Knowledge_Preparation_UTI_2%5b1%5d
advertisement

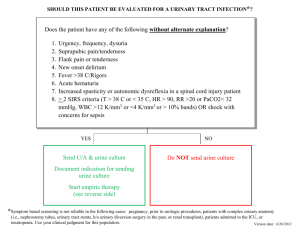
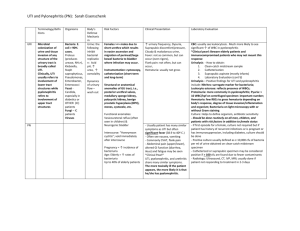
BSN Program Nursing Practice II Knowledge Preparation on Presenting Health Challenges Student__Rebekah Abebe__________ Date_January 25 2010____ Health Challenge/Diagnosis_Urinary Tract Infection____________ ***Please note that this research is standardized for any client with this health challenge and as such, once completed can be re-used with any other client with this specific health challenge. In future semesters, additional knowledge including pathophysiology and diagnostic tests will be expected. Description/Definition (in your own words) Clinical Manifestations Collaborative Care (Medical, Pharmacological, Surgical etc Treatments) Urinary Tract infection occurs when bacteria trespasses into the urinary tract. Specifically bacterial counts 10 by 5 colony-forming units per millilitre or higher typically indicate a clinically significant UTI. -Dysuria Frequent urination (more often then every 2 hours), urgency, and suprapubic discomfort, or pressure. -The urine may contain blood and sediment. -Pain, chills and fever indicate symptoms of an upper urinary tract infection. Suprapubic pain. -In older adults the above symptoms mentioned are not often seen. Instead older adults ten to experience non localized abdominal discomfort. -Older adults will also have cognitive impairment. -Clients over 80 may experience a slight decline in temperature. -Some may have non specific symptoms such as fatigue and anorexia. For minor UTI’s antibiotics given for 1 to 3 days. Example: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra) For more complicated UTI’s antibiotics given for 7 to 14 days or even longer. -Over the counter prescription drugs used to reduce pain and improve comfort associated with a UTI. Some of these medications can tint the colour of urine reddish orange Example: phenazopyridine (Pyridium) or bluish green. Example: combination agent Urised (methanamine, phenylsalicylate, atropine, hyoscyamine). -suppressive antibiotics are sometimes administered to clients who experience repeated UTI’s. Such therapy should only be short term, or negative results will occur such as a higher risk for a UTI due to a suppressed immune system caused by antibiotics. -Adequate fluid intake. -Counselling about risk of recurrence and reduction of risk factors. -Repeat urine culture and sensitivity testing. Sproule/Douglas/NPII/Student Clinical Prep 28/08/2010 Page 1 of 2 BSN Program Nursing Practice II Nursing Management Nursing Assessment Foci: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Implementation Nursing Interventions & Rationales Symptoms -Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia; chills -Lassitude, malaise -Urinary frequency, urgency, hesitancy; nocturia -Suprapubic or low back pain, pressure in bladder area, costovertebral tenderness; bladder spasms, dysuria, burning on urination, sense of incomplete emptying. General Fever Urinary -Hematuria;cloudy, foul-smelling urine; tender, enlarged kidney. 1.)Impaired urinary elimination related to effects of urinary tract infection (UTI) as evidenced by pain and burning or urination and flank, suprapubic, and/ or lower back pain. 1.1 Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain to include location, characteristics, onset and duration, frequency, quality, intensity or severity, and precipitating factors to establish history and baseline pain level. 1.2 Use of nonpharmacological techniques (e.g. heating pad to suprapubic area or lower back, warm showers) along with other relief measures to supplement pain medication and increase pain relief. 2.)Impaired urinary elimination related to urinary tract infection (UTI) as evidenced by bothersome urgency, daytime voiding frequency, nocturia, or hematuria and verbalization of concern over altered elimination pattern. 2.1 Monitor urinary elimination including frequency, consistency, odour, volume, and colour (as appropriate) to assess elimination status. 2.2 If needed Obtain midstream voided specimen for urinalysis (as appropriate) to determine pathogen causing UTI or to monitor effectiveness of treatment. 2.4 Advise client and monitor for signs and symptoms of UTI to monitor effectiveness of treatment and recognize symptoms of recurrence. 2.4 Encourage client to drink 236 mL of liquid meals, between meals, and in early evening to help prevent infection and dehydration. 3. Ineffective Therapeutic regimen management related to lack of knowledge regarding treatment regimen and prevention of recurrent infections as evidenced by response to questions regarding therapeutic management and verbalization of desire to manage treatment of illness and prevent infections. 3.1 Assess client’s current level of knowledge related to specific disease process to plan individualized teaching. 3.2 Describe the reason behind non pharmacological therapy, to promote compliance with treatment. References: It is anticipated that the required textbook Medical-Surgical Nursing in Canada (Lewis et.al., 2010) is used for this research. If other sources are used, please provide a brief list here. Sproule/Douglas/NPII/Student Clinical Prep 28/08/2010 Page 2 of 2