Ocean Chemistry Webquest
advertisement

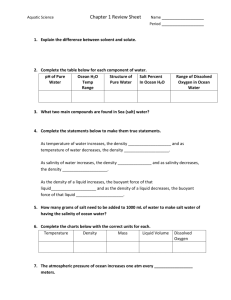
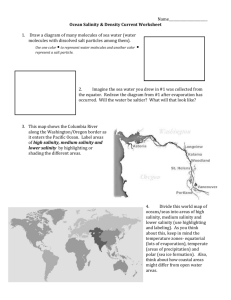
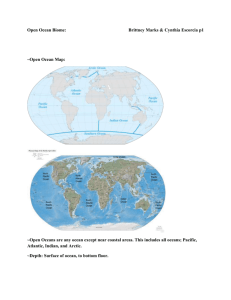
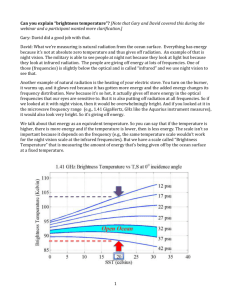
Webquest For Water Chemistry http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Water/dissolved_salts.html 1. Define Salinity: 2. In what units do scientists report salinity? Give an example of what the unit means. 3. What is the average salinity of the ocean? 4. What % of the ocean is salt? 5. List the 6 main dissolved salts in the ocean: http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Water/ocean_chemistry.html 6. What makes the ocean salty? 7. What greenhouse gas dissolves in ocean water? http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/climate/ocean_acidification.html 8. What does CO2 become when too much of it dissolves in the ocean? 9. What do many marine creatures use to build their shells? 10. What does acid do to marine shells? http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Water/density.html 11. What is the average density of ocean water? Is it more or less dense than fresh water? 12. What are the 2 main factors that affect the density of sea water? 13. What happens to the density of the ocean as you go to the bottom of the ocean? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TDEzBWjQpQI&feature=related 14. Why do you think this man is able to float so easily in the dead sea? http://www.extremescience.com/dead-sea.htm 15. What percent of the dead sea is salt? 16. How much more salty than the ocean is the dead sea? 17. Why do you think only certain types of bacteria can survive in the dead sea? Why do fish instantly die? 18. Why is the dead sea very dense? 19. What affect does this density have on people swimming in the dead sea? http://globetrooper.com/notes/why-cant-we-drink-sea-salt-water/ 20. Give 2 reasons why our bodies need water. 21. How do our bodies cool off if we are hot? 22. Under normal conditions, our bodies should be in an __________________ state, where the concentrations of water in our cells equals that of outside of our cells. 23. If the salinity (amount of salt) outside of you cells is greater than the salinity inside, what will happen? 24. Why do runners need to drink sports drinks that have sodium and potassium? 25. What will happen to your cells to you if you drink salt water? 26. So if at the aquarium you get stuck on a tiny boat in the salt water tank and get really thirsty, is it okay to take a quick drink of water to quench your thirst? http://www.doctortee.com/dsu/tiftickjian/cse-img/cell-biol/membranes/osmosisanimal.jpg 27. Define isotonic: 28. Draw a cell in an isotonic solution (normal) 29. Define Hypotonic Solution: 30. Draw and describe what happens to a cell placed in a hypotonic solution. 31. Define Hypertonic Solution: 32. Draw and describe what happens to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IRQLRO3dIp8 33. What happens to the Red Blood Cells in this hypertonic solution? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IRQLRO3dIp8 34. What happens to the Red Blood Cells in this hypotonic solution? http://marinebio.org/oceans/ocean-chemistry.asp Based on the diagram of a water molecule, what do you notice about the polarity (charges) of the water molecule itself? http://dl.clackamas.edu/ch105-05/definiti.htm What determines the pH value of water? (What are we determining the concentration of?) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXGF3XS-yAI How hot is the water coming out of the vent? What type of organism thrives in the vents? http://www.marinebio.net/marinescience/04benthon/dsvents.htm When did we discover deep sea hydrothermal vents? Why is this date so surprising? Through what process do the bacteria get their “cell food” or energy? How does it work? Why is this discovery so amazing?