Sociology 1: Unit Two/Chpt
advertisement

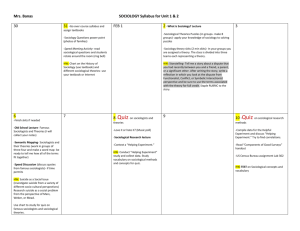
Name (First, Last)____________________Date _________ Sociology 1: Unit One (Chapter 1)/”Sociological Perspective” Assignment/Study Sheet Directions: Read pgs. 3-61 in Chapter One in the textbook, and answer the following questions. Your answers do not have to be in complete sentences. Write small; use your own paper if you run out of room. You may use this on quizzes/tests! Learning Objectives: Understand what is meant by the broader social contexts that underlie human behavior, and how and why sociologists study these broader social contexts. Explain the sociological perspective: what it is, what it offers, and why C. Wright Mills referred to it as "the intersection of biography (the individual) and history (the social factors that influence the individual). Define and discuss science as application (the systematic methods used to obtain knowledge) and product (the knowledge and/or information that are obtained by those methods). Identify, understand, and make distinctions between the natural sciences and the social sciences. Understand how sociology views and studies human behavior, and how its particular areas of focus are similar to and different from each of the other social sciences. Discuss the social changes and the changing social conditions that fostered the development of sociology as a distinct academic discipline in the middle of the nineteenth century. Identify and critique the sociological contributions of the following mid-to-late nineteenth and early twentieth century European sociologists: Auguste Comte, Herbert Spencer, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, Max Weber, and Harriet Martineau. Understand how and why levels of social integration may affect rates of suicide and how Emile Durkheim's nineteenth century study of suicide helped to demonstrate how social forces affect people's behaviors. Explain the role of values in social research as prescribed by Max Weber and the ensuing controversies over whether sociological research can be and/or should be value free. Distinguish between "Verstehen," as envisioned by Max Weber, and "social facts," as defined by Emile Durkheim; and explain how, despite their differences, both approaches can be combined when conducting social research. Trace the history of sociology in North America from the late 1800s to the present while identifying the sociological contributions of the following American sociologists: Albion Small, George Herbert Mead, Ernest Burgess, Robert E. Park, Jane Addams, Talcott Parsons, W.E.B. DuBois, and C. Wright Mills. Discuss the current state of American sociology as it relates to the debate between social reform and social analysis, and the role applied sociology plays in this debate. Define what is meant by theory and explain why theory is an important part of sociology. Identify the three major theoretical perspectives in sociology-symbolic interactionism, functional analysis, and conflict theory-and describe the particular level of analysis, characteristics, viewpoints, and concerns associated with each of these. Describe the current trends that are shaping the future of sociology in the United States and how globalization, in particular, may expand American sociology's horizons in the twenty-first century. 1. What is the sociological perspective? 2. What is an important feature of the sociological perspective? 3. What is social location? 4. What information do sociologists typically use to determine social location? 5. What term did C. Wright Mills use regarding each society being located in a broad stream of human events? 6. What are the natural sciences? 7. What are the social sciences? List the five specialized fields with a short definition and example of each. SOCIAL SCIENCE FIELD 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DEFINITION EXAMPLE 8. Who were the following people and what were their sociological contributions? NAME CONTRIBUTION NAME CONTRIBUTION August Comte Karl Marx Max Weber Albion Small Ernest Burgess Jane Addams W.E.B. DuBois Lewis Coser Herbert Spencer Emile Durkheim Harriet Martineau George Herbert Mead Robert E. Park Talcott Parsons C. Wright Mills Soc 1 Unit 1: Sociological Perspective Terms Assignment 1 9. Which of the people listed in the previous table was the first to propose that the scientific method could be applied to the study of social life/the social world? 10. What does the scientific method involve? 11. What is Social Darwinism? Which of the people on the previous table is associated with this theory? What did this person believe was a key element in understanding human history? 12. What is class conflict/class struggle? Which of the people on the previous table believed that it is a key element in understanding human history? 13. What is the bourgeoisie? What is the proletariat? What do these terms have to do with class conflict? 14. What concept did Durkheim introduce? How is this connected with suicide rates and social groups? 15. What is society? 16. What is verstehen and who introduced this concept? 17. What did Weber stress about social research? This means what about sociologists when they conduct research? 18. Durkheim and Weber differed on what sociologists should focus. What did they each stress and what is the difference? 19. Which of the sociologists mentioned in the textbook won a Nobel Peace Prize in 1931 and why? 20. Which of the sociologists was associated with Harvard University and why? 21. Which of the sociologists wrote a book about race relations? When was it written? Title: 22. What is symbolic interactionism (the short version)? What do symbolic interactionists analyze/study? How d symbolic interactionists explain our increasing divorce rate? 23. What is functionalism (the short version)? What do functionalists say we need to look at in order to understand society? How would functionalists explain our increasing divorce rate? 24. What is the conflict theory? What do conflict theorists stress (as opposed to functionalists)? How would a conflict theorist explain the increasing U.S. divorce rate? 25. What did Lewis Coser point out about conflict and where it might occur? 26. When you examine basic inequalities in relationships between men and women, which perspective are you taking as a sociologist? 27. Robert Merton discussed what he believed to be the intended beneficial consequences of people’s actions. Define the following terms that are associated with his discussion: Manifest function: Manifest dysfunction: Latent function: Latent dysfunction: 28. What are social facts? Which sociologist stressed this term? 29. Who developed the concept of the power elite? What does it mean? 30. What are some non-profit agencies in West Michigan that address social problems? (list @ least 5) Soc 1 Unit 1: Sociological Perspective Terms Assignment 2