузер. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5. Вся эта деятельность возможна благодаря десяткам тысяч компьютерных сетей, подключенных к Интернет и обменивающихся информацией в одном режиме. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 6. Пользователи общаются через электронную почту, дискуссионные клубы, чэт-каналы (многоканальный разговор в реальном времени) и другие средства информационного обмена. ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 18 The Development of Computers The first computers used thousands of separate electrical components connected together with wires. In the late 1940s, computers were made using vacuum tubes, resistors, and diodes. These computers were called first generation computers. In 1956, transistors were invented. Transistors are made from materials called semiconductors. Computers using transistors were called second generation computers. Second generation computers were smaller than first generation computers. Second generation computers also used less electrical power. Both first and second generation computers were very expensive. Computer components (such as transistors, diodes, resistors) can now be made from semiconductor materials of different shapes. Nowadays, complete circuits can be made from a single piece of semiconductor, called a chip. Such circuits are called integrated circuits (ICs). Computers using integrated circuits were first produced in the 1960s. They were known as third generation computers. Their integrated circuits had about 200 components on a single chip. Today we can produce more than 100,000 components on a single chip. A chip can be as small as 0, 5 cm square. With the invention of chips, computer manufacture has become much simpler. The manufacture does not have to connect thousands of components together. Most of the connections are made inside the chip. It is even possible to build a complete processor in a single chip. A processor on a single chip is called a microprocessor. Впишите характеристики компьютеров разных поколений (на русском языке). Вид компьютера Компьютеры I поколения Компьютеры II поколения Компьютеры III поколения Компьютеры IV поколения Его характеристики Выберите из текста предложения, характеризующие размеры, конструкцию, скорость обработки данных в компьютерах различных поколений. Составьте таблицу на английском языке. Сравните обе таблицы. Внесите в таблицу на русском языке дополнительные данные. _____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ТЕМА 3.5. ИЗВЕСТНЫЕ ЛЮДИ В ОБЛАСТИ НАУКИ И ИНФОРМАТИКИ. Практическое занятие № 19 Bill Gates – the Founder of Microsoft William Henry Gates was born in Seattle, Washington, in 1955. He is an American business executive, chairman and chief officer of the Microsoft Corporation. Gates was the founder of Microsoft in 1975 together with Paul Allen, his partner in computer language development. While attending Harvard in 1975, Gates together with Allen developed a version of the BASIC computer programming language for the first personal computer. In the early 1980s, Gates led Microsoft’s evolution from the developer of computer programming languages to a large computer software company. This transition began with the introduction of MS-DOS, the operating system for the new IBM Personal Computer in 1981. Gates also led Microsoft towards the introduction of application software such as the Microsoft World processor. Much of Gates’ success is based on his ability to translate technical visions into market strategy. Although Gates has accumulated great wealth from his holdings of Microsoft stock, he has been known as a tough competitor who seems to value winning in a competitive environment over money. Gates still continues to work personally in product development at Microsoft. Answer the questions: 1. What education has he received? _________________________________ 2. How did he begin his career? ____________________________________ 3. What is Microsoft now? ________________________________________ Questions for discussion: 1) Some people think that Internet is very harmful, especially for young people, because it carries a lot of information about sex, drugs, violence and terrorism. Do you think that some kind of censorship (цензура) is necessary on the WWW? 2) World famous authors and publishers say that the Internet violates their copyright because the Web-programs put all kinds of books, pictures, music, films and programs free on the Internet and this produces their sales and profits. 3) Has anyone in your group experience on the Internet? Ask them: 1. about the difficulties they had; 2. useful information retrieved; 3. fun they got. 4) Why so few people have experience working on the Internet? Практическое занятие № 20 M.V. Lomonosov Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov was a famous Russian writer, chemist and astronomer who made a lot in literature and science. Lomonosov was born on November 19, 1711, in Denisovka (now Lomonosov), near Archangelsk, and studied at the University of the Imperial Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg. After studying in Germany at the Universities of Marburg and Freiberg, Lomonosov returned to St. Petersburg in 1745 to teach chemistry and built a teaching and research laboratory there four years later. Lomonosov is often called the founder of Russian science. He was an innovator in many fields. As a scientist he rejected the phlogiston theory of matter commonly accepted at the time and he anticipated the kinetic theory of gases. He regarded heat as a form of motion, suggested the wave theory of light, and started the idea of conservation of matter. Lomonosov was the first person to record the freezing of mercury and t observe the atmosphere of Venus. Interested in the development of Russian education, Lomonosov helped to found Moscow State University in 1755, and in the same year he wrote a grammar that reformed the Russian literary language by combining Old Church Slavonic with modern language. In 1760 he published the first history of Russia. He also revived the art of Russian mosaic and built a mosaic and colored-glass factory. Most of his achievements, however, were unknown outside Russia. He died in St. Petersburg on April 15, 1765. New words: to anticipate – предвидеть, предугадывать to revive – возродить art – искусство Old Church Slavonic language – церковно-славянский язык Answer the questions: 1. Why Lomonosov is often called the founder of Russian science? ____________________________________________________________ 2. What had Lomonosov done in the field of Russian education? ____________________________________________________________ Give a short summary of the text: __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 21 James Watt James Watt was born in Greenock, Scotland, and was taught at home. Later he went to Greenock Grammar School. His technical expertise seems to have been obtained from working in his father’s workshop and from early in life he showed academic promise. His early formal training was an instrument maker in London and Glasgow. Watt combined the expertise of a scientist with that of a practical engineer, for later he was not only to improve the heat engine but also to devise new mechanisms. Watt was interested in making experimental models of steam engines and this marks a historical milestone in engineering development, for they were the first experimental apparatus purposely constructed for engineering research. Watt’s early interest in steam arose from experience in repairing a model steam engine in 1764, and in 1765 he invented the separate steam engine condenser. In 1769 he took out a patent on the condenser in which steam came into direct contact with cold water. That was a milestone by which steam engineering reached its practical and usable form. In 1784 he took out a patent for a reaction turbine at a time when continental engineers were only considering similar approaches. An improved centrifugal governor was to follow in 1788 and a design for a pressure gauge in 1790. In the development of the steam engine James Watt represents the perfection of a sequence of stages beginning with the Newcomer engine and ending with the parallel motion and sun gearing. The latter is said to have been invented by William Murdock but patented by Watt. In the scientific field Watt’s finest memorial, apart from steam engines, is his establishment of the unit of power – the rate of doing work. He coined the term horsepower (hp), one horse being defined as equivalent to 33,000 ft lb/min. James Watt died in 1819 in Heathfield, after a life of incomparable technical value. Later, a statue to Watt was placed in Westminster Abbey. New words: expertise – мастерство instrument – прибор milestone – веха governor – регулятор pressure gauge – манометр (прибор для измерения давления) sequence – последовательность sun gearing – планетарная передача to coin the term – ввести термин ft lb/min – футо-фунтов в минуту На основании полученной из текста информации заполните таблицу: Time 1764 1765 Watt’s activity and its results 1769 1784 1788 1790 Give a short summary of the text: __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Практическое занятие № 22 Faraday Puts Electricity to Work Michael Faraday, who was born in 1791 and died in 1867, gathered together and set in order all the work of the scientists who had worked on electrical problems before him. In 1823, he discovered how to make an electrical motor. In 1831, he built the first generator, than called dynamo. The modern car has both a starting motor and a generator. The starting motor draws electric current from the car battery to start engine. The generator is driven by the engine to recharge the battery and to furnish electric power for all the electrical conveniences in the car. In 1833, Faraday discovered the laws of electrolysis. The works of many other scientists were influenced by the discoveries made by Faraday. As a result of Faraday’s work Morse was able to invent the electromagnetic telegraph, Bell – the telephone and Edison – the electric light. Their inventions have profoundly changed the lives of nearly everyone in the world. Thus, Edison’s Congressional Medal of Honor certificate declared: “He illuminated the path of progress by his invention”. Назовите значения следующих интернациональных слов: electrical, problem, motor, generator, dynamo, modern, starting motor, battery, electrolysis, telegraph, telephone, to start, to illuminate. _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Найдите все словосочетания с прилагательными electric и electrical и переведите их на русский язык: Electric motor – электродвигатель. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Найдите в тексте словосочетания: обобщить работу, привести работу в порядок, получать электрический ток, запустить двигатель, перезарядить аккумуляторную батарею, снабжать электрической энергией, открыть закон, изобрести электрическое освещение. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Найдите предложения со сказуемым в страдательном залоге и переведите их. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Преобразуйте предложения в предложения со сказуемым в страдательном залоге. 1. Watt started engine manufacturing in 1870. ____________________________________________________________ 2. The scientist named his device steam governor. ____________________________________________________________ 3. In 1781 Watt produced a rotary-motion steam engine. ____________________________________________________________ 4. Watt compared his device to a horse. ____________________________________________________________