Citizenship in the World
advertisement

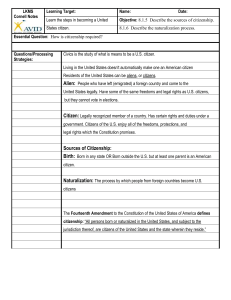
Citizenship in the World Teacher Packet A Study Guide for Boy Scouts Dear Scout, Did you ever think of a course on Citizenship as being fun and interesting as well as educational? This course is designed to be all of those! Today, if you seriously apply yourself you can qualify to pass off the Citizenship in the World merit badge that is required for Eagle. You will learn many new and exciting concepts that will help you make greater contributions to your community, nation, and world. Our job today is to provide you with the material and knowledge you will need to go to a counselor and pass off this merit badge. Your job is to carefully fill in the blanks and learn the concepts so you can take this completed study guide with you and discuss these ideas with your counselor. And now if you are ready to explore the exciting field of good citizenship, let’s begin! Citizenship in the World 1. What is citizenship? 1. A person who is a recognized member of his community, state, or nation is known as a _______CITIZEN_________. 2. The set of privileges, freedoms, duties, and responsibilities is known as ________CITIZENSHIP____________________. 3. What is a good citizen of the world? 2. Becoming a good citizen. 1. Anyone born in the United States, or whose ____PARENTS__ are citizens of the U.S., is automatically a citizen of the U. S. 2. People from foreign lands who come to America can become __NATURALIZED___ citizens. 3. A foreigner who lives in the U.S. but is not a citizen is called an ____ALIEN_____. 4. Similarities and Differences between Countries Citizenship US Rights 1. LIFE Similarity: Similarity: 2. LIBERTY Difference: Difference: 3, PROPERTY 1. STAY RIGHTEOUS Similarity: Similarity: 2. LEARN ABOUT GOVERNMENT 3, VOTE Difference: Difference: 1. OBEY LAW Similarity: Similarity: 2. DEFEND COUNTRY Difference: Difference: Duties Obligations YOUR CHOICE YOUR CHOICE 3, PAY TAXES 3. World event and foreign country activity 1. Discuss a current world event. 2. Select a foreign country. Discuss how it’s geography, natural resources, and climate influence its economy and its global partnerships with other countries. 4. International Law and International Organizations: 1. The law that applies to relations between different countries is called _INTERNATIONAL_______ law. This law is usually by __TREATY______ or merely recognized as ___CUSTOM___. An example of a treaty is the agreement of nations to outlaw certain weapons. In another example, the communists argued they had the ____CUSTOMARY________ right of air space when they shot down KAL 007 in 1983. National law is easier to enforce than international law because there is no police force or prison system in the international arena. 2. International Organizations i. In theory, the United Nations, was supposed to be the means of bringing __PEACE__ to the entire family of nations. And yet, there have been more tragic __WARS___ since its beginning than during the same time period before. This is because the member nations do not have the same foundation of ____MORAL____ principles. ii. The same problem exists with the World Court. How can the United States, for example, get a fair and impartial hearing from a bench of judges who are __OPPOSED____ to our system of government? iii. The World Organization of the Scout Movement and the International Committee of the Red Cross are examples of international organizations that have been very _____SUCCESSFUL_________ because they have _____SIMILAR_______ humanitarian and moral principles and they do not attempt to control the ___INTERNAL_____ affairs of their members. 5. Various forms of Government 1. A constitution is a written ___PLAN___ of government. Today, there are about ___190__ countries in the world. Of these, about __125__ have written constitutions. Can you guess which country has the oldest constitution? ___US_______. Most countries follow their constitution only as long as it is _____CONVENIENT_____ for their leaders to do so. Some countries, such as _____ENGLAND______ have never had written constitutions. Its only law is what the leaders say the law is. 2. 3. Country 4. Type of Government 5. UNITED STATES 6. CONSTITUTIONAL REPUBLIC 7. ENGLAND 8. PARLIAMENTARY REPUBLIC 9. CUBA 10. COMMUNIST 11. SAUDIA ARABIA 12. ABSOLUTE MONARCHY 13. GERMANY 14. DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST 15. Find these 5 countries on a map. 6. International Representation 1. The government of one country is represented in another country by a __DIPLOMAT______. In order for a diplomat to be "legal agents" for the nation he represents, he must be ___ACCREDITED_____. This means a diplomat has a formal letter from his government authorizing him to represent the nation. 2. Foreign Relations i. The head diplomat is known as an _________AMBASSSADOR__________. He is in charge of the _____EMBASSY______. ii. A person who deals mostly with American citizens and American businesses in a foreign land is known as a ____CONSUL_____. iii. The United States Information Agency promotes _EDUCATION_____ and ___CULTURAL_____ exchange activities between the U.S. and foreign nations. iv. The U.S. Agency for International Development manages U.S. economic and humanitarian assistance in over ___100____ countries of the world. v. The U.S. Foreign Commercial Service assists American businesses and _____ENTREPRENEURS_____ abroad. 3. International travel permissions i. An official agreement that a government issues to its citizens to permit them to travel abroad is called a ___PASSPORT_______. ii. A special endorsement stamped in a passport that allows a person to enter a country is called a _____VISA______. 7. Staying Current on International Matters 1. US State Department Web Site 2. International News Organization Web Site: “Find a news story about a human right realized in the United States that is not recognized in another country.” 1