castle builder
advertisement
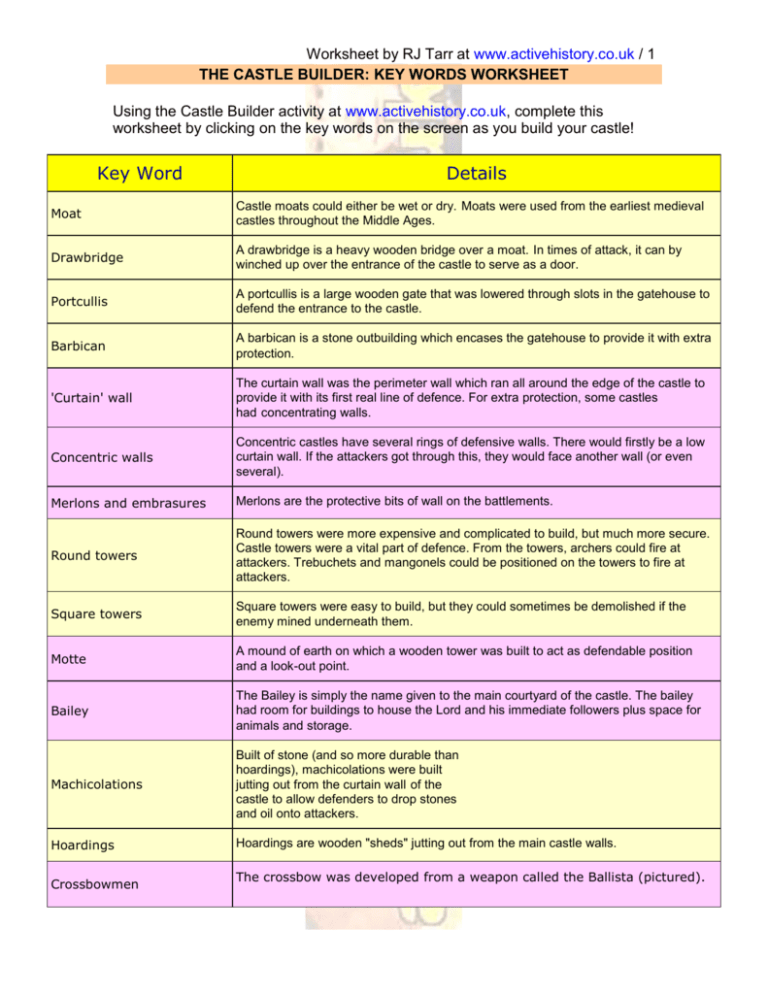
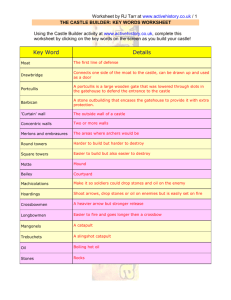
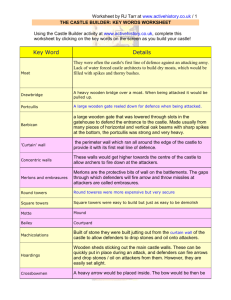
Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 1 THE CASTLE BUILDER: KEY WORDS WORKSHEET Using the Castle Builder activity at www.activehistory.co.uk, complete this worksheet by clicking on the key words on the screen as you build your castle! Key Word Details Moat Castle moats could either be wet or dry. Moats were used from the earliest medieval castles throughout the Middle Ages. Drawbridge A drawbridge is a heavy wooden bridge over a moat. In times of attack, it can by winched up over the entrance of the castle to serve as a door. Portcullis A portcullis is a large wooden gate that was lowered through slots in the gatehouse to defend the entrance to the castle. Barbican A barbican is a stone outbuilding which encases the gatehouse to provide it with extra protection. 'Curtain' wall The curtain wall was the perimeter wall which ran all around the edge of the castle to provide it with its first real line of defence. For extra protection, some castles had concentrating walls. Concentric walls Concentric castles have several rings of defensive walls. There would firstly be a low curtain wall. If the attackers got through this, they would face another wall (or even several). Merlons and embrasures Merlons are the protective bits of wall on the battlements. Round towers Round towers were more expensive and complicated to build, but much more secure. Castle towers were a vital part of defence. From the towers, archers could fire at attackers. Trebuchets and mangonels could be positioned on the towers to fire at attackers. Square towers Square towers were easy to build, but they could sometimes be demolished if the enemy mined underneath them. Motte A mound of earth on which a wooden tower was built to act as defendable position and a look-out point. Bailey The Bailey is simply the name given to the main courtyard of the castle. The bailey had room for buildings to house the Lord and his immediate followers plus space for animals and storage. Machicolations Built of stone (and so more durable than hoardings), machicolations were built jutting out from the curtain wall of the castle to allow defenders to drop stones and oil onto attackers. Hoardings Hoardings are wooden "sheds" jutting out from the main castle walls. Crossbowmen The crossbow was developed from a weapon called the Ballista (pictured). Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 2 Longbowmen the weight of the arrow meant that it did not travel as far as one loosed from a longbow. Mangonels The magnonel is a type of catapult. A large arm, loaded with rocks, would be attached at right angles to a a shaft of wood. Trebuchets The trebuchet works by tying a massive weight to one end of a beam that is hinged at its centre. On the other end, the missiles are placed. Oil Stones and boiling oil can be dropped onto attackers over the sides of the castle walls. Stones Stones and boiling oil can be dropped onto attackers over the sides of the castle walls. Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 3 Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 4 Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 5 Worksheet by RJ Tarr at www.activehistory.co.uk / 6