enterprenureship & small business management
advertisement
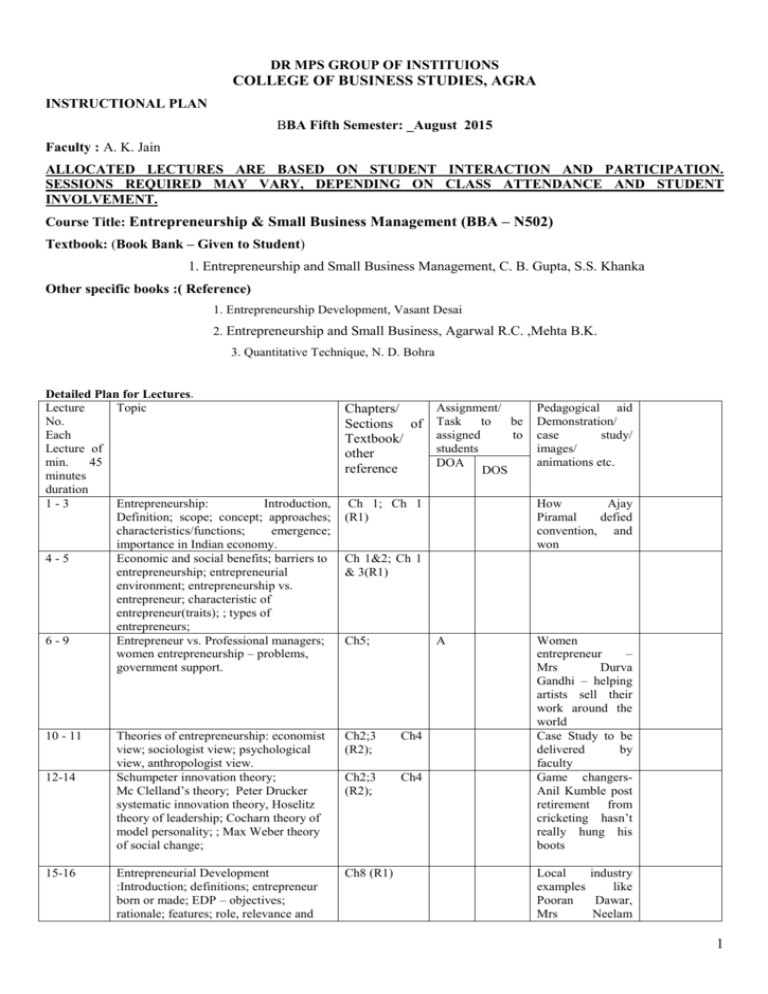
DR MPS GROUP OF INSTITUIONS COLLEGE OF BUSINESS STUDIES, AGRA INSTRUCTIONAL PLAN BBA Fifth Semester: _August 2015 Faculty : A. K. Jain ALLOCATED LECTURES ARE BASED ON STUDENT INTERACTION AND PARTICIPATION. SESSIONS REQUIRED MAY VARY, DEPENDING ON CLASS ATTENDANCE AND STUDENT INVOLVEMENT. Course Title: Entrepreneurship & Small Business Management (BBA – N502) Textbook: (Book Bank – Given to Student) 1. Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management, C. B. Gupta, S.S. Khanka Other specific books :( Reference) 1. Entrepreneurship Development, Vasant Desai 2. Entrepreneurship and Small Business, Agarwal R.C. ,Mehta B.K. 3. Quantitative Technique, N. D. Bohra Detailed Plan for Lectures. Lecture Topic No. Each Lecture of min. 45 minutes duration 1-3 Entrepreneurship: Introduction, Definition; scope; concept; approaches; characteristics/functions; emergence; importance in Indian economy. 4-5 Economic and social benefits; barriers to entrepreneurship; entrepreneurial environment; entrepreneurship vs. entrepreneur; characteristic of entrepreneur(traits); ; types of entrepreneurs; 6-9 Entrepreneur vs. Professional managers; women entrepreneurship – problems, government support. 10 - 11 12-14 15-16 Assignment/ Chapters/ Sections of Task to be assigned to Textbook/ students other DOA reference DOS Pedagogical aid Demonstration/ case study/ images/ animations etc. Ch 1; Ch 1 (R1) How Ajay Piramal defied convention, and won Ch 1&2; Ch 1 & 3(R1) Ch5; A Theories of entrepreneurship: economist view; sociologist view; psychological view, anthropologist view. Schumpeter innovation theory; Mc Clelland’s theory; Peter Drucker systematic innovation theory, Hoselitz theory of leadership; Cocharn theory of model personality; ; Max Weber theory of social change; Ch2;3 (R2); Ch4 Ch2;3 (R2); Ch4 Entrepreneurial Development :Introduction; definitions; entrepreneur born or made; EDP – objectives; rationale; features; role, relevance and Ch8 (R1) Women entrepreneur – Mrs Durva Gandhi – helping artists sell their work around the world Case Study to be delivered by faculty Game changersAnil Kumble post retirement from cricketing hasn’t really hung his boots Local industry examples like Pooran Dawar, Mrs Neelam 1 significance. Singh 17-18 Phases of entrepreneurial development; problems; role of government in entrepreneurial development; infrastructural support ; environmental analysis First lane syndrome – Bharat Banka/ the second life – Nandni Vaidyanathan 19-21 Institutions for Entrepreneurial Development: NIESBUD; CED; EDII; IED; SIDO; SISI; IDC; TCO Projects and reports: Introduction; opportunity analysis; sources of business ideas; project conceptualization; project classifications – quantifiable/nonquantifiable, techno-economic, financial institutions classification(new/expansion/diversificat ion/modernisation), R&D, welfare projects. Ch 12; website visit 24-26 Identification of projects; Project preparation (contents; aspects; sample format of feasibility report); feasibility analysis; network analysis (objective; planning – CPM/PERT: procedure; advantages; limitations; similarity and difference between CPM & PERT. Ch6 Ch9; 27-29 Project Appraisal: objectives; Market feasibility; Techno Economic feasibility; Financial analysis (profitability analysis – pay back period; ARR; NPV; IRR; BEP); social cost benefit analysis (SCBA). Ch 4 (R1) Sample format of bank or institution 30 Plant layout: Introduction; objectives of good layout; factors influencing layout; types of layout – their advantages and limitations; principles of layout. Small Industry Set up: meaning; types of small industry; types of organization(sole proprietorship; partnership; joint stock company; co-operative organization); their merits and limitations; Ch7 pictograms Discussion based Simulative exercise / want to start up in Gujarat or UP 38-39 Location of starting small industry unit – factors determining location; impact of government policy on deciding location; selection; process of establishing a small industry; facilities for starting enterprise; financial assistance to entrepreneurs; government policies – incentives; subsidies available, export opportunities. Transportation – North West Corner rule Pizza hut home delivery services. 40-41 Matrix Minima & VAM 42 MODI Method Ref. to Quantitative Technique by N. D. Bohra Ref. to Quantitative Technique by N. D. Bohra Ref. to 22-23 31-32 33-37 Stem to rescue – Stemade (stem cells) Ch6 (R1) (R1); Discussion based 2 43-45 Quantitative Technique by N. D. Bohra Ref. to Quantitative Technique by N. D. Bohra Assignment problem Details of Assignments Planned: (Sample – actual assignment may differ in number, content and context) Assignment Details Nature of Assignment Expected outcome No. 1 2 3 To be defined at time of class participation Field activity to designed at Practical appropriate session Collect information from secondary Use of secondary data sources about SME companies with for understanding operations in India. traits of successful start ups. Learn and understand basics of setting up a small enterprise. Understanding advantages and disadvantages/challenges that help small start up to build a bottom-up movement. Scheme for Class Assessment: (out of 100) : Component Attendance Quiz Case Study (evaluative ) Frequency Marks out of 100 Continuous 20 Two 10 Two 20 Term paper/Sessional Tests/Internal Two Exams Assignments Three 20 30 P.S.: No class notes will be given (only handouts when deemed necessary will be given), as all the classes will be based on analytical interaction. Students are expected to come prepared in class with their own understanding and notes written by them based on suggested chapter readings. 3