Warfarin OD fact sheet
advertisement
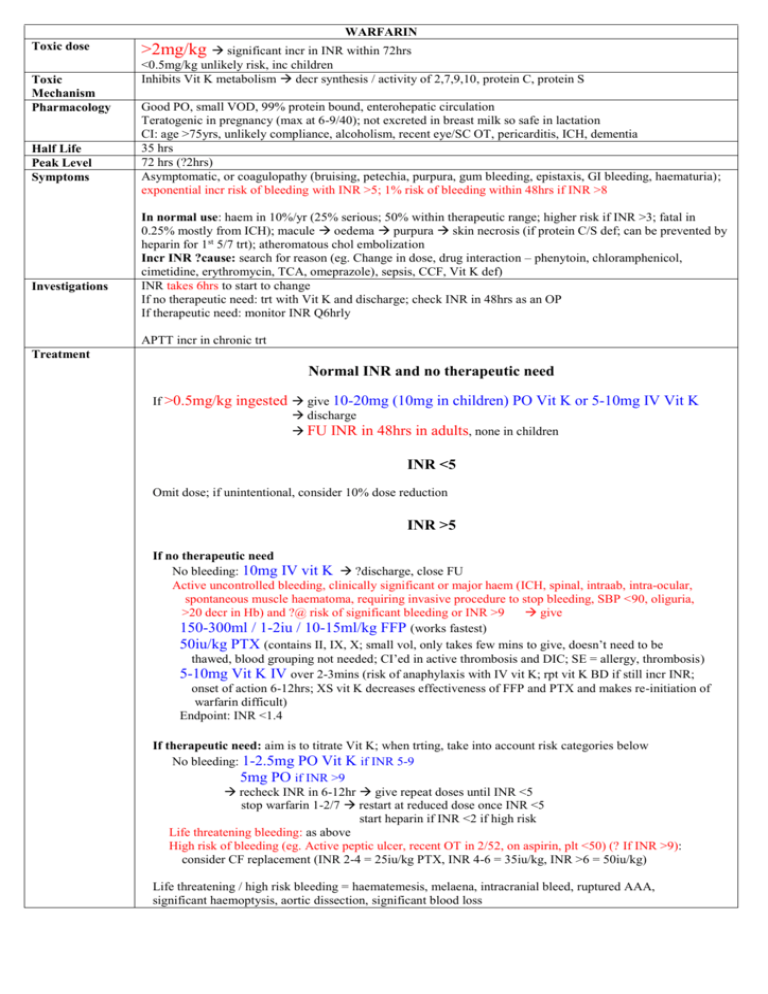
WARFARIN Toxic dose Toxic Mechanism Pharmacology Half Life Peak Level Symptoms Investigations >2mg/kg significant incr in INR within 72hrs <0.5mg/kg unlikely risk, inc children Inhibits Vit K metabolism decr synthesis / activity of 2,7,9,10, protein C, protein S Good PO, small VOD, 99% protein bound, enterohepatic circulation Teratogenic in pregnancy (max at 6-9/40); not excreted in breast milk so safe in lactation CI: age >75yrs, unlikely compliance, alcoholism, recent eye/SC OT, pericarditis, ICH, dementia 35 hrs 72 hrs (?2hrs) Asymptomatic, or coagulopathy (bruising, petechia, purpura, gum bleeding, epistaxis, GI bleeding, haematuria); exponential incr risk of bleeding with INR >5; 1% risk of bleeding within 48hrs if INR >8 In normal use: haem in 10%/yr (25% serious; 50% within therapeutic range; higher risk if INR >3; fatal in 0.25% mostly from ICH); macule oedema purpura skin necrosis (if protein C/S def; can be prevented by heparin for 1st 5/7 trt); atheromatous chol embolization Incr INR ?cause: search for reason (eg. Change in dose, drug interaction – phenytoin, chloramphenicol, cimetidine, erythromycin, TCA, omeprazole), sepsis, CCF, Vit K def) INR takes 6hrs to start to change If no therapeutic need: trt with Vit K and discharge; check INR in 48hrs as an OP If therapeutic need: monitor INR Q6hrly APTT incr in chronic trt Treatment Normal INR and no therapeutic need If >0.5mg/kg ingested give 10-20mg (10mg in children) PO Vit K discharge FU INR in 48hrs in adults, none in children or 5-10mg IV Vit K INR <5 Omit dose; if unintentional, consider 10% dose reduction INR >5 If no therapeutic need No bleeding: 10mg IV vit K ?discharge, close FU Active uncontrolled bleeding, clinically significant or major haem (ICH, spinal, intraab, intra-ocular, spontaneous muscle haematoma, requiring invasive procedure to stop bleeding, SBP <90, oliguria, >20 decr in Hb) and ?@ risk of significant bleeding or INR >9 give 150-300ml / 1-2iu / 10-15ml/kg FFP (works fastest) 50iu/kg PTX (contains II, IX, X; small vol, only takes few mins to give, doesn’t need to be thawed, blood grouping not needed; CI’ed in active thrombosis and DIC; SE = allergy, thrombosis) 5-10mg Vit K IV over 2-3mins (risk of anaphylaxis with IV vit K; rpt vit K BD if still incr INR; onset of action 6-12hrs; XS vit K decreases effectiveness of FFP and PTX and makes re-initiation of warfarin difficult) Endpoint: INR <1.4 If therapeutic need: aim is to titrate Vit K; when trting, take into account risk categories below No bleeding: 1-2.5mg PO Vit K if INR 5-9 5mg PO if INR >9 recheck INR in 6-12hr give repeat doses until INR <5 stop warfarin 1-2/7 restart at reduced dose once INR <5 start heparin if INR <2 if high risk Life threatening bleeding: as above High risk of bleeding (eg. Active peptic ulcer, recent OT in 2/52, on aspirin, plt <50) (? If INR >9): consider CF replacement (INR 2-4 = 25iu/kg PTX, INR 4-6 = 35iu/kg, INR >6 = 50iu/kg) Life threatening / high risk bleeding = haematemesis, melaena, intracranial bleed, ruptured AAA, significant haemoptysis, aortic dissection, significant blood loss Decontamination Elimination Antidote Monitoring Procedures Charcoal if <1hr and patient usually on anticoagulants No Vit K Onset: 6-12hr PO, 3-6hrs IV (?1-3hrs) Admit those usually on warfarin; can often give Vit K then discharge those not on warfarin Dental: wash mouth Q6hrly with 500mg tranexamic acid Jt aspiration / pleural tap: target INR <2 Major OT: stop 3/7 before and give heparin once INR under therapeutic range LOW RISK MODERATE RISK HIGH RISK Atrial fibrillation without valvular heart disease, previous stroke or embolism Atrial fibrillation with valvular heart disease, previous stroke or embolism Mechanical mitral valve Cardiomyopathy without heart failure, previous stroke or embolism Cardiomyopathy with heart failure, previous stroke or embolism Mechanical aortic valve with arrhythmia or history of thromboembolism Biological heart valves (except first 3 months) Biological heart valves (during first 3 months) Uncomplicated DVT (> 2 months) Previous history of multiple PE/DVT Cerebrovascular disease Uncomplicated DVT (< 2 months) Post AMI (mural thrombus prophylaxis) DVT/PE with laboratory-confirmed hypercoagulable state Vascular surgical prosthetic grafts Past systemic arterial emboli Post vascular-stent insertion Mechanical aortic valve without arrhythmia or history of thromboembolism







