MCA2020A01
advertisement
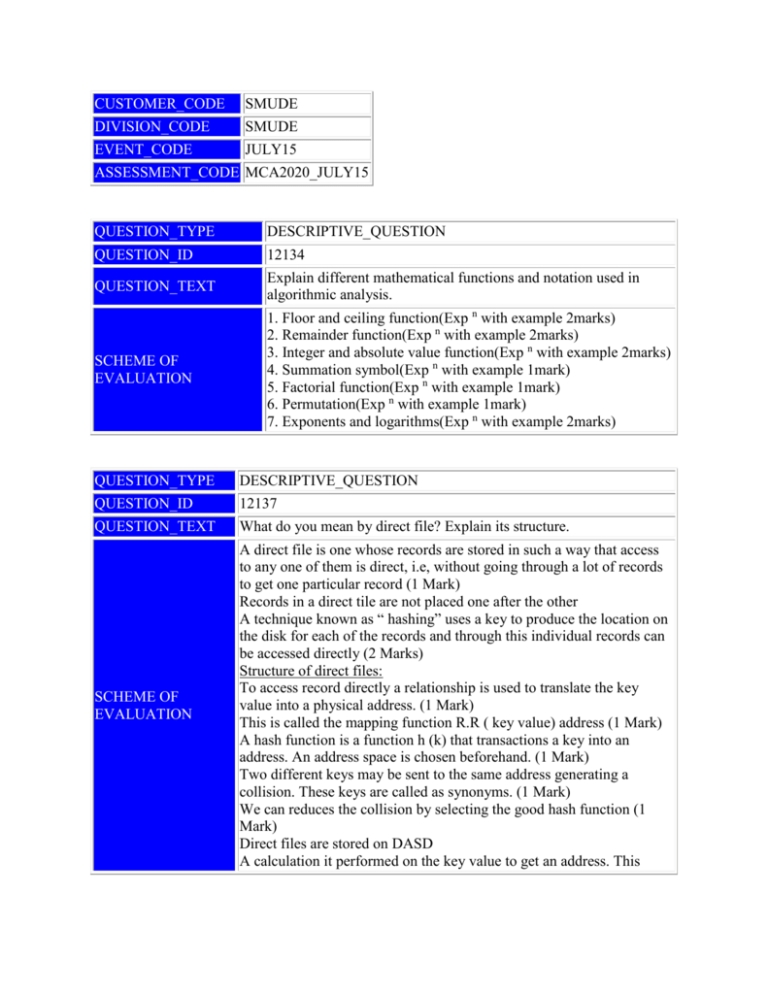
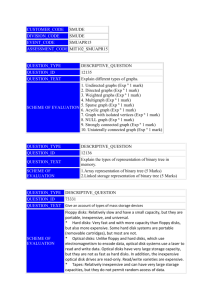
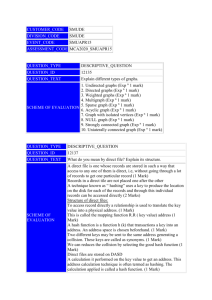
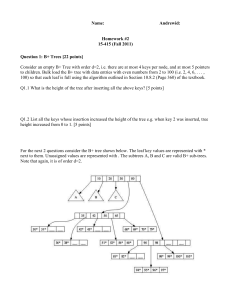
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE EVENT_CODE JULY15 ASSESSMENT_CODE MCA2020_JULY15 QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 12134 QUESTION_TEXT Explain different mathematical functions and notation used in algorithmic analysis. SCHEME OF EVALUATION 1. Floor and ceiling function(Exp n with example 2marks) 2. Remainder function(Exp n with example 2marks) 3. Integer and absolute value function(Exp n with example 2marks) 4. Summation symbol(Exp n with example 1mark) 5. Factorial function(Exp n with example 1mark) 6. Permutation(Exp n with example 1mark) 7. Exponents and logarithms(Exp n with example 2marks) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 12137 QUESTION_TEXT What do you mean by direct file? Explain its structure. SCHEME OF EVALUATION A direct file is one whose records are stored in such a way that access to any one of them is direct, i.e, without going through a lot of records to get one particular record (1 Mark) Records in a direct tile are not placed one after the other A technique known as “ hashing” uses a key to produce the location on the disk for each of the records and through this individual records can be accessed directly (2 Marks) Structure of direct files: To access record directly a relationship is used to translate the key value into a physical address. (1 Mark) This is called the mapping function R.R ( key value) address (1 Mark) A hash function is a function h (k) that transactions a key into an address. An address space is chosen beforehand. (1 Mark) Two different keys may be sent to the same address generating a collision. These keys are called as synonyms. (1 Mark) We can reduces the collision by selecting the good hash function (1 Mark) Direct files are stored on DASD A calculation it performed on the key value to get an address. This address calculation technique is often termed as hashing. The calculation applied is called a hash function. (1 Mark) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 12139 QUESTION_TEXT Explain the 2 types of magnetic disks. Discuss the way of organizing data on magnetic disk. SCHEME OF EVALUATION There are two types of disks: the hard disk & the floppy disk. 1.Hard Disk: Divided into 2 groups ,the disk & the fixed disks -Disk pack contains………protective sulfaces -Disk packs are easily ……….gigabytes -Disk cartridges are …..standard disk packs.(1 mark each 1*3=3 marks)) -Fixed disks: (2 marks) 2.Floppy disks: They come in several sizes………density. Organizing data on disk: Before data ………sectors (1 mark) Tracks: Concentric rings….consecutive number (2 marks) Sectors: Each track ……..entire track. (2 marks) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 73335 QUESTION_TEXT Define AVL tree. Explain the insertion operation on AVL tree. SCHEME OF EVALUATION Definition: 2 Marks A non empty binary tree T is an AVL tree if given TL and TR to be the left and right subtrees of T and h(TL) and h(TR) to be the heights of subtrees TL and TR respectively. TL and TR are AVL trees and h(TL)h(TR)≤1. h(TL)- h(TR) is known as the balance factor which can be either 0, 1 or -1. Insertion operation on AVL tree has 4 scenarios: 2x4=8 Marks Left rotation Right rotation Left right rotation Right left rotation QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 120231 QUESTION_TEXT What is static hashing? Explain linear hashing. SCHEME OF EVALUATION Static hashing Static hashing is a simple form of hashing, where hashing is the technique use mathematical functions to sort incoming data in a speedy and organized fashion. Hashing involves a hashing function, which accepts a piece of incoming data and assigns to that data a specific value; based on that value the data is stored away in a table. Static hashing is a simple form of hashing often used for a temporary solution, until a better form of hashing such as linear hashing or extendible hashing can be used. Its advantage is its relative simplicity compared to other types of hashing. Here hashing is called static because the number of buckets is static, meaning that the number is determined first and remains constant throughout the assembly and use of hash. A simple example of hash function is h(x)=xmod N. this means that the remainder of x divided by N is what is returned. Once this hash value has been determined, the whole piece of data is then sorted into a bucket with a number of other data entries with the same hash value. These buckets usually have a static size as well and they each have overflow buckets in case the first bucket gets full. To locate a particular item, the search information provided is passed through the hash function again, so the search is quickly narrowed down to roughly 1/N of the total pieces of data that might otherwise be searched. The defect in static hashing is the fact that the number of buckets remain static. This means that if all the values tend to produce one particular hash value, all of the data records will go to one bucket, not saving much time. Other methods of hashing allow for the creation of new buckets on the fly, which can be assigned more specific hash values to break down a clump of data. Static hashing is good for speedy data. (5 marks) Linear hashing Linear Hashing is a dynamically updateable disk-based index structure which implements a hashing scheme and which grows or shrinks one bucket at a time. The index is used to support exact match queries, i.e. find the record with a given key. Linear hashing does not use a bucket directory, and when an overflow occurs it is not always the overflow bucket that is split. The name linear hashing is used because the number of buckets grows or shrinks in a linear fashion. Overflows are handled by creating a chain of pages under the overflow bucket. The hashing function changes dynamically and at any given instant there can be at most two hashing functions used by the scheme. Some of the main points that summarize linear hashing are; Full buckets are not necessarily split, and buckets split are not necessarily full. Every bucket will be split sooner or later and so all Overflows will be reclaimed and rehashed. Split points s decides which bucket to split and s is independent to overflowing bucket and at level i , s is between 0 and 2i. s will be incremented at each point if it reaches end it will be reset to 0. (5 marks) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 120237 Define binary tree. Explain the different types of binary tree. QUESTION_TEXT Define (1 mark) Types Skewed binary tree (Explain 3) SCHEME OF EVALUATION 1. 2. Full binary tree (Explain 3) 3. Complete binary tree (Explain 3)