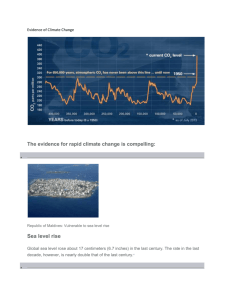
Global Climate Change The Evidence of Climate Change 2.1 Short
advertisement

Global Climate Change The Evidence of Climate Change 2.1 Short Answer Questions 1) Describe four lines of evidence that the climate is warming. Answer: Various answers may include: increasing global air temperature, increased ocean heat content, rising sea levels due to thermal expansion, melting ice sheets, retreating glaciers, earlier spring onset, fewer frost days, melting permafrost, etc. 2) What two factors are causing the rise in sea-level over the past several decades? Explain how each increases sea level. Answer: Thermal expansion and melting ice. Warmer water expands thus raising sea levels. When ice that is located on land melts, it eventually makes its way to the oceans thus adding to the volume of sea water and raising sea levels. 3) Describe two aspects of measured Arctic sea ice that show the Arctic has been warming over the past few decades. Answer: Observed decrease in sea ice extent, thickness, and volume. 4) Antarctica is divided into three regions. List each region and briefly describe the stability of the ice in each region. Answer: East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) which is very stable. West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) which is unstable. Antarctic Peninsula which is very unstable. 5) Describe how melting Arctic permafrost causes a climate positive feedback. Answer: Warming climate melts permafrost which releases methane gas. Methane is a very powerful greenhouse gas. 6) How might melting glaciers influence society? Answer: Various answers may include: rising sea levels, decreased freshwater availability for drinking and irrigation, river flooding, negative impacts on recreation, etc. 7) Why does increasing global temperature increase the frequency and intensity of drought? Answer: Warming climate increases the rate of evaporation from groundwater sources thus increasing the frequency and severity of drought if weather systems do not allow this moisture to return as precipitation. 8) Why does increasing global temperature increase the intensity and frequency of floods? Answer: Warming climate increases the rate of evaporation from groundwater sources thus increasing the water in the atmosphere. With a wetter atmosphere, weather systems will produce greater rainfall rates leading to increased flooding. 9) How is a warming climate expected to affect hurricanes? Answer: An increase in hurricane intensity by as much as 2-11% by 2100 is most likely as the surface temperature of the ocean increases. Warmer water temperatures allow more water vapor to evaporate into a growing storm. When this water later condenses to form rain, it releases latent heat that feeds the intensity of the storm. This added moisture will also result in greater precipitation rates and flooding. 10) What are the only two factors that could have caused the observed warming over the past 100 years? Answer: Increases in solar radiation or increases in heat-trapping greenhouse gases such as CO2. 2.2 True/False Questions 1) Global air temperature change is plotted as actual physical temperature in degrees Celsius— the international standard. Answer: False. Temperature change is plotted as anomalies. 2) The minimum number of years to consider as a base period should be at least ten years. Answer: False. At least 30 years is recommended. 3) The National Weather Service is one of six organizations that publishes global temperature anomaly data. Answer: False. The National Weather Service does not collect or publish this data. 4) The location of a thermometer (high altitude, near airports, in countryside, etc.) greatly influences the long-term temperature anomaly. Answer: False. Actual temperatures may be influenced by siting location but the change is not just as a rising tide lifts all boats equally. 5) Sea surface temperature is a good approximation of air temperatures just above the ocean. Answer: True. 6) Satellite-based and thermometer-based global air temperature anomalies show good agreement. Answer: True. 7) The current rate of warming based on both satellite and thermometer-based measurements is between 1.4-1.7°C/decade. Answer: False. The current rate of warming is between 0.14-0.17°C/decade. 8) The CRU model likely underestimates the amount of global warming due to the way it deals with missing data from the polar regions. Answer: True. 9) The IPCC Fourth Assessment Report suggests that sea levels will rise by as much as 1-2 meters by the year 2100. Answer: False. The IPCC suggested 18 cm-59 cm because it did not include current research pertaining to dynamic ice melt processes however, many experts do expect 1-2 m rise by 2100. 10) Sea level is falling in some regions such as the Eastern Pacific and Western Indian Oceans. Answer: True. 11) The current rate of global sea level rise is about 3.1 mm/year. Answer: True. 12) Melting Arctic and Antarctic sea ice has contributed to significant sea level rise. Answer: False. Sea ice is floating on the water already so melting cannot "add" water. 13) It is possible that the Arctic Ocean could be ice free during summers by the year 2030. Answer: True. 14) If Greenland were to completely melt it would increase sea levels by as much as 7 meters. Answer: True. 15) If Antarctica were to completely melt it would increase sea levels by as much as 21 meters. Answer: False. 61 meters from complete melt. 16) The most unstable portion of Antarctic ice is the Antarctica Peninsula. Answer: True. Section: 2.4 - The Melting Cryosphere Bloom's Taxonomy: #1 - Knowledge Learning Outcome: 2.5 - Predict how the cryosphere will respond to further global warming Pearson Outcomes: G2 17) Melting permafrost can act as a positive climate feedback. Answer: True. 18) Melting glaciers are responsible for about 50% of current global sea level rise. Answer: False. 27%. 19) As increases in greenhouse gases continue, it is expected that days will warm faster than nights. Answer: False. Greenhouse gases do not influence incoming sunlight but do inhibit some heat loss during nights. 20) Climate change can cause both drought and floods. Answer: True. 2.3 Essay Questions 1) While in a conversation at a party, the other person states that global warming is not happening. How would you use your knowledge of the evidence of climate change to convince that person otherwise? Answer: Various correct answers 2) Describe the main factors that cause global sea level to rise and compare modern day rates to that of the rates observed in the early part of the 20th century. Next, compare and contrast the current contribution of sea level rise due to the melting ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica. Finally, what sea level rise is expected if all the ice melted on Greenland? Antarctica? Answer: Various correct answers 3) Describe the various ways scientists measure global temperatures on land and at sea. Explain why climate change temperature data is plotted as temperature anomalies and not as actual temperatures. Answer: Various correct answers 2.4 Visual-based Questions Figure 2.30 1) Refer to figure 2.30 to answer the following questions: a - How has the number of cold nights and cold days changed over the previous few decades? b - How has the number of warm nights and warm days changed over the previous few decades? c - Which is warming greater over time? Days or nights? Is this consistent with an increase in solar radiation? Explain. Answer: a) The number of cold days and nights is decreasing. b) The number of warm days and nights is increasing. c) Nights are warming more than days over time which is not consistent with an increase in solar radiation. The sun can only influence daytime temperatures. Figure 2.31 2) Refer to figure 2.31. a - Which regions of the world are expected to become drier? Name one country that should be planning for severe drought in the decades ahead. b - Which regions are expected to become wetter? Name one country that should be planning for severe flooding in the decades ahead. c - Find your location. Is your location headed for increased drought or flood? Explain. Answer: Various correct answers. 2.5 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The region in the Northern Hemisphere showing the greatest evidence of climate change is: A) Tropics B) Mid-latitude land C) Mid-Latitude ocean D) Arctic Answer: D 2) Stochastic means: A) Cyclical B) Random C) Warming D) Cooling Answer: B 3) If incoming vs. outgoing radiation at the top of the atmosphere is balanced, then climate change is likely due to: A) A decrease in greenhouse gases B) An increase in greenhouse gases C) Internal variability D) Stochastic variability Answer: C 4) The difference in incoming vs. outgoing radiation at the top of the atmosphere is about: A) 0.75 Wm-2 B) -0.75 Wm-2 C) 7.5 Wm-2 D) -7.5 Wm-2 Answer: A 5) If satellites can measure the planet's energy imbalance, why do we still need global thermometer measurements? A) Satellites cannot cover the entire globe. B) Satellites can only measure temperatures during the day. C) Satellites can only measure temperatures during the night. D) The imbalance is at the limit of satellite instrument resolution. Answer: D 6) The minimum number of years for a temperature base period should be at least: A) 10 years B) 30 years C) 50 years D) 100 years Answer: B 7) Which of the following organizations does NOT report global temperature anomaly data? A) The Weather Channel (TWC) B) Goddard Institute for Space Sciences (GISS) C) Climate Research Unit (CRU) D) Remote Sensing Systems (RSS) Answer: A 8) Which of the following organizations uses the longest base period for calculating global temperature anomalies? A) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) B) University of Alabama Huntsville (UAH) C) Climate Research Unit (CRU) D) National Climate Data Center (NCDC) Answer: D 9) Which of the following statements about temperature anomalies is NOT true? A) They are remarkably uniform up to distances of 1,200 km. B) Choosing a different base period will skew the values. C) Location of thermometers will skew the values. D) They are always much smaller in value than actual temperatures. Answer: C 10) The best way to obtain global air temperature just above the oceans is: A) Ship reports B) Buoys C) Satellite data D) All of the above combined Answer: D 11) How do air balloons measure air temperatures? A) On board thermometers B) On board barometers C) On board microwave detectors D) On board satellites Answer: C 12) Which of the following does NOT influence the air temperature inferred from NASA and NOAA satellites? A) Orbital drift B) Sensor variation C) Time of day D) Infrared radiation interference Answer: D 13) The trend in global air temperature increase measured by satellites and ground-based instruments is between: A) 0.10 - 0.13°C per decade B) 0.14 - 0. 17°C per decade C) 0.18 - 0. 21°C per decade D) 0.22 - 0. 25°C per decade Answer: B 14) The largest international data set of global temperatures is maintained by: A) University of Alabama Huntsville (UAH) B) Climate Research Unit (CRU) C) National Climate Data Center (NCDC) D) Goddard Institute for Space Sciences (GISS) Answer: C 15) The Global Historic Climatology Network (GHCN) uses data from as far back as: A) 30 years B) 50 years C) 100 years D) 300 years Answer: D 16) The GHCN-M version 3 data set merged with the ERSST dataset yields global temperature anomalies beginning from: A) 1880 B) 1900 C) 1970 D) 1979 Answer: A 17) The CRU model accounts for missing data in the Arctic by: A) Using satellite data B) Assuming temperature changes proportional to rest of the Northern Hemisphere C) Extrapolating data from the nearest weather stations D) Not reporting anomalies for this region Answer: B 18) The GISS model accounts for missing data in the Arctic by: A) Using satellite data B) Assuming temperature changes proportional to rest of the Northern Hemisphere C) Extrapolating data from the nearest weather stations D) Not reporting anomalies for this region Answer: C 19) The projected sea level rise over the next 100 years by the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report is: A) 1.7 - 3.1 mm B) 18 - 59 cm C) 1 - 2 m D) 6 m or more Answer: B 20) Why are the sea level rise projections of the IPCC NOT reassuring? A) These values would completely submerge Florida. B) These values are likely too high. C) These values are likely too low. D) Rising sea level is a positive feedback to global warming. Answer: C 21) Which of the following does NOT contribute to global sea level rise in the long term? A) Warmer ocean temperatures B) Ice melt C) Growth of undersea mountain chains D) Increased rainfall Answer: D 22) 12,000 years ago at the end of the last glacial advance, sea levels were: A) 120 m higher than today B) 120 m lower than today C) 1 km higher than today D) 1 km lower than today Answer: B 23) Which of following statements is NOT true? A) Southeast England is slowly sinking. B) The Mississippi Delta is slowly sinking. C) East Pacific Ocean sea level is decreasing. D) West Indian Ocean sea level is increasing. Answer: D 24) The current rate of global sea level rise is: A) 1.8 mm/year B) 3.1 mm/year C) 1.8 m/year D) 3.1 m/year Answer: B 25) Most of the observed rise in global sea level in the past 60 years is due to: A) Thermal expansion B) Ice sheet melt C) Glacier melt D) Subsidence Answer: A 26) What percentage of the Earth's surface is covered by permanent ice and snow? A) 17% B) 25% C) 33% D) 50% Answer: A 27) What percentage of global sea level rise is due to the observed melting of land-based ice? A) 27% B) 40% C) 50% D) 67% Answer: B 28) Which of the following statements is NOT true about sea ice? A) Antarctic sea ice growth can double the area of Antarctica. B) Antarctic sea ice is younger than Arctic sea ice. C) Arctic sea ice is growing due to increased snowfall. D) Arctic sea ice is thicker than Antarctic sea ice. Answer: C 29) Arctic sea ice is predicted to be gone during summer as early as the year: A) 2015 B) 2020 C) 2030 D) 2050 Answer: C 30) How long has it been since the Arctic was ice free? A) 100 years B) 1000 years C) 100,000 years D) 1,000,000 years Answer: D 31) The best indicator of the impact of climate change on sea ice is a change in: A) Sea ice extent B) Sea ice thickness C) Sea ice volume D) Sea ice albedo Answer: C 32) Which of the following statements about sea ice is NOT true? A) Annual ice returns every winter and is thin. B) Multi-year ice in the Arctic is now gone. C) Melting sea ice has not increased global sea levels. D) All of the above statements are true. Answer: B 33) Most of the melting Arctic sea ice has been caused by: A) Rising air temperatures B) Changing wind currents C) Changing water currents D) Rising water temperatures Answer: D 34) Greenland's area can be best described as being comparable to: A) Manhattan B) Four times the size of the state of Texas C) The United States D) About 1.5 times the area of the United States Answer: B 35) Much of the ice on Greenland has an age of: A) 1000 years B) 10,000 years C) 100,000 years D) 1,000,000 years Answer: C 36) Average air temperature over Greenland since the year 2000 has risen by about: A) 1°C B) 2°C C) 3°C D) 4°C Answer: C 37) Which satellite is tracking the ice loss of Greenland? A) ICESat B) GRACE C) ICOADS D) ASTER Answer: B 38) Where in Greenland is ice actually increasing? A) North B) South C) West D) Central Answer: D 39) If all the ice on Greenland were to melt, the expected rise in global sea level would rise: A) 3 m B) 6 m C) 7 m D) 21 m Answer: C 40) How long would it take all of Greenland's ice to melt? A) 50 years B) 100 years C) 1000 years D) Many thousands of years Answer: D 41) Which of the following statements about Antarctica is true? A) It is about four times the size of Texas. B) It contains about 90% of the world's freshwater. C) Sea ice growth can add 50% to Antarctica's area. D) All of the above are true. Answer: B 42) If all the ice on Antarctica were to melt, the expected rise in global sea level would rise: A) 3 m B) 7 m C) 21 m D) 61 m Answer: D 43) The East Antarctic Ice Sheet is: A) Grounded on bedrock and considered to be very stable B) Grounded on bedrock and considered to be unstable C) Grounded on ocean floor and considered to be very stable D) Grounded on ocean floor and considered to be unstable Answer: A 44) The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is: A) Grounded on bedrock and considered to be very stable B) Grounded on bedrock and considered to be unstable C) Grounded on ocean floor and considered to be very stable D) Grounded on ocean floor and considered to be unstable Answer: D 45) If the West Antarctic Ice Sheet melted or collapsed, the expected global sea level rise is: A) 1-2 m B) 3-4 m C) 5-6 m D) 10 m or greater Answer: C 46) The Larsen B Ice Shelf collapsed from the: A) Antarctic Peninsula B) West Antarctic Ice Sheet C) East Antarctic Ice Sheet D) Greenland Answer: A 47) Why do collapsing ice shelves concern scientists? A) They add to global sea level rise. B) They hold back ice flow from the interior. C) They slow ice streams. D) They can increase global warming. Answer: B 48) What percentage of the world's landmass is affected by permafrost? A) 10% B) 20% C) 30% D) 40% Answer: B 49) Melting permafrost: A) Releases methane, a powerful greenhouse gas B) Releases CO2 C) Causes a positive feedback mechanism for warming D) All of the above Answer: D 50) Which factor is the most important control on glacier size? A) Winter temperatures B) Winter precipitation C) Summer temperatures D) Summer precipitation Answer: C 51) Which of the following statements about glaciers is most accurate? A) All glaciers are melting. B) Very few glaciers are advancing. C) Glaciers are causing a majority of sea level rise. D) Before satellites, very few glaciers were accurately measured. Answer: B 52) How much has glacier melt contributed to global sea level rise since 1900? A) 27% B) 33% C) 42% D) 57% Answer: A 53) Which satellite is tracking the ice loss from mountain glaciers? A) ICESat B) GRACE C) ICOADS D) ASTER Answer: D 54) Climate change has resulted in: A) More intense heat waves B) Stronger floods C) More serious fires D) All of the above Answer: D 55) Which statement about observed climate change is true? A) Daytime temperatures have warmed the most. B) Evening temperatures have warmed the most. C) Ocean temperatures have warmed the most. D) Low latitude locations have warmed the most. Answer: B 56) How much has precipitation increased in the United States since 1900? A) 0% B) 10% C) 25% D) 50% Answer: B 57) Which region of the United States is expected to experience the greatest flooding due to climate change? A) Upper Midwest B) Southeast C) Southwest D) West Coast Answer: A 58) Which region of the United States is expected to experience the greatest drought due to climate change? A) Upper Midwest B) Southeast C) Southwest D) West Coast Answer: C 59) Which of the following world regions is NOT expected to experience increased drought? A) Northern Mexico B) Amazon Basin C) Mediterranean D) Northwestern Australia Answer: D 60) Which of the following changes is expected for Atlantic hurricanes in a warmer world? A) Greater intensity B) Greater rainfall C) Greater storm surge D) All of the above Answer: D 61) Which of the following inhibits hurricane formation and strength? A) El Niño B) Warm SST C) AMO D) None of the above Answer: A 62) Given our current understanding about climate change and hurricanes, which statement below is most accurate? A) Hurricane Katrina was caused by global warming. B) Hurricane Katrina was influenced by global warming. C) Hurricane Katrina could not have occurred without global warming. D) Sea level rise made Hurricane Katrina's winds blow 2-11% faster. Answer: B 63) Which of the following is most certain in a future warming world? A) Increased fires B) Increased frequency of hurricanes C) West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse D) Rising global sea level Answer: D 64) Which of the following would NOT be evidence for manmade global warming? A) Nights warming faster than days B) Winters warming faster than summers C) Interior locations warming faster than coastal locations D) High latitudes warming faster than low latitudes Answer: C 65) If emission of CO2 were stopped today which of the following is likely to occur in the short term? A) Global air temperatures will continue to rise. B) Glaciers will continue to melt. C) Sea level will continue to rise. D) All of the above Answer: D