SCIBio.Task5
advertisement
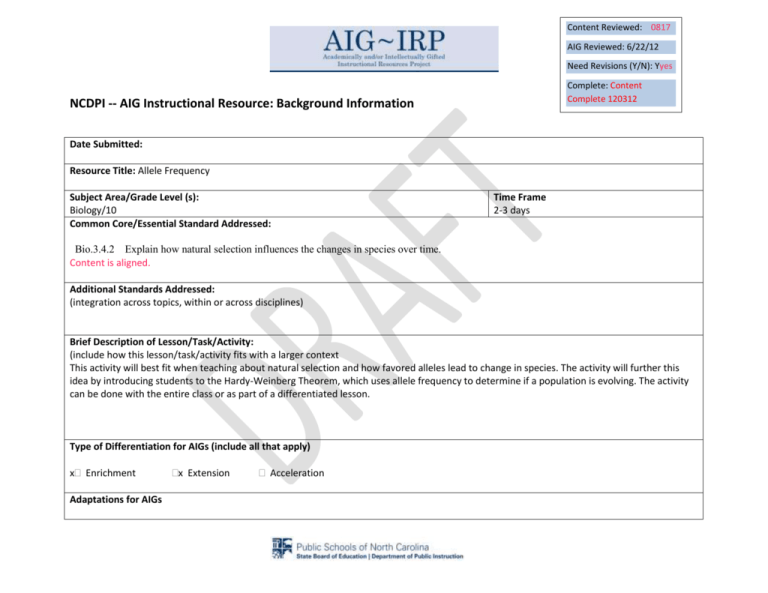
Content Reviewed: 0817 AIG Reviewed: 6/22/12 Need Revisions (Y/N): Yyes Complete: Content Complete 120312 NCDPI -- AIG Instructional Resource: Background Information Date Submitted: Resource Title: Allele Frequency Subject Area/Grade Level (s): Biology/10 Common Core/Essential Standard Addressed: Time Frame 2-3 days Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences the changes in species over time. Content is aligned. Additional Standards Addressed: (integration across topics, within or across disciplines) Brief Description of Lesson/Task/Activity: (include how this lesson/task/activity fits with a larger context This activity will best fit when teaching about natural selection and how favored alleles lead to change in species. The activity will further this idea by introducing students to the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem, which uses allele frequency to determine if a population is evolving. The activity can be done with the entire class or as part of a differentiated lesson. Type of Differentiation for AIGs (include all that apply) x Enrichment Adaptations for AIGs x Extension Acceleration x Content Process Product Explanation of How Resource is Appropriate for AIGs This resource will require students to move beyond the regular curriculum by learning how to use Hardy-Weinberg theorem to generate data and a conclusion on if/how a population is evolving. The activity will require students to use knowledge about the H-W theorem and evolution to reach their own conclusions. The activity will require students to apply their understanding of H-W theorem and evolution to their own surroundings. Needed Resources/Materials Internet, calculator Sources (all sources must be cited) TEACHER NOTES NCDPI AIG Curriculum Resource Outline Describe processes, steps, and materials needed at each stage of the lesson/activity. STAGE ONE: Engage Hook xPrior knowledge X Instructional input Modeling Description: Is the human population evolving as we speak???? This is the question the students will answer once they do internet research. To determine if a population is evolving we need to know several things: We first need to determine the allele frequency of a gene in your target population and the allele frequency of the general population. In order to fully understand this idea of evolution, you need to review the role of alleles in phenotype and natural selection. Students should then either research or be introduced to the H-W theorem and equation. An internet search on whether or not humans are still evolving will give students a variety of answers. Students need to understand that the change in allele frequency is what is used to determine if evolution is occurring. Students should be able to explain the 5 conditions that, if met, will allow a population’s allele and genotype frequencies to remain constant, which means the population is stable and not evolving in terms of a specific trait. Students will next practice using the equations and then determine the p and q values of several traits. STAGE TWO: ELABORATE Guided and independent practice Guiding questions Description: Students should review and practice using the H-W equation. Several suggested websites are: http://nhscience.lonestar.edu/biol/hwe/q1d.html http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab8/hardwein.html http://bcs.whfreeman.com/pierce1e/pages/bcsmain_body.asp?s=23000&n=00020&i=23020.01&v=chapter&o=|00010|00020|00030|00060|&ns=0 1) Students will research and find the allele frequency of several traits, such as PTC tasting or tongue rolling, within the North American population. 2) Students will then gather data by surveying their school population for the determined trait and calculate the frequency of each allele. Students will analyze their data using the H-W equation and determine if their school’s allele frequency matches the national average, the North American Frequency. If the data does not match, they should develop a hypothesis as to why not. They should include, within their explanation, which of the five principles of H-W are not being meet by their target population. 3) Students should include in their discussion the actual meaning of allelic frequency and why a change in frequency may not be enough evidence to determine if evolution is occurring. 4) Students will research evidence of examples modern evolution. The research does not need to be limited to humans. 5) Students will report what they learn by creating a poster/brochure comparing the allelic frequencies of the North American Population and the school population of the trait they chose and if the difference between the two is enough to say the school population is or is not evolving in terms of that one trait. They will also explain a modern day example of evolution on another poster/ brochure and give the evidence for the example. They should present the posters/brochures to their class or social studies class and explain how evolution actually occurs and how scientists determine if a population is evolving. Another option to facilitate students understanding of H-W Theorem is to have them complete an activity that models H-W and evolution. One such activity can be found at the following website: http://www.cunygk12.net/gk12/teddy STAGE THREE: EVALUATE Assessment Description: Develop a rubric that will take into consideration the following: Depth of research- did they find more than one source that gives the allelic frequency Correct use of H-W to determine allelic frequency of target population (school) Correct analysis of data In-depth explanation of whether or not their target population is evolving based on their one set of data Correct examples of modern day evolution Aesthetics of brochure/poster Correct information in brochure or on poster Correct use of terminology on brochure/poster Correct grammar on brochure/poster Correctly done works cited page TEACHER NOTES: