the oxidation states of manganese
advertisement

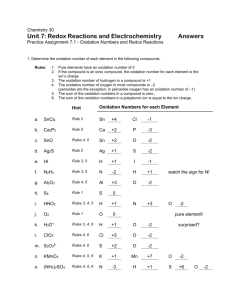
SUBDOMAIN 204.3 THE OXIDATION STATES OF MANGANESE SCA4/5 Task Late Nite Lab By Nienke Adamse 12/3/10 ABSTRACT In this experiment the various oxidation states that are formed by the redox reaction of permanganate ion, MnO4 and the bisulfite ion, HSO4 have been studied. The reducing agent that was used was sodium bisulfate, NaHSO3 . The redox reaction was studied inacidic, basic and neutral aqueous solutions. In the acidic solution the oxidation state of manganese was +2,and the oxidation state of sulfur was +6, in neutral solution the oxidation state of manganese was +3 and the oxidation state of sulfur was +6, and in basic solution the oxidation state of manganese was +6 and the oxidation state of sulfur was +6. EXPERIMENT Tools: In this experiment the following tools and glassware were used: 3 pH meters 5 test tubes Chemicals: H2O H2SO4 KMnO4 NaHSO3 NaOH MnO2 Procedure: 1. Take 5 clean test tubes and place them on the workbench. 2. Add 5 mL of water to the first test tube. This is your color standard against which the pale pink Mn+2 ion can be compared. 3. Add 5 mL of KMnO4 to the second test tube. This is your color standard for the purple permanganate ion. 4. Add 2 mL of KMnO4 to test tubes 3, 4 and 5. 5. Add 1 mL of NaOH to test tube 3 6. Add 1 mL of H2SO4 to test tube 5. 7. Take 3 pH meters and place them into test tubes 3, 4 and 5. Record the pH in the test tubes. You will see that test tube 3 is the basic solution, test tube 4 is neutral, and test tube 5 is acidic. 8. Add five 1 mL increments of NaHSO3 to test tube 3. Observe and record the results of the reaction, color and precipitation, after each addition of 1 mL. 9. Add five 1 mL increments of NaHSO3 to test tube 4. Observe and record the results of the reaction, color and precipitation, after each addition of 1 mL. 10. Add five 1 mL increments of NaHSO3 to test tube 5. Observe and record the results of the reaction, color and precipitation, after each addition of 1 mL. RESULTS Table 1: color of solution and precipitation: Color of: 1ml 2 ml 3 ml 4 ml 5 ml #3 NaHSO3 green NaHSO3 green NaHSO3 green NaHSO3 green NaHSO3 green solution #3 No No No No precip No precip. precip. precip. precip. #4 pink pink clear clear Clear #4 No brown brown brown brown precip. precip. #5 pink pink pink pink Very precip. solution solution light pink #5 no no no no no precip Table 2: pH values solution pH 1ml 2 ml 3 ml 4 ml 5 ml NaHSO3 NaHSO3 NaHSO3 NaHSO3 NaHSO3 #3 13.65 13.56 13.48 13.41 13.35 #4 7.00 7.38 7.41 7.38 7.35 #5 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.08 0.14 ANALYSIS Test tube #3: The reaction between NaHSO3 and KMnO4 (after adding 5 ml of NaHSO3 ) in a basic solution (test tube #3) can be described with the following equation: 2KMnO4 3NaHSO3 2NaOH 2H2O NaOH Na2 MnO4 NaHMnO4 K2SO4 NaHSO3 3H2O The green solution indicates that the oxidation state of manganese is +6, it shows the existence of the manganate ion, MnO42 in the basic solution. The oxidation state of sulfur in the NaHSO3 in this test tube is +4. The sodium bisulfate functions here as a reducing agent and the oxidation state of sulfur increases from +4 to +6. HSO3 is converted to the sulfite ion SO32 . Test tube #4: The reaction between NaHSO3 and KMnO4 (after adding 5 ml of NaHSO3 ) in a neutral solution (test tube #4) can be described with the following equation: KMnO4 NaHSO3 H2O KMnO4 MnO2 K2SO4 Na2SO4 NaHSO3 H2O The clear solution with the brown precipitation shows that the oxidation state of manganese is +4, it shows that the manganese dioxide, MnO2 has been formed in the reaction in the neutral solution, this is a black solid. The reducing agent here is sodium bi sulfate and the oxidation state of the sulfur increases from +4 to+6. It is being oxidized to the bisulfate ion HSO . 3 Test tube #5: The reaction between NaHSO3 and KMnO4 (after adding 5 ml of NaHSO3 ) in a acid solution (test tube #5) can be described with the following equation: KMnO4 H2SO4 NaHSO3 H2O H2SO4 MnSO4 K2SO4 Na2SO4 NaHSO4 H2O The light pink solution in the test tube shows that the oxidation state of manganese is +2, it shows that Mn 2 exists in the acidic solution. The manganate ion MnO42 has been reduced to Mn 2 . Sodium bisulfite is the reducing agent in this redox reaction. The oxidation state of sulfur increases to +6. In this acidic solution sodium bisulfite is converted into sulfurous acid H2SO3 and is oxidized into the bisulfate ion HSO4 . CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION Oxidation is the process where a molecule, atom or ion increases its oxidation state. Reduction is the process where a molecule, atom or ion decreases its oxidation state. In a redox reaction (an oxidation-reduction reaction) , the atoms change their oxidation number (oxidation state). An oxidizing agent is the oxidant that gains electrons and is reduced. The reducing agent is the reductant that loses electrons and is oxidized. Substances, such as the permanganate ion, that have the ability to oxidize other substances are oxidizers or oxidizing agents. The oxidizing agent is also called the electron acceptor because it accepts or removes electrons from other substances and is thus itself reduced. Substances, such as sodium bisulfite, that have the ability to reduce other substances are reducing or reducing agents. The reducing agent is also called an electron donor because it transfers electrons to another substance, thus becoming oxidized itself. The oxidation states ( or oxidation numbers) concept of the redox reactions is a way to keep track of the electrons. (Zumdahl, 2009) defines the oxidations states of the atoms in a covalent bond as: “ the imaginary charges the atoms would have shared if the shared electrons were divided equally between identical atoms bonded to each other or, for different atoms, were all assigned to the atom in each bond that has the greater attraction for electrons.” In test tube # 5, the +2 oxidation state of Mn results from removal of the two 4s electrons, leaving a "high spin" ion in which all five of the 3d orbitals contain a single electron. The pale pink color of the solution is the result of the absorption of almost all visible light by this ion In test tube #3, manganese exists in the +6 oxidation state as the manganate ion, MnO42 , this ion is green in color and is only stable in basic solution,. In test tube #4, the manganese ion exists in the +4 oxidation state as manganese dioxide, MnO2 . This a solid that is fairly stable, Mn 4 does not exist in aqueous solutions. The reducing agent inthis reaction was sodium bisulfite: NaHSO3 . The oxidation state for sulfur in sodium bisulfite is +4 and increases to +6. In neutral solutions the bisulfate ion HSO3 exists SO 2 . In an and in basic solutions it is oxidized to the sulfate ion 4 acidic solution it is oxidized to sulfuric acid, H2SO3 . REFERENCES Late Nite labs: Laboratory Simulations for Science Education. (2006)- Oxidation States of Manganese. http://www.latenitelabs.com/ Zumdahl, S.S and Zumdahl, S.A (2009) Chemistry. Seventh Edition Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company