click here - Oasis Academy MediacityUK
advertisement

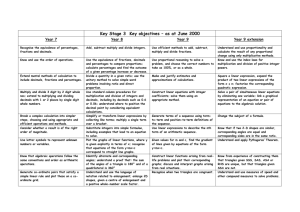
Mathematics Introduction to subject Mathematics is the means of looking at the patterns that make up our world and the intricate and beautiful ways they are constructed and realised. Numeracy is the means of making that knowledge useful. The subject transcends cultural boundaries and its importance is universally recognised. Mathematics helps us to understand and change the world. The mathematics department at Oasis Academy: MediaCityUK aim to ensure all students receive a curriculum that both stretches and engages their learning. We wish to instil an enthusiasm for mathematics to show students how relevant the subject is to their everyday life. Key stage 3 overview Students follow the National Curriculum at Key Stage 3 and cover a range of topics across the four attainment areas, (Number, Algebra, Shape & Space and Handling Data). Students will build on skills previously learnt in Year 6 and develop their understanding further into more complex areas. Our scheme of work is designed to ensure all students develop the key mathematical skills and knowledge required for them to make outstanding progress. There is also a particular emphasis on using and applying their mathematical knowledge in a variety of contexts. Key stage 4 overview All students study the Edexcel linear Specification GCSE award in mathematics. We use the linear GCSE scheme as this provides the students with a holistic approach enabling the development of cross subject knowledge required for further mathematical development. Students will either follow the Foundation or Higher GCSE syllabus throughout Years 9, 10, and 11 depending on their ability. The department regularly monitors the progress students are making and will advise students individually on which examination tier of entry is most suitable for them. Within the new GCSE curriculum there is a particular emphasis on the ability to solve complex mathematical problems in context. This is developed within lessons through the use of group work and students are encouraged to work with a variety of different students in order to learn various strategies from each other. During the course we also encourage students to develop a facility with mental and written calculations, the effective and efficient use of a calculator and appropriate use of Information Technology. Oasis Academy:MediaCityUK Curriculum 2014-15 Mathematics programme of study Year 7 Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Integers, Powers and Roots. Sequences, Functions and Graphs: Coordinates Fractions, decimals and percentages Sequences, Functions and Graphs. Measure and mensuration Mental calculations Lines, Angles and Shapes Calculating and checking Written calculations Construction and Loci Geometrical reasoning Transformations and coordinates Probability Statistical enquiry Processing and Interpreting data Ratio and Proportion Equations, Formulae, Expressions and Identities Equations, Formulae, Expressions and Identities Area Year 8 Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Integers, Powers and Roots. Sequences, Functions and Graphs: Coordinates Fractions, decimals and percentages Sequences, Functions and Graphs. Measure and mensuration Mental calculations Lines, Angles and Shapes Calculating and checking Written calculations Construction and Loci Geometrical reasoning Transformations and coordinates Probability Statistical enquiry Processing and Interpreting data Ratio and Proportion Equations, Formulae, Expressions and Identities Equations, Formulae, Expressions and Identities Area Year 9 (Foundation) Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Integers and Place Value Tables, Charts and Graphs, including Pie Charts and Scatter Graphs. Statistics and questionnaires. Averages. Fractions, Decimals and Percentages. Angles, lines and Symmetry Decimals. Indices, powers and roots Factors, multiples and primes. Polygons and Parallel Lines Algebra: expanding and factorising brackets, expressions, and substitution into formulae. Equations, inequalities, sequences Year 9 (Higher) Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Calculations, checking and rounding Averages and range Polygons, angles and parallel lines Indices, roots, reciprocals and hierarchy of operations Representing and interpreting data Pythagoras’ Theorem and trigonometry Scatter graphs Graphs: the basics and real-life graphs Fractions Percentages Ratio and proportion Quadratic, cubic and other graphs Factors, multiples and primes Standard form and surds Perimeter, area and 3D forms Algebra: the basics Circles, cylinders, cones and spheres Setting up, rearranging and solving equations Accuracy and bounds Sequences Year 10 (Foundation) Qualification: Edexcel GCSE Mathematics Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Integers Charts and graphs Properties of quadrilaterals and parallel lines Decimals Symmetry, Similarity and Congruence Coordinates Types of number Angles, lines and triangles Introduction to algebra Reading scales and converting units Constructions Collecting data Patterns and sequences Fractions Pie charts Fractions, decimals and percentages Applications of percentages Algebra using powers and brackets Year 11 (Foundation) Qualification: Edexcel GSCE Mathematics Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Ratio and proportion Compound measures Revision Linear equations and inequalities Timetables and distance-time graphs Perimeter and area Volume 3-D shapes Probability Real-life graphs Formulae Straight line graphs Angles properties of polygons Year 10 (Higher) Qualification: Edexcel GCSE Mathematics Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Integers and decimals Construction and loci Formulae and linear equations Coordinates Types of number Linear graphs Fractions Patterns and sequences Simultaneous equations Algebra 2-D and 3-D shapes Probability Shape and angles Perimeter and area Ratio and scale Collecting data Fractions, decimals and percentages Averages and range Displaying data Pythagoras and trigonometry Year 11 (Higher) Qualification: Edexcel GSCE Mathematics Term 1 Topics Term 2 Topics Term 3 Topics Trial and Improvement Index notation and surds Revision Surface area and volume Circle theorems Compound measures Sine and cosine rules Transformations Vectors Similarity and Congruence Further graphs and functions Year and subject Quadratic functions, equations and graphs Transformations of functions