here - Southeastern Louisiana University
advertisement

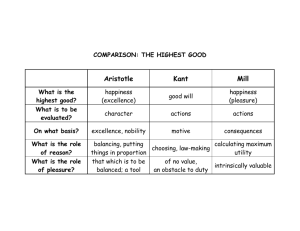
Philosophy 313 Midterm: October 15, 2015 Study sheet for Midterm The following list of terms and concepts is to assist you in studying for the short answer section of the test. There will be 10 short answer questions on the test, of which you are to answer 8 (5 points each): Socratic method knowledge vs. opinion fact/value distinction justice parts of the soul more reality/more satisfaction analogy of the cave Ideas (or Forms) teleology righteous indignation habituation good will good with/without qualifications argument for free will respect/person happiness mean pleasure/happiness distinction reason vice and virtue good friends first nature/second nature TRC overcompensation capital punishment moderation in all things categorical/hypothetical imperative duty consistency in actions universality test Two of the following essay questions will be on the midterm (just as they appear here), and you are to write on one of them (60 points): 1. In the Euthyphro, Socrates questions Euthyphro about the nature of holiness. This form of questioning has often been called the Socratic method. Explain Socrates' manner of questioning. This process of questioning also led both to Socrates' eventual trial and conviction, and it led to his conclusion that if he is wise it is only insofar as he knows that he knows nothing. What is the positive significance of recognizing that one knows they know nothing, and how, especially for Socrates, does this tie in to ethics? 2. Aristotle argues that to be happy we must make the right decisions as consistently and often as we can. Detail the argument that Aristotle lays out to justify this claim and elaborate what it means and entails. Be sure to give specific examples to clarify the points you make (preferably your own examples). Turn then to discuss why only the virtuous person can be happy, and how one might correct their vices in order to become happy. And finally, discuss the TRC as it relates to what Aristotle argues. 3. Kant argues, unlike Aristotle, that happiness is not the highest end of human action for without a good will even happiness can be a bad thing. Explain the argument behind Kant’s claim. With this argument in place, explain what leads Kant to the categorical and practical imperative. Be sure to give examples throughout your essay.