grade 6
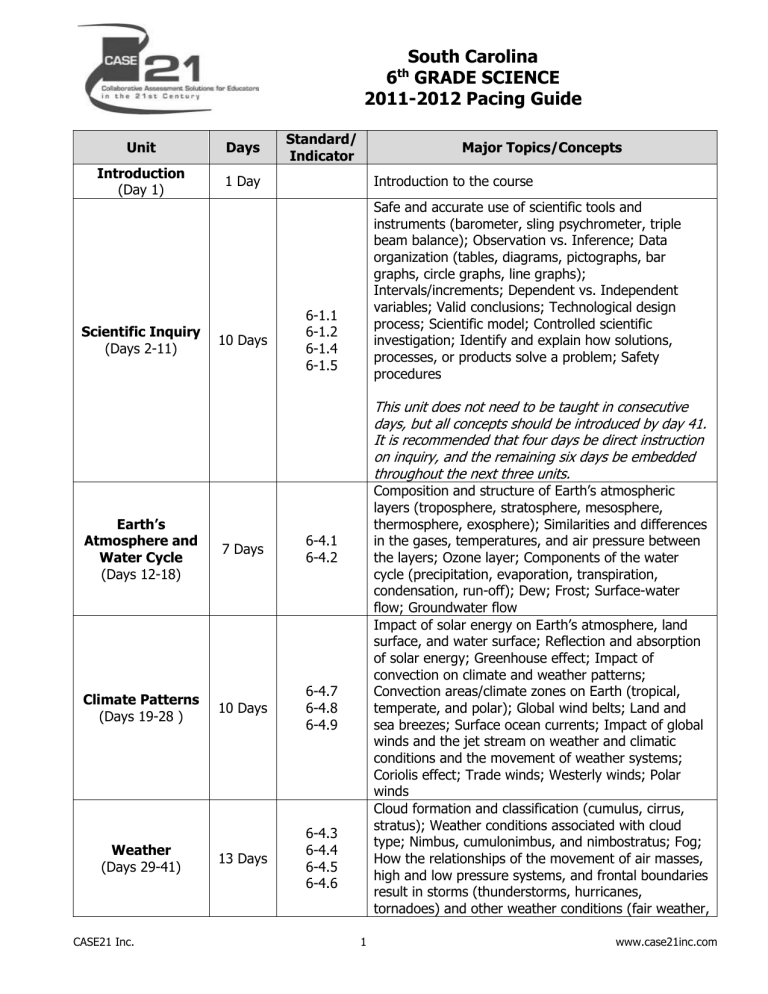
South Carolina
6
th
GRADE SCIENCE
2011-2012 Pacing Guide
Unit Days
Standard/
Indicator
Major Topics/Concepts
Introduction
(Day 1)
Scientific Inquiry
(Days 2-11)
Earth’s
Atmosphere and
Water Cycle
(Days 12-18)
Climate Patterns
(Days 19-28 )
Weather
(Days 29-41)
1 Day
10 Days
7 Days
10 Days
13 Days
6-1.1
6-1.2
6-1.4
6-1.5
6-4.1
6-4.2
6-4.7
6-4.8
6-4.9
6-4.3
6-4.4
6-4.5
6-4.6
Introduction to the course
Safe and accurate use of scientific tools and instruments (barometer, sling psychrometer, triple beam balance); Observation vs. Inference; Data organization (tables, diagrams, pictographs, bar graphs, circle graphs, line graphs);
Intervals/increments; Dependent vs. Independent variables; Valid conclusions; Technological design process; Scientific model; Controlled scientific investigation; Identify and explain how solutions, processes, or products solve a problem; Safety procedures
This unit does not need to be taught in consecutive days, but all concepts should be introduced by day 41.
It is recommended that four days be direct instruction on inquiry, and the remaining six days be embedded throughout the next three units.
Composition and structure of Earth’s atmospheric layers (troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere); Similarities and differences in the gases, temperatures, and air pressure between the layers; Ozone layer; Components of the water cycle (precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, condensation, run-off); Dew; Frost; Surface-water flow; Groundwater flow
Impact of solar energy on Earth’s atmosphere, land surface, and water surface; Reflection and absorption of solar energy; Greenhouse effect; Impact of convection on climate and weather patterns;
Convection areas/climate zones on Earth (tropical, temperate, and polar); Global wind belts; Land and sea breezes; Surface ocean currents; Impact of global winds and the jet stream on weather and climatic conditions and the movement of weather systems;
Coriolis effect; Trade winds; Westerly winds; Polar winds
Cloud formation and classification (cumulus, cirrus, stratus); Weather conditions associated with cloud type; Nimbus, cumulonimbus, and nimbostratus; Fog;
How the relationships of the movement of air masses, high and low pressure systems, and frontal boundaries result in storms (thunderstorms, hurricanes, tornadoes) and other weather conditions (fair weather,
CASE21 Inc. 1 www.case21inc.com
Unit Days
Standard/
Indicator
Major Topics/Concepts showers or light rain, humid, clear and cold, cloudy);
Identify fronts; Predict weather conditions along fronts or within air masses; Fronts (warm, cold, stationary, occluded); Characteristics of high and low pressure systems; Tools and processes for collecting data related to wind speed, wind direction, air temperature, humidity, and air pressure; Interpreting the scale on weather instruments (anemometer, thermometer, sling psychrometer, barometer, rain gauge); Predict weather based on data collected from observations, weather maps, satellites, and radar; Interpret weather maps, station models, and hurricane tracking maps;
Identify weather symbols on maps; Use a series of maps to show patterns or weather system movement;
Meteorologists; Isobars
Days 42-43 Review/1 st Benchmark (covering all content through day 41)
Scientific Inquiry
(Days 44-54)
11 Days
Conservation of
Energy
(Days 55-64)
Magnetism and
Electricity
(Days 65-73)
10 Days
9 Days
6-1.1
6-1.2
6-1.4
6-1.5
6-5.1
6-5.2
6-5.5
6-5.3
6-5.4
Safe and accurate use of scientific tools and instruments (spring scale); Observation vs. Inference;
Data organization (tables, diagrams, pictographs, bar graphs, circle graphs, line graphs);
Intervals/increments; Dependent vs. Independent variables; Valid conclusions; Technological design process; Scientific model; Controlled scientific investigation; Identify and explain how solutions, processes, or products solve a problem; Safety procedures
Eleven days are allowed to provide time for inquiry concepts to be embedded and reinforced through actual experimentation during the next three units.
Sources and properties of types of energy (heat, solar, chemical, electrical, mechanical); Kinetic vs. Potential mechanical energy; Law of Conservation of Energy;
Mechanical energy transformations KE PE and the involvement of other types of energy; Heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation;
Directional transfer of heat; Types of heat transfer based upon particle behavior given temperature differences
Interrelated nature of magnetism and electricity;
Electromagnets; Generators; Simple electric motors;
Magnetic field; Magnet; Electric current; Turbines;
Generators vs. Motors; Transformation of electrical energy into light, sound, heat, and mechanical motion in an electric circuit; Complete electric circuit;
Examples of devices and the energy transformations they complete
CASE21 Inc. 2 www.case21inc.com
Unit
Work and
Machines
(Days 74-84)
Days
11 Days
Standard/
Indicator
6-5.6
6-5.7
6-5.8
Major Topics/Concepts
Energy; Work; Examples of work; Force; Spring scale;
Newtons; Simple machine (lever, pulley, inclined plane); Effort force; How simple machines reduce or change the direction of the effort force; Compare simple machines to determine which machine reduces the amount of force the most
Review/2 nd Benchmark (covering content from day 1-84) Days 85-86
Scientific Inquiry
(Days 87-92)
Characteristics and
Classification of
Living Things
(Days 93-100)
Comparing
Invertebrates and Vertebrates
(Days 101-114)
6 Days
8 Days
14 days
11 Days
6-1.1
6-1.2
6-1.3
6-1.4
6-1.5
6-2.1
6-2.2
6-3.1
6-3.2
6-3.3
6-3.4
Safe and accurate use of scientific tools and instruments (spring scale); Observation vs. Inference;
Data organization (tables, diagrams, pictographs, bar graphs, circle graphs, line graphs);
Intervals/increments; Dependent vs. Independent variables; Valid conclusions; Use dichotomous key to identify and classify organisms, objects, and materials;
Technological design process; Scientific model;
Controlled scientific investigation; Identify and explain how solutions, processes, or products solve a problem;
Safety procedures
Six days are allowed to provide time for inquiry concepts to be embedded and reinforced through actual experimentation during the next four units.
Characteristics of living things (energy resources, respond to stimuli, reproduce, growth and development); Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs;
Photosynthesis; stimulus/response; Asexual vs. Sexual reproduction; Taxonomy; Levels of Classification
(kingdom, phylum/divisions, class, order, family, genus, species); Five kingdoms (Plants, Animals,
Fungi, Protists, Monerans); Vascular vs. Nonvascular plants; Vertebrates vs. Invertebrates; Scientific name
Animal kingdom composed of 35 phyla; Common characteristics of all animals; Characteristics of the classes of vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals); Endoskeleton; Respiration through lungs, gills, and /or skin; Ectothermic vs. endothermic characteristics; Identify and classify ectothermic and endothermic animals; Metamorphosis; Distinguish major characteristics of vertebrates and invertebrates;
Major invertebrate phyla (sponges, segmented worms, echinoderms, mollusks, arthropods); Classify animals based upon characteristics; Animal survival mechanisms/structures for defense, movement, and obtaining resources (camouflage, mimicry, venom, claws, horns, quills, stingers, shells, ink, sensory organs, legs, feet and arms, wings, paws, toenails, tails, fins, beaks, teeth, tongues, tentacles, pincers, fangs, filtering structures)
Physical responses of animals to environmental stimuli
CASE21 Inc. 3 www.case21inc.com
Classification of
Flowering Plants
(Days 137-145)
Unit
Response to
Stimuli
(Days 115-125)
Learned and
Inherited
Behaviors
(Days 126-130)
Days 131-133
Plants
(Days 134-136)
Survival in a
Changing
Environment
(Days 146-152)
Fungi
(Days 153-155)
Days 156-160
Days 161-165
Days 165-180
Days
5 Days
Standard/
Indicator
6-3.5
6-3.6
6-3.7
Major Topics/Concepts
(shedding, sweating, panting, shivering, blinking, food gathering, storing nutrients as fat); Behavioral responses of animals to environmental stimuli
(hibernation, migration, defense, courtship); Ejection;
Grouping (herds, packs, schools); Internal stimuli for survival (hunger, thirst, sleep)
Learned behaviors (imprinting, conditioning); Inherited behaviors/instincts (babies crying, fish swimming, bird building nest)
Review/3 rd Benchmark (covering content from day 1-130)
3 Days 6-2.3
Vascular vs. Nonvascular plant characteristics; Seed vs. Spore-bearing plant characteristics; Embryo;
Cotyledons; Flowering vs. Cone-bearing plant characteristics; Conifers; Fruit; Monocot vs. Dicot plant characteristics; Identify and classify plants into groups based upon characteristics
9 Days
7 Days
6-2.4
6-2.5
6-2.6
6-2.7
6-2.8
Flowering plant structures for defense (thorns, poisonous fruits and leaves, thigmotropism);
Structures for survival (leaves, stems, roots, seeds);
Xylem vs. Phloem; Root hairs; Fibrous roots vs.
Taproots; Seed coats; Structures for reproduction
(flowers, seeds, petals, stamen, pistil, fruit); Filament;
Anthers; Pollen; Ovary; Ovules; Stigma; Style;
Pollination; Life cycle of flowering plants (germination, plant development, fertilization, seed production);
Sexual vs. Asexual reproduction (tubers, bulbs, runners, stem cuttings, roots, leaves); Requirements for sexual reproduction
Photosynthesis vs. Respiration in plants; Chloroplasts;
Chlorophyll; Stomata; Guard cells; Transpiration;
Movement of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and food through a plant; Responses to environmental stimuli
(dormancy, phototropism, gravitropism, hydrotropism, thigmotropism); Tropism
3 Days 6-2.9
Effects of fungi on plants; Characteristics of the Fungi
Kingdom; Disease-causing fungi; Benefits of fungi
(decomposers, source of penicillin, food)
Review/Optional Comprehensive Benchmark
(covering all content objectives)
PASS Testing
Review/Enrichment/Special Projects
CASE21 Inc. 4 www.case21inc.com