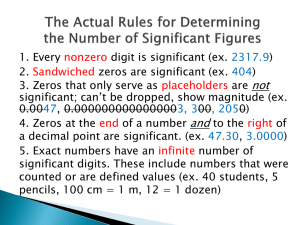
Second level mental maths planner NEW
advertisement

Second Level Addition and Subtraction MNU 2-01a I can use my knowledge of rounding to routinely estimate the answer to a problem then, after calculating, deciding my answer is reasonable, sharing my solution with others. MNU 2-02a I have extended the range of whole numbers I can work with and having explored how decimal fractions are constructed, can explain the link between a digit, its place and value. MNU 2-03a Having determined which calculations are needed, I can solve problems involving whole numbers using a range of methods, sharing my approaches and solutions with others. MNU 2-03b I have explored the contexts in which problems involving decimal fractions occur and can solve related problems using a Class: ________________________________ Session:__________________________ Second Level (1) Second Level (2) Second Level (3) RECALL Sums and differences of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 RECALL Sums and differences of decimals, e.g. 6.5 + 2.7 and 7.8 – 1.3 RECALL Addition and subtraction facts for multiples of 10 to 1000, e.g. 650 + = 930 Addition doubles of numbers 1 to 100, e.g. 38+38, and the corresponding halves. Doubles and halves of decimals (without bridging), e.g. half of 5.6, double 3.4 Numbers which can be added to any three digit number to make the next multiple of 100, e.g. 521+ = 600 Link Number Talks – Subtraction: Adding up (pg 207-210) Numbers which can be added to any four digit number to make the next multiple of 1000, e.g. 4087 + = 5000 Link Number Talks – Subtraction: Adding up (pg 207-211) Number pairs which total 60, then 100, e.g. ? + 24 = 60, ? + 43 = 100 Numbers which can be added to a decimal with units and tenths to make the next whole number, e.g.7.2 + =8 Addition and subtraction facts for decimal numbers with one decimal place, e.g. – 1.4 = 2.5 Numbers which can be added to a decimal with units, tenths and hundredths to make the next whole number, e.g. 7.26 + =8 Pairs of fractions and decimal fractions that total 1 SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) Add any pair of two-digit numbers, including crossing the tens and 100 boundary, e.g. 47+58 Add a near multiple of 10 e.g. 56+29, Link Number Talks – Addition:Making landmark Add or subtract any pair of threedigit numbers, including crossing the tens and 100 boundary, e.g. 247+358, 591-235 Add or subtract pairs of decimals with units, tenths or hundredths, e.g. 0.7 + 3.38 Add or subtract a near multiple of 100 to any 2 or 3 digit number e.g. 235+198 = 235+200-2 Find doubles of decimals each with units and tenths (with bridging), e.g. double 1.6 variety of methods MNU 2-04a I can show my understanding of how the number line extends to include numbers less than zero and have investigated how these numbers occur and are used. MNU 2-07a I have investigated the everyday contexts in which simple fractions, percentages or decimal fractions are used and can carry out the necessary calculations to solve related problems. MNU 2-07b I can show the equivalent forms of simple fractions, decimal fractions and percentages and can choose my preferred form when solving a problem, explaining my choice of method numbers (pg189-192), Breaking into place value (pg197-198), adding up in chunks (pg201- 203) Subtract any pair of two-digit numbers, including crossing the tens and 100 boundary, e.g. 91-35 Subtract a near multiple of 10, e.g. 86-38 Link Number Talks – Subtraction: Removal (pg212216), adjusting one number (pg221-224), keeping a distance (pg226-227) Add near doubles of three digit numbers, e.g. 138 + 137 Link Number Talks – Addition:Double/Near-Doubles (pg193-196) Add or subtract two digit or three digit multiples of 10, e.g. 120-40, 140+150, 370-180 Link Number Talks – Removal (pg 212-216) Link Number Talks – Addition:Making landmark numbers (pg189-192), breaking into place value (pg197-200), adding up in chunks (pg 201-204) Add or subtract a near multiple of 10 with three digits to any two or three digit number, e.g. 351+229 = 351+230-1, 625-139 = 625-140+1 (bridging 100’s) Link Number Talks – Subtraction: adjusting one number (pg221-225), keeping a distance (pg226-229) Find the difference between near multiples of 100 or 1000, without bridging, e.g. 597-302 = 597-300-2, 502-397 = 502-400+3 Find the difference between near multiples of 100 or 1000, with bridging, e.g. 6070-4097 = 6070-4000100+3 Add or subtract any pairs of decimal fractions each with units and tenths, e.g. 5.7 + 2.5, 6.3 - 4.8 Mentally subtract a larger number from a smaller number (negative numbers) Link Number Talks – Subtraction: negative numbers (pg217-220) Add near doubles of decimals, e.g. 2.5+2.6 Add or subtract a decimal with units and tenths, that is nearly a whole number, e.g. 4.3+2.9, 6.53.8 STRATEGIES – Learners should understand when to and be able to apply these strategies. See Addition and Subtraction mental maths booklet: Partitioning (pg38-54) – – – – – – – Emphasise the use of estimation and rounding in calculations use knowledge of place value and related calculations, e.g. work out 140 + 150 = 290 using 14 + 15 = 29, 6.3-4.8 using 63-48 use knowledge of place value and of doubles of two-digit whole numbers Count on or back in hundreds, tens and ones. Progress to tenths then hundredths. Subtract by counting up from the smaller to the larger number. Partitioning strategies: 47+58 - add tens and ones separately then recombine. Progress to hundreds. 91-35 - subtract tens then ones. Progress to hundreds. 56+29 - add or subtract a multiple of 10 and adjust, add or subtract a multiple of 100 and adjust 38+37 - double and adjust. 4.3+2.9 = 4.3+3 – 0.1 – add or subtract a whole number and adjust How long from 3.45pm to 4.20pm? Count on and back in minutes and hours, bridging through 60 (analogue and digital times, progressing to 12 hour and 24 hour clock) Use knowledge of place value and related calculations, e.g. 140+150=290 using 14+15=29. Progressing to decimals – 6.3-4.8 using 6348, 0.68+0.43 using 68+43 Emphasise the importance of using mental maths skills and recall in a variety of contexts, e.g. Money Second Level Class: ________________________________ Session:__________________________ Multiplication and Division Second Level (1) MNU 2-01a I can use my knowledge of rounding to routinely estimate the answer to a problem then, after calculating, deciding if my answer is reasonable, sharing my solution with others. RECALL Multiplication facts for the 6,7,8,9 times tables and corresponding division facts MNU 2-02a I have extended the range of whole numbers I can work with and having explored how decimal fractions are constructed, can explain the link between a digit, its place and value. MNU 2-03a Having determined which calculations are needed, I can solve problems involving whole numbers using a range of methods, sharing my approaches and solutions with others. MNU 2-03b I have explored the contexts in which problems involving decimal fractions occur and can solve related problems using a variety of methods. With increasing speed and confidence, all multiplication facts to 10 x 10 and the corresponding division facts. Doubles of numbers 1 to 100, e.g. double 58 and corresponding halves. Second Level (2) RECALL Squares to 10 x 10 Division facts corresponding to tables up to 10x10, and the related unit fractions, e.g. 7x9 = 63 so one ninth of 63 is 7 and one seventh of 63 is 9. Percentage equivalents of one half, one quarter, three quarters, tenths and hundredths. Factor pairs to 100 Doubles of multiples of 10 and 100 and corresponding halves. Fraction and decimal fraction equivalents of one half, quarters, tenths and hundredths, e.g.3/10 is 0.3 and 3/100 is 0.03. SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) Double any two-digit number, e.g. double 39. Link x2,x4,x8 Link Number Talks –Making landmark numbers (pg269) Give the factor pair associated Second Level (3) RECALL Multiplication facts for the 11 and 12 times tables. Squares to 12 x 12. Squares of the multiples of 10 e.g. 90 x 90. Prime numbers less than 100. Equivalent fractions, decimal fractions and percentages for hundredths, e.g. 35% is equivalent to 0.35 or 35/100. More complex but commonly used equivalent fractions, decimal fractions and percentages. e.g. 33 1/3% is equivalent to 1/3 or 0.3… or 66 2/3 is equivalent to 2/3 or 0.6… SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) SKILLS (mentally, with jottings and materials if needed) Multiply and divide two digit number by 4 or 8, e.g. 26x4, 96÷8 (using repeated doubling or halving). Link Number Talks –Repeated Addition (pg265-266), landmark numbers (pg269- Multiply pairs of two digit and two digit numbers, e.g. 28x3. Link Number Talks – Doubling and Halving (pg276-279) Divide a two digit number by a single digit number, MNU 2-04a I can show my understanding of how the number line extends to include numbers less than zero and have investigated how these numbers occur and are used. MNU 2-07a I have investigated the everyday contexts in which simple fractions, percentages or decimal fractions are used and can carry out the necessary calculations to solve related problems. MNU 2-07b I can show the equivalent forms of simple fractions, decimal fractions and percentages and can choose my preferred form when solving a problem, explaining my choice of method. with a multiplication fact, e.g. identify that if 2x3=6 then 6 has the factor pair 2 and 3 Break factors into smaller factors when multiplying Link Number Talks – Breaking into smaller factors (pg282284) Double any multiple of 10 or 100, e.g. double 340, double 800. Halve the corresponding multiples of 10 and 100, e.g. half of 60, half of 400. Halve any even number to 200 Halving and doubling strategy when calculating two-digit x onedigit multiplication problems Link Number Talks – Doubling and Halving (pg276-279) Find unit fractions and simple non-unit fractions of numbers and quantities, e.g. 1/7 of 21, 3/8 of 24. Multiply and divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (wholenumber answers) e.g. 325x10, 42x100, 120 ÷ 10, 600 ÷ 100, 850 ÷ 10. Multiply a multiple of 10 to 100 by a single-digit number, e.g. 40 x3. Link Number Talks –Partial 271) Factor pairs to 100, e.g. 30 has the factor pairs – 1x30, 2x15, 3x10, 5x6. Break factors into smaller factors when multiplying Link Number Talks – Breaking into smaller factors (pg 282285) Multiply two digit numbers by 5 or 20, e.g. 320x5, 14x20. Multiply by 25 or 50, e.g. 48 x 25, 32 x 50. Link Number Talks – Partial products (pg 272-275) Halving and doubling strategy when calculating two-digit x twodigit multiplication problems Link Number Talks – Doubling and Halving (pg276-281) Double three digit multiples of 10 to 500 and find corresponding halves, e.g. 380x2, 760÷2. Divide a double digit by one digit Link Number Talks – Repeated subtraction (pg287-290), Multiplying up (pg293-296) Find the remainder after dividing a two digit number by a single digit number (within tables), e.g. 27÷4 = 6r3. e.g. 68÷4 (exploring partitioning method). Divide a double digit by one digit Link Number Talks – Repeated subtraction (pg287292) Divide a two digit number by a two digit number Link Number Talks – Partial Quotient (pg287292),multiplying up (pg293297) Divide by 25 or 50, e.g. 4500÷25, 3200÷50. Double decimals with units and tenths and find the corresponding halves, e.g. double 7.6, half of 15.2. Multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100, e.g. 600x20, 300x400. Divide multiples of 100 by a multiple of 10 or 100 (whole number answers), e.g. 600÷20, 800÷400, 2100÷300. Multiply and divide two digit decimal fractions by a single digit such as 0.8x7, 4.8÷6. Find multiples of 10% of whole numbers and quantities, e.g. 30% of 50ml, 40% of £30, 70% of 200g. Use knowledge of multiplication facts to simplify fractions. products (pg272-275) Multiply numbers to 20 by a single digit number, e.g. 17x3. Identify the remainder when dividing by 2, 5 or 10. Multiply and divide whole numbers and decimal fractions by 10, 100 or 1000, e.g. 4.3x10, 0.75x100, 25÷10, 673÷100, 74÷1000. Multiply pairs of multiples of 10 e.g. 60x30 and a multiple of 100 by a single digit number, e.g. 900x8. Divide a multiple of 10 by a single digit number (whole number answers) e.g. 80÷4, 270÷3. Find fractions of whole numbers or quantities e.g. 2/3 of 39, 4/5 of 70kg. Find 50%, 25% or 10% of whole numbers or quantities, e.g. 25% of 20kg, 10% of £80. Link Number Talks – Proportional reasoning (pg298-299) Scale up and down using known facts, e.g. given that three oranges cost 24p, find the cost of four oranges. Identify numbers with odd and even numbers of factors and no factor pairs other than 1 and themselves STRATEGIES – Learners should understand when to and be able to apply these strategies. See Multiplication and Division mental maths booklet: Partitioning (pg38-54) Emphasise the use of estimation and rounding in calculations Partition: double or halve the tens and ones separately, then recombine 32x5, 14x20 - Form an equivalent calculation, e.g. to multiply by 5 – multiply by 10 then halve, to multiply by 20 – double then multiply by 10 or multiply by 10 then double. 32 x 50, 48 x 25, e.g. to multiply by 50 – multiply by 100 then halve. To multiply by 25 – multiply by 100, then halve and halve again. When dividing by 50, form an equivalent calculation e.g. divide by 100 then double. To divide by 25 – divide by 100 then multiply by 4. Use understanding that when a number is multiplied or divided by 10 or 100, its digits move one or two places to the left or the right relative to the decimal point, and zero is used as a place holder Use knowledge of multiplication facts and place value, e.g. 7 x 8 = 56 to find 70 x 8, 7 x 80 Use knowledge of multiplication and division facts to find factor pairs Multiply or divide by 2, 4 or 8 by repeated doubling or halving Form an equivalent calculation, e.g. to multiply by 5, multiply by 10, then halve; to multiply by 20, double, then multiply by 10 Use knowledge of doubles/ halves and understanding of place value, e.g. when multiplying by 50 multiply by 100 and divide by 2 Use knowledge of division facts, e.g. when carrying out a division to find a remainder Use understanding that when a number is multiplied or divided by 10 or 100, its digits move one or two places to the left or the right relative to the decimal point, and zero is used as a place holder Scale up or down using multiplication and division – e.g. if three oranges cost 24p: one orange costs 24÷3 = 8p then four oranges cost 8x4 = 32p. Use knowledge of equivalence between fractions and percentages, e.g. to find 50%, 25% and 10% partition: use partitioning and the distributive law to divide tens and ones separately, e.g.92 ÷ 4 = (80 + 12) ÷ 4 = 20 + 3 = 23 Use partitioning and the distributive law to multiply, e.g. 13 × 4 = (10 + 3) × 4= = (10 × 4) + (3 × 4) = 40 + 12 = 52