أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة
advertisement
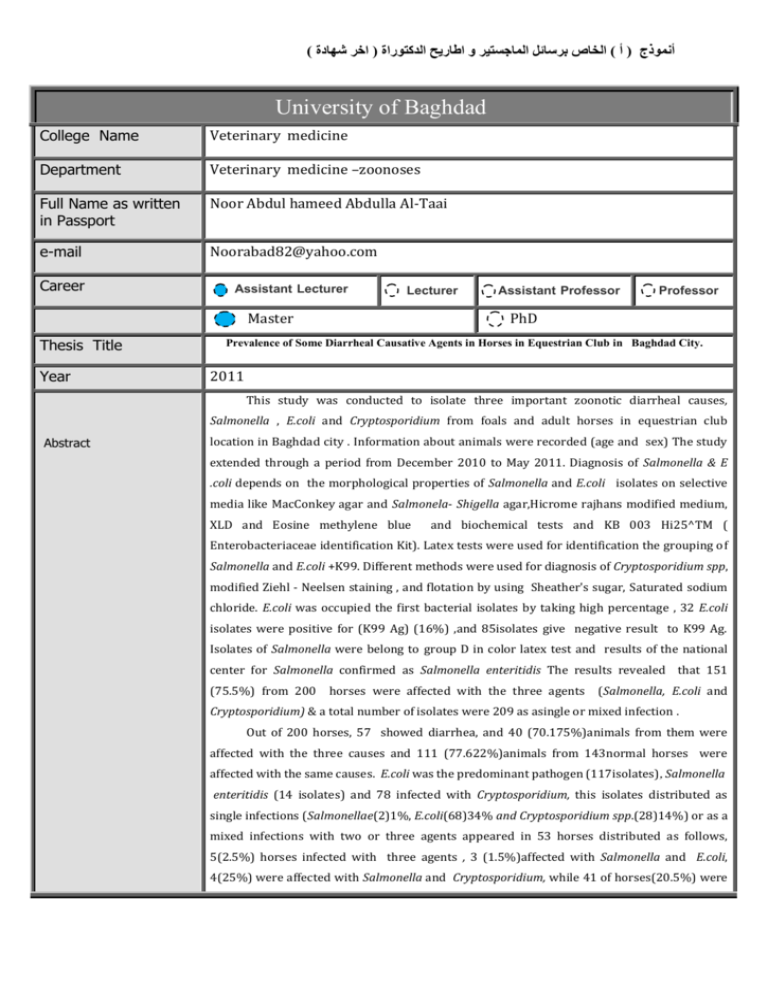
) أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة University of Baghdad College Name Veterinary medicine Department Veterinary medicine –zoonoses Full Name as written in Passport Noor Abdul hameed Abdulla Al-Taai e-mail Noorabad82@yahoo.com Career Assistant Lecturer Lecturer Master Thesis Title Year Assistant Professor Professor PhD Prevalence of Some Diarrheal Causative Agents in Horses in Equestrian Club in Baghdad City. 2011 This study was conducted to isolate three important zoonotic diarrheal causes, Salmonella , E.coli and Cryptosporidium from foals and adult horses in equestrian club Abstract location in Baghdad city . Information about animals were recorded (age and sex) The study extended through a period from December 2010 to May 2011. Diagnosis of Salmonella & E .coli depends on the morphological properties of Salmonella and E.coli isolates on selective media like MacConkey agar and Salmonela- Shigella agar,Hicrome rajhans modified medium, XLD and Eosine methylene blue and biochemical tests and KB 003 Hi25^TM ( Enterobacteriaceae identification Kit). Latex tests were used for identification the grouping of Salmonella and E.coli +K99. Different methods were used for diagnosis of Cryptosporidium spp, modified Ziehl - Neelsen staining , and flotation by using Sheather's sugar, Saturated sodium chloride. E.coli was occupied the first bacterial isolates by taking high percentage , 32 E.coli isolates were positive for (K99 Ag) (16%) ,and 85isolates give negative result to K99 Ag. Isolates of Salmonella were belong to group D in color latex test and results of the national center for Salmonella confirmed as Salmonella enteritidis The results revealed that 151 (75.5%) from 200 horses were affected with the three agents (Salmonella, E.coli and Cryptosporidium) & a total number of isolates were 209 as asingle or mixed infection . Out of 200 horses, 57 showed diarrhea, and 40 (70.175%)animals from them were affected with the three causes and 111 (77.622%)animals from 143normal horses were affected with the same causes. E.coli was the predominant pathogen (117isolates), Salmonella enteritidis (14 isolates) and 78 infected with Cryptosporidium, this isolates distributed as single infections (Salmonellae(2)1%, E.coli(68)34% and Cryptosporidium spp.(28)14%) or as a mixed infections with two or three agents appeared in 53 horses distributed as follows, 5(2.5%) horses infected with three agents , 3 (1.5%)affected with Salmonella and E.coli, 4(25%) were affected with Salmonella and Cryptosporidium, while 41 of horses(20.5%) were ) أنموذج ( أ ) الخاص برسائل الماجستير و اطاريح الدكتوراة ( اخر شهادة effected with E.coli and Cryptosporidium ; 49(24%) of horses showed negative results to these agents. All age groups of horses 7days-12 years were showed a significant difference in the infection rate with these causes. As single or mixed ,and the age group 7days-6 months, gave the highest infection rate with E.coli (+ve K99 ). The highest infection with E. coli recorded at January &February while the highest percentage of infection with Salmonella & Cryptosporidium occurred during February and March with a significant differences at (P < 0.05) in different months Regarding the relation between sex of animals and distribution of causes, infection with E.coli in females appeared higher than in males and mixed infection showed significant differences (P < 0.05), while infection of Cryptosporidium in males higher than in females. The antimicrobial sensitivity test of the Salmonella enteritidis isolates against antibiotics drugs revealed that all isolates were resistant to erythromycin, nitrofurantion, ceftxime and oxytetracycline, While most of the isolates were highly sensitive against chloromphenicol, cefotaxime, trimetheprime, gentamycin ,ciprofloxacine, amoxicillin and cephlaxin. Pathogenic E.coli (+K99) was highly resistant (100%) to erythromycin, oxytetracycline, ceftxime ,cloromphenicol, cefotaxime, ( trimetheprime, gentamycin ,ciprofloxacine, amoxicillin, and cephlaxin antibiotics but it has intermediate sensitive to ciprofloxacin and nitrofurantion. Isolates of E.coli (-K99) showed (100%) resistance to four antimicrobial drugs ( erythromycin, oxytetracycline, amoxicillin and ,ceftxime), and 100% sensitive to ciprofloxacine.