MATH-13 E03
advertisement

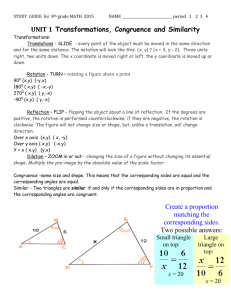
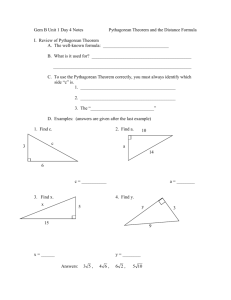
MATHEMATICS-13 ESSENTIAL UNIT 3 (E03) (Exponents and Roots) (July 2013) Unit Statement: In Unit Three, the student will learn to operate with numbers in scientific notation, approximate the values of irrational numbers, model the Pythagorean Theorem, and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real life problems. Unit three will prepare students to evaluate expressions containing exponents in future math courses, express the magnitude of interstellar distances, and to use right triangle geometry in future math courses. The student is expected to be familiar with the Key Terms and Concepts listed below. Essential Outcomes: (must be assessed for mastery) Problem solving and higher order thinking components are essential for A level mastery. Each outcome can contain problem solving and higher order thinking components (as found in suggested text). 1. The Student Will evaluate expressions with negative exponents and evaluate the zero exponent. (3-1, p. 92-95) 2. TSW apply the properties of exponents. (3-2, p. 96-99) 3. TSW express large and small numbers in scientific notation and compare two number written in scientific notation. (3-3, p. 100-104) 4. TSW operate with scientific notation in real-world situations. (3-4, p. 105-108) 5. TSW identify the action taking place in a problem, and decide whether to add, subtract, multiply, or divide throughout the unit. ( p. 111) 6. TSW find square roots. (3-5, p. 112-115) 7. TSW estimate square roots to a given number of decimal places and solve problems using square roots. (3-6, p. 116-119) 8. TSW determine if a number is rational or irrational. (3-7, p. 123-126) 9. TSW use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. (3-8, p. 132-135) 10. TSW use the Distance Formula and the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. (3-9, p. 138-141) 11. TSW use exponents to apply concepts and skills from the unit in a real-world concept. (p. 143) Introduced and Practiced Outcomes: (taught not assessed) 1. The Student Will use a graphing calculator to multiply and divide numbers written in scientific notation. (Technology Lab, p. 109) 2. TSW use a graphing calculator to evaluate expressions that have negative exponents. (Technology Lab, p. 122) 10 QSI MATHEMATICS-13 E03 Copyright © 1988-2013 3. TSW classify numbers as rational or irrational and graph them on a number line. (p. 128-129) 4. TSW use geometry software to explore the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem. (Technology Lab, p. 136-137) Key Terms and Concepts: Hypotenuse Perfect square Irrational number Pythagorean Theorem Real number Scientific notation Suggested Resources: Lesson Quiz (HMM TE) after each lesson Ready To Go On? After lesson 3.4, and 3.9 -assign Ready to Go On? Intervention and Enrichment worksheets after completion. (HMM “Are you Ready? Intervention and Enrichment”) Teacher created assessment (ExamView) Chapter 3 test (HMM Assessment Resources) Journal entries (HMM TE) Suggested Assessment Tools and Strategies: Attached rubric or teacher generated rubric that assesses ALL essential outcomes (TSWs) Use base 10 blocks to explore cube roots. (Hands-On Lab, p. 120-121) Use scissors and paper to explore right triangles. (Hands-On Lab, p. 131) Additional Resources: Something Out of Nothing: Marie Curie and the Discovery of Radium by Carla Killough McClafferty TE p. 91 Technology Links: Destiny WebPath Express (located on school’s automated library system) www.tenmarks.com This site is free, but requires users to sign up. After opening an account, teachers are able to generate and track assignments for individual students. This site is a great way to differentiate instruction in the math classroom. https://www.khanacademy.org/ Khan Academy provides students with videos of lessons and interactive manipulatives to enhance student learning. There are also sample problems for a wide variety of topics. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/category/math This website maintained by the University of Colorado offers many simulations, games, and activities. Many subject areas and topics are covered. This website offers a great opportunity to develop cross curricular projects. Suggested rubric on the following page………………………. 11 QSI MATHEMATICS-13 E03 Copyright © 1988-2013 MATHEMATICS-13 SUGGESTED UNIT EVALUATION RUBRIC E03: Student Name: __________________________ Date: _______________________ To receive a ‘B’, the student must show ‘B’ level mastery on ALL Essential Outcomes (TSWs). To receive an ‘A’, the student must show ‘A’ level mastery in all available ‘A’ level TSW’s and ‘B’ level mastery on all of the remaining TSW’s. TSW 1- evaluate expressions with negative exponents and evaluate the zero exponent 2- apply the properties of exponents 3- express large and small numbers in scientific notation and compare two number written in scientific notation 4- operate with scientific notation in real-world situations ‘A’ LEVEL ‘B’ LEVEL Example of A level mastery: The student can give a nonexample (i.e., 53 + 2 3) and justify why the properties of exponents would not work. Example of A level mastery: The student can create and solve word problems that provide real-world examples of scientific notation 5- find square roots The student consistently demonstrates the ability evaluate expressions with negative exponents and evaluate the zero exponent The student consistently demonstrates the ability to apply the properties of exponents. The student consistently demonstrates the ability to express large and small numbers in scientific notation and compare two numbers written in scientific notation The student consistently demonstrates the ability to operate with scientific notation in real-world situations The student consistently demonstrates the ability to find square roots The student consistently demonstrates the ability to estimate square roots to a given number of decimal places and solve problems using square roots 6- estimate square roots to a given number of decimal places and solve problems using square roots 7- determine if a number is rational or irrational The student consistently demonstrates the ability to determine if a number is rational or irrational 8- classify numbers as rational or irrational and graph them on a number line 9- use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems The student consistently demonstrates the ability to classify numbers as rational or irrational and graph them on a number line The student consistently demonstrates the ability to use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems The student consistently demonstrates the ability to use the Distance Formula and the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems 10- use the Distance Formula and the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems The student is able to reflect on the problem, consistently justify the mathematical concepts used and explain how the concepts apply to the problem 12 QSI MATHEMATICS-13 E03 Copyright © 1988-2013 Notes