Day 14- Solns and Solub Text Review Qs typed out

Solutions and Solubility Review Questions p.325
4. How does the bonding in water molecules account for the fact that water is an excellent solvent?
7. Explain the expression “ like dissolves like” in terms of intermolecular forces.
8. What factors affect the rate of dissolving of a solid in a liquid?
9. Which of the following would you expect to be soluble in water? Explain why? (potassium chloride, carbon tetrachloride, sodium sulfate, butane)
11. What mass of boric acid is present in 250g of solution that is 2.25% (M/M) acid in water?
13. What value of pure ethanol is needed to make 800 mL of a solution of ethanol in water that is 12%
(v/v)?
14. The concentration of sodium fluoride is maintained at 2.9 x 10-5 mol/L. a) What mass in mg of sodium fluoride is dissolved in 1L of solution? b) Express this concentration in ppm.
ADD 15.A saturated solution of sodium acetate can be prepared by dissolving 4.65 g in 10.0 mL of water at 20 degrees Celcius. What is the molar concentration of the solution?
18. Calculate the molar concentration of the solution after dilution. a) 20mL if 6.0mol/L HCl diluted to
70mL.
19. Calculate the molar concentration of each solution. a) 85.0 mL of 1.50 mol/L ammonium chloride added to 250mL of water.
20. A standard solution of 0.250 mol/L calcium ion is prepared by dissolving solid calcium carbonate in an acid. What mass of calcium carbonate is needed to prepare 1.00 L of the solution?
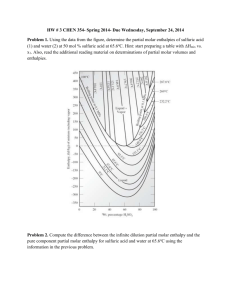
ADD 24,25. Solubility Curve p.365
2. Identify the spectator ions and write the balanced ionic equation
10. Aqueous solutions of iron(III)chloride and ammonium sulfide react in a DDR. a) Write the name and formula of the substance that precipitates. b) Write the chemical equation for the reaction (including the states). c) Write the net ionic equation.
S14
15. 50.0 mL of 0.200mol/L calcium nitrate is mixed with 200mL of 0.180 mol/L potassium sulfate. What is the concentration of sulfate ions in the final solution?
20. minimum volume to ppt question(omit S14) p.355
13.A student mixes 15.0 mL of0.250 mol/L aqueous NaOH with 20.0 mL of 0.400 mol/L aqueouse aluminum nitrate. A) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction (including the states). b)
Calculate the maximum mass of precipitate that forms. p.347
4. Would you expect QA of a solution to give you the amount of each ion present? Explain why/why not.
7. All the solutions in the photo on p.347 have the same concentration of 0.1 mol/L. Which ion causes the colour in each solution? How much confidence do you have in your inferences? What could you do to increase your confidence?
ADD: A mystery solution contains Cu+2 and/or Ba+2 cations. Make a plan to determine which cation(s) are in the solution. How confident are you that this plan will identify what is in the mystery solution? p.410
1-7 True/False Topics: solubility of gasses and temp, molar conc defn, solubility defn, insoluble defn, solute, solvent, c=n/v, rate of solubility
12-15 MC Topics: g/mL convert to mol/L, C=n/v for ions, C1V1-C2V2, net ionic eqn
23. The allowable drinking water concentration of phosphorus is 0.05 ppm. What is the maximum mass of phosphorous that could be present in a 250mL glass of tap water?
29. A chemist has a large beaker containing ice water and another container with boiling water. Explain how to maximize the solubility of the following in water. a) magnesium chloride in water b) benzene in water c)carbon monoxide gas in water
S14