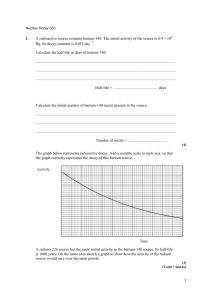
Chapter 25 - Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement
Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 1 of 7 Chapter 25 - Nuclear Chemistry The study of ____________ ____________ and their uses in chemistry Radiation • The penetrating rays & particles emitted by a radioactive source Radioactivity • Process that occurs when nuclei change ____________ Radioisotopes • Atoms containing ____________ ____________ Recall… What are isotopes? o How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions? Chemical Reactions • Atoms become stable by ____________or ____________electrons • Rate ____________changed by catalysts, temperature, pressure, etc. • Mass & charge ____________ Nuclear Reactions • Nuclei become stable by undergoing changes that ____________of energy • Rate ____________be changed • Charge conserved, mass ___________________ o A ____________small amount of mass is converted into energy Nuclear Stability • Most nuclei are stable • The stability of a nucleus depends on its neutron to proton ____________ • The stable nuclei are in the ‘________________________’ Radioactive Decay • Occurs in atoms with too _______or too _______neutrons • The nucleus will attempt to become more stable by releasing energy through ______________ • Transmutation o when the unstable nucleus of one element is ____________ into a stable nucleus of a different element o Occurs naturally and artificially Types of Radioactive Decay o Alpha particles, o Beta particles, o Positron emission o Gamma rays, Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 2 of 7 Alpha Decay – α • Gives off ____________ particles (helium nuclei) • Occurs when the neutron: proton ratio is low • A radioactive element gives off 2 protons and 2 neutrons o The charge on the nucleus ________________________ • Alpha particles do not travel far & are not very penetrating due to their large mass and charge o Sheet of paper or surface of skin stops them 240 o o o o 94Pu → 23692U + 42He (α) Atomic # # of protons Mass # # of neutrons - Beta Decay – β • Gives off ____________ particles (electrons) • Occurs when the neutron: proton is high • A neutron breaks apart into a proton, which stays in the nucleus, and an electron which is released o 10n → 11H + 0-1e (β) o Charge on the nucleus ________________________ • More penetrating than α particles o Can pass through paper, but are stopped by aluminum foil or thin pieces of wood 228 o o o o 88Ra → 22889Ac + 0-1e (β) Atomic # # of protons Mass # # of neutrons - Positron Emission • Gives off a ____________ (positive electron) • Occur when the neutron: proton is low • A proton breaks apart into a neutron, and a unit of positive charge o 11p → 10n + 0+1e (positron) o Charge on the nucleus ________________________ 22 o o o o Atomic # # of protons Mass # # of neutrons - 11Na → 2210Ne + 0+1e Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 3 of 7 Gamma Decay – γ • Gives off high energy photons called ________________________ • _____________________________________________ • Very dangerous - extremely penetrating o Pass easily through paper, wood, & the human body o Some can be stopped by several meters of concrete or several centimeters of lead 240 o o o o o 94Pu → 24094Pu Atomic # # of protons Mass # # of neutrons Nucleus changes only in its energy state Summary of Radiation Particle Mass Charge Symbol 4 2He, α Penetrating Power Low Alpha 4 amu 2+ Beta Positron 0 amu 0 amu 11+ 0 e, β -1 0 e +1 Moderate Moderate Gamma Ray 0 amu None γ High Nuclear Equations • Similar to chemical equations… • Mass and charge must balance on both sides • 14 • By using the concept of conservation of charge and mass number, you can identify a missing particle in an equation. 7N + 42He → 178O + 11H Sample Exercises 1. What product is formed when radium-226 undergoes alpha decay? 2. What element undergoes alpha decay to form lead-208? 3. What product is formed when Mg-27 decays by beta emission? Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 4 of 7 1H _____ + 0-1e 6. 14 3Li 94Be + _____ 7. 241 Am 95 4. 3 5. 9 6C 0-1e + _____ 8. 16 7N 166O + _____ 42He + _____ 9. What forms when francium-220 decays? 10. What forms when potassium-37 decays? 11. What forms when potassium-42 decays? + 10n 42He + _____ 12. 6 Li 3 13. 27 13Al 14. 27 14Si 83Bi 42He + _____ 29Cu 6630Zn + _____ 15. 214 + 42He _____ + 01e 16. 66 0-1e + _____ 17. 235 92U 9038Sr + _____ + 10n + 40-1e Half-Life • Time required for ____________ of the nuclei of a radioactive sample to decay into products • After each half-life, __________of the existing radioactive atoms have decayed into atoms of a new element Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 5 of 7 Table N • Each element has a characteristic half-life • Anywhere from a fraction of a second to billions of years • ½ life is ________________________ Uses for Half-Life • Dating • Nuclear medicine Half-Life Calculations • No formula; make a ________________________ chart • Always start with time = ____________ • If no mass is given, start with ________________________ Sample Problems 1. Most chromium atoms are stable, but Cr-51 is an unstable isotope with a half-life of 28 days. a. What fraction of a sample of Cr-51 will remain after 168 days? b. If a sample of Cr-51 has an original mass of 52.0g, what mass will remain after 168 days? 2. How much was present originally in a sample of Cr-51 if 0.75mg remains after 168 days? 3. According to Reference Table N, how much of a 100. microgram (μg) sample of nitrogen-16 will remain after 28.52 seconds of decay? 4. In 5.49 seconds, 1.20g of Ar-35 decay to leave only 0.15g. What is the half-life of Ar-35? 5. Na-24 has a half-life of 15 hours. How much Na-24 will remain in an 18.0g sample after 60 hours? Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 6 of 7 6. How many half-lives are required for a radioisotope to decay to 1/32 of its initial value? 7. What fraction of 226Ra will be left after 4797 years? Artificial Transmutations • Particle Accelerators o Collision of a proton or α particle with a target nucleus o Uses magnetic or electrostatic fields to accelerate particles & overcome the repulsive forces • Neutron Collisions o Occurs when a neutron collides with a target nucleus o Used to prepare radioactive nuclei from stable nuclei ▫ 23892U + 10n → 23992U ▫ 59 27Co ▫ 32 16S + 10n → 6027Co + 10n → 3215P + 11H Nuclear Fission • ____________ of the nucleus into smaller fragments o Occurs when the nucleus is bombarded with ____________ o Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239 are the only fissionable isotopes ________________________________________________ • • Releases huge amounts of ____________ Very exothermic o 1 kg U-235 = 20,000 tons of dynamite o Atomic bombs & nuclear reactors Nuclear Reactors • Uses controlled fission • Energy from fission reaction heats the coolant • Heated coolant is used to produce steam • Steam turns a turbine • Turbine drives a generator to produce electricity Chemistry Regents Mr. Markic Page 7 of 7 Nuclear Fusion • Light nuclei ____________ to produce a nucleus of greater mass • Solar fusion – H nuclei fuse to make He nuclei ________________________________________________ Fusion as an Energy Source • Produces ____________ energy than fission • Occurs only at high temperatures (over 40,000,000ºC) • More appealing than fission because: o Availability/low cost of light isotopes o Products are generally not ________________________ Detecting Radiation • Radiation ____________ be seen, heard, felt, or smelled • Ionizing radiation o radiation with enough energy to knock electrons off atoms of the bombarded substance to produce ions o Can be detected by Geiger counters, scintillation counters, and film badges Using Radiation • Medicine o Diagnostic tools o Treatment for cancer o Help to determine mechanisms for chemical reactions o Trace movements of atoms in biological systems • Radiation in the body should: o Have a ____________ half-life o Be ____________ eliminated from the body Other Uses of Radiation • Tracers o Any radioisotope used to follow the path of a substance o Ex. Used in agriculture to test the effects of herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers • Industrial Applications – o Used to measure the thickness or strength of a material based on radioactive absorption • • Food Irradiation – o Kills insects, bacteria, & mold o Prevents the ‘sprouting’ of fruits & vegetables Dating o Using half-lives, ‘age’ of objects can be determined o C-14 → C-12: o U-238 → Pb-206: