Lab Report 6
advertisement

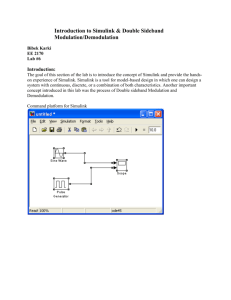
Charlie Haley EE 2170 lab 6 3/3/2010 Introduction: The goal of this lab is to learn about Simulink by experimenting with modulators and demodulators. How many cycles of the square wave appear in the scope window? What is its period? Five cycles of the square wave. T=2. How does the graph compare to the theoretical Fourier Transform magnitude for a sine wave? In the theoretical Fourier Transform, there is a spike at 50 and -50 rad/s. The spike at 50 is the fundamental of the wave, which represents the frequency in radians per second. The spike is higher than it should be in the theoretical Fourier Transform. Discuss how the Fourier Transform magnitude computed with Simulink compares to the theoretical value. The Fourier Transform magnitude computed with Simulink is a lot larger than the theoretical value, because MatLab squares the output. How does changing the sample time affect the resulting plots? It shows a zoomed in version of the time graph. The Fourier Transform graph does the same thing, but it shows a wider view due to the larger number of time samples. Explain the appearance of the Fourier Transform of the modulator output. The Fourier Transform modulator output is shifted to the right by 1000 rad/s. Explain all your observations and results. Now a square wave shows up in the shape of the graph of the function over time. The Fourier Transform of this signal has spikes at 0, 2000, and -2000 because 2000 has become the fundamental frequency of these two multiplied signals. Explain your observations and results. The lowpass filter gets rid of the higher frequency vibrations and it recreates the original signal created by the Fourier Transform. Indicate why the filter is lowpass. The filter is lowpass because lower frequencies are passed through. We know this because low frequencies have a higher magnitude and phase in these graphs. Conclusion: In this lab, I learned how to use Simulink to simulate products and sums of wave forms, and saw how a lowpass filter works. We created a double-sideband modulator/demodulator, and have graphs of both the modulated and the modulated/demodulated signal.