ZIRVE UNIVERSITY, 2010-2011 ACADEMIC YEAR GRAMMAR
advertisement

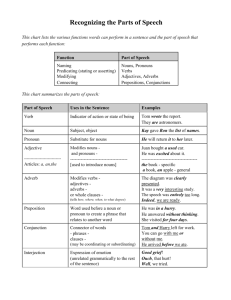
ZIRVE UNIVERSITY, 2010-2011 ACADEMIC YEAR GRAMMAR OBJECTIVES FOR LEVEL C 1 Week Fundamentals of English Grammar Teach Special PRESENT AND PAST, SIMPLE AND PROGRESSIVE Simple Present Present Progressive Non-progressive verbs Simple past Regular and irregular verbs Regular verbs: pronunciation of –ed endings Past progressive Past Time Clauses when/while, before, after, as soon as, until PRE. PERFECT AND PERF. PROG. Present Perfect Present perfect vs simple past Present Perfect progressive 2 3 MODALS, PART 1 Ability: can/be able to, Possibility: may/might/could+present inf. Advice-Criticism: should/ought to/ had better +present inf. Necessity-Obligation: have to, must, have got to, Absence of Necessity: needn’t/don’t have to/don’t need to+V1 Prohibition: mustn’t, can’t Asking for Permission: can I/could I/may I Giving or refusing permission: may/can - may not/cannot Logical assumptions: can’t/couldn’t+present infinitive, must+present inf. Talking about permission: be allowed to - was/were allowed to MODALS PART2 Requests-Offers-Suggestions: Can you/Will you/Could you/Would you Suggestions: Shall I/we - Let’s+V1 - Why don’t we..? Ability in the past: could/was able to Possibility in the past: may/might/could+perfect infitive Advice-Criticism in the past: should/ought to+perfect inf. Necessity-Obligation in the past: had to Absence of Necessity in the past: didn’t need to/didn’t have to Logical assumptions in the past: can’t/couldn’t+perfect infinitive must+perfect inf As these topics were covered in the previous levels you should focus more on doing exercise and activities than presenting the subjects. FUTURE TIME Simple future: will and be going to will vs. be going to Expressing the future in time clauses when/while, before, after, as soon as, until, if Future Progressive We don’t have a certain book for these topics, but the necessary PPTs to explain the rules, worksheets, games, and other activities are in the shared drive. We don’t have a certain book for these topics, but the necessary PPTs to explain the rules, worksheets, games, and other activities are in the shared drive. As these topics were covered in the previous levels you should focus more on doing exercise and activities than presenting the subjects. In the shared drive, we have a presentation explaining the Present Modals named “Presentation of Present Modals” and a list of all modals named “Present and Past Modals”. We don’t have a certain book for these topics, but the necessary PPTs to explain the rules, worksheets, games, and other activities are in the shared drive. In the shared drive, we have a presentation explaining the Present Modals named “Presentation of Past Modals” and a list of all modals named “Present and Past Modals”. 4 Chapter 10: THE PASSIVE 10-1: Active and passive sentences 10-2: Form of the passive 10-3: Transitive and intransitive verbs 10-4: Using the by phrase 10-5: The passive forms of the present and past progressive 10-6: Passive modal auxiliaries 5 Chapter 11: COUNT/NONCOUNT NOUNS AND ARTICLES 11-2: Count and noncount nouns 11-3: Noncount nouns 11-5: Using several, a lot of, many/much, a few/ a little 11-6: Nouns that can be count or noncount 11-7: Using units of measures with noncount nouns 11-8: Guidelines for articles usage 11-9: Using the or no article with names 6 Chapter 12: ADJECTIVE CLAUSES 12-1: Adjective Clauses: introduction 12-2: Using who and whom in adjective clauses 12-3: Using who, whom and that in adjective clauses 12-4: Using which and that in adjective clauses 12-5: Singular and plural verbs in adj clauses 12-6: Using prepositions in adjective clauses 12-7: Using whose in adjective clauses 7 Chapter 14: NOUN CLAUSES 14-1: Noun Clauses: introduction 14-2: Noun clauses that begin with a question word 14-3: Noun clauses with who, what, whose + be 14-4: Noun clauses that begin with if or whether 14-5: Noun clauses that begin with that