Description and schedule
advertisement

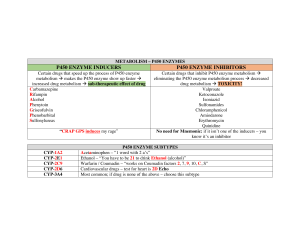
Title: Interactions between food/ feed components and hepatic metabolism (5 HEC) Course Organizers Galia Zamaratskaia and Vladimir Zlabek; Department of Food Science, Food in Focus at SLU Key words: Metabolism; Cytochrome P450; Toxicity; Diet Background The health of humans is to a great extent determined by the quality and quantity of the diet. Food products contain a variety of components that may affect metabolic reactions and therefore processes of detoxification. Thus, investigation on the interaction between food components and hepatic metabolism is a key part not only in toxicology and pharmacology, but also in food science and nutrition. Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system is the most effective systems in the organism metabolizing wide range of endogenous and exogenous compounds, including xenobiotics. This course will focus on following central questions: how CYP450 acts, how it is regulated in different organisms and how dietary components are involved in those processes? This course is designed to provide an overview on the most relevant mechanisms of CYP450 actions, function and regulations in humans, livestock animals and fish. Duration: 28 September – 5 November 2010 (126 hours) - lectures (19 hours) home work including literature study and project work (96 hours) project presentations (3 hours) examination and course evaluation (8 hours) Target group: PhD students; post-docs and master students within food science can attend the course as long as there are places available. Language: English Course design: The course will consist of 7 physical meetings (total 6 week) including lectures, group discussions, as well as project work. In the project work each student will select a topic of interest (from given topics), write an abstract (1 page) and present it at the seminar (15 min presentation + 5 min discussion). Examination: Project work writing and presentation. Other: Minimum number of students 3, maximum number of students 15. Course literature: selected chapters from the book “Biochemistry” by Champe and Harvey (J.B. Lippincott Company), selected scientific articles. Learning Outcomes After completion of the course the student will be able to: - Describe the general mechanism of metabolic reactions - Describe the mechanism of CYP450 inhibition and induction, list the major modifier in food which can modulate CYP450 - Describe the major enzymes present in selected organism and explain the differences between mammal/fish and their response to dietary components - Provide examples of assays suitable for measurement of enzyme expression and activity and explain the basic principles of those assays Course content Date Time and place Mee ting 28 September, 9.30-11.00 Conference room 1 11.00-12.00 1 Tuesday Title of the lecture Introduction to the course. Hours Lector 1 GZ 1 VZ Basic principles of metabolism. * Models and mechanisms of action Inhibition or induction of enzymes 1 Regulation of metabolism 1 GZ 1 Instructions to project work 1 GZ 2 Nutrition status and metabolism 2.5 VZ,GZ 2 Biotransformation of xenobiotics 1.5 GZ 9.30-10.30 B3:21 Akvariet 3 Cytochrome P450 in human and livestock animals (important isoforms, regulations et cetera…) 1 VZ 10.30-12.30 B3:21 Akvariet 3 Cytochrome P450 in fish (effect of environmental pollutants) 2 VZ 21 October, Thursday 9.30-12.30 B3:21 Akvariet 4 Drug-Nutrient considerations 3 VZ, GZ 2 November, Tuesday 9.30-11.30 B3:21 Akvariet 5 In vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450 (microsomes preparation methods, measurements of activities, inhibition studies, investigations on substrate specificity) 2 GZ 11.30-12.30 C3:21 Glasburen 5 In vivo evaluation of cytochrome P450 1 VZ 9.30- 6 Presentation of project; examination, course evaluation 13.00-14.30 12 October, 9.30-12.00 Tuesday B3:21 Akvariet 13.00-14.30 B3:21 Akvariet 19 October, Tuesday Date to be decided (close to Christmas) GZ (Galia Zamaratskaia) 10 hours; VZ (Vladimir Zlabek) 9 hours *Titles of the lectures might be slightly modified Presentati ons: 20 min per student; evaluatio n 30 min