TEST C: Light and Optics Chapter 5 CP Physics Burns
advertisement
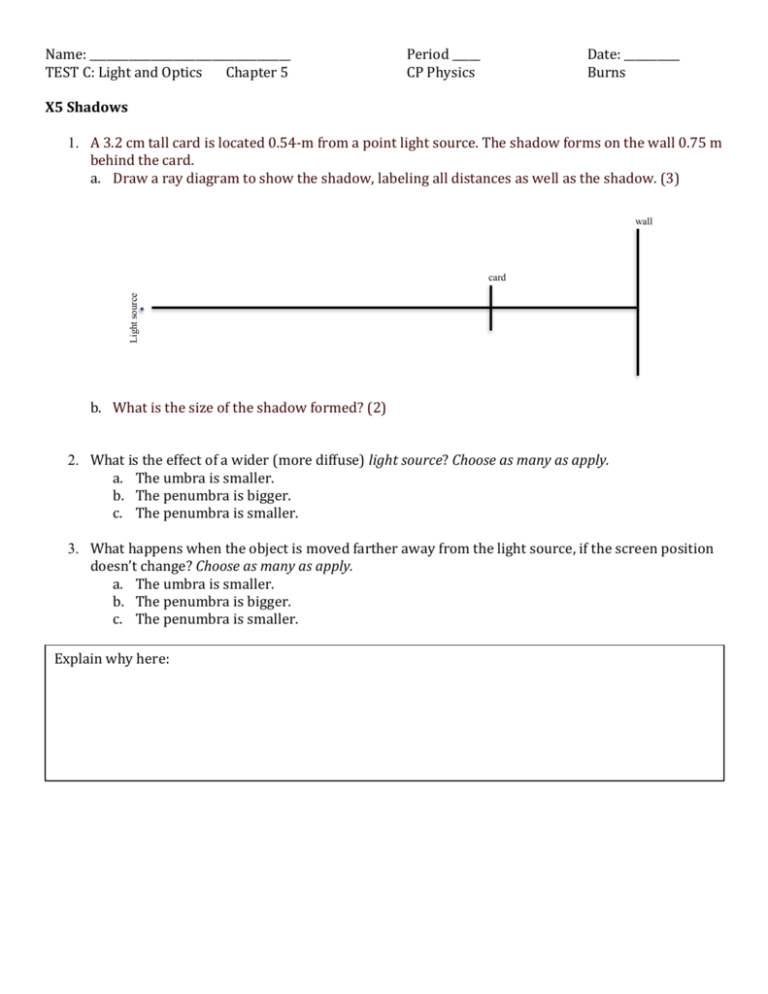
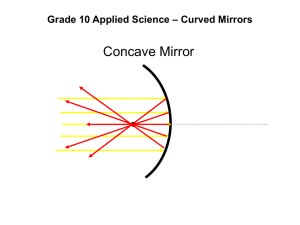
Name: ____________________________________ TEST C: Light and Optics Chapter 5 Period _____ CP Physics Date: __________ Burns X5 Shadows 1. A 3.2 cm tall card is located 0.54-m from a point light source. The shadow forms on the wall 0.75 m behind the card. a. Draw a ray diagram to show the shadow, labeling all distances as well as the shadow. (3) wall Light source card b. What is the size of the shadow formed? (2) 2. What is the effect of a wider (more diffuse) light source? Choose as many as apply. a. The umbra is smaller. b. The penumbra is bigger. c. The penumbra is smaller. 3. What happens when the object is moved farther away from the light source, if the screen position doesn’t change? Choose as many as apply. a. The umbra is smaller. b. The penumbra is bigger. c. The penumbra is smaller. Explain why here: 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 = 𝑑𝑠 𝑠 𝟏 𝒇 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 𝒉 𝒅 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 X6 Plane Mirrors 4. An object is placed at position X as shown in the diagram, and a person is looking at the image from position Y. At what position will the image of the object appear to be? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 5. The diagram to the right demonstrates how light travels from an object location to an eye location when the image of the object is viewed in a plane mirror. a. Label the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection on the diagram. b. Use a ruler and a protractor to prove the Law of Reflection. 6. The diagram to the right shows the top view of an object (the arrow) placed in front of a plane mirror. a. Use a ruler and a protractor to locate the image of the object in the mirror. Use at least 2 lines in order to locate the head and the tail of the image. b. If the plane mirror could be bent to form a convex mirror, what would happen to the size of the arrow? c. If the plane mirror was replaced with a concave mirror of focal length f, where should the object be placed in order to create a real image that is the same exact size? 7. 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 = 𝑑𝑠 𝑠 𝟏 𝒇 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 𝒉 𝒅 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 X7 Curved Mirrors 8. A ray diagram for an object in front of a concave mirror is shown to the right. Which of the following sign combinations must be true for the image distance and for the image height as shown in this diagram? a. + di and + hi b. + di and - hi c. - di and - hi d. - di and + hi 9. Wording on the mirror on the passenger side of an automobile reads “Objects in the mirror may be closer than they appear.” This is because the image of an object seen in the mirror is smaller than would normally be expected. The image is not inverted. a. This mirror can only be a plane mirror. b. This mirror can only be a concave mirror c. This mirror can only be a convex mirror d. This mirror could be either a convex mirror or a concave mirror e. This mirror could be any type of mirror, depending on the viewing angle. 10. A 1.2-cm tall object is placed 15.0 cm from a concave mirror having a focal length of 5.0 cm. (8) a. Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of the image. This does not have to be to scale. b. Calculate the image distance. c. Calculate the image height. 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 = 𝑑𝑠 𝑠 𝟏 𝒇 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 𝒉 𝒅 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 X8 Refraction 11. What is the index of refraction? a. A value that provides a measure of the relative speed of a light wave in a particular medium. b. A property of light c. The slope of the graph of the angle of incidence vs. the angle of refraction. d. The slope of the graph of the angle of reflection vs. the angle of incidence. e. None of the above. 12. A laser beam enters an acrylic block as shown in the diagram. When the light beam exits the block, it will travel along the path labeled a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 13. A beam of light traveling in a medium with index of refraction of 1.45 has an angle of incidence of 30.0º when it leaves the medium, entering air which has an index of refraction of 1.00. a. Draw a ray diagram showing this situation. (3) b. What is the angle of refraction of the beam inside the medium? (2) c. What is the critical angle between this medium and the air? 14. Suppose a new material is discovered that is completely transparent so that you cannot see a beam of light as it passes through the material. If a sample of this material has parallel faces similar to the acrylic block used in Section 8, design an experiment to measure the index of refraction of this sample. Include in your description a. The equipment you will need. b. How you will make the measurements you need (a drawing may be helpful). c. How you will use your measurements to calculate the index of refraction? 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 𝟏 = 𝑑𝑠 𝒇 𝑠 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 𝒉 𝒅 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 X9 Lenses 15. A ray diagram for an object in front of a convex mirror is shown to the right. Which of the following sign combinations must be true for the image distance and for the image height as shown in this diagram? a. + di and + hi b. + di and - hi c. - di and - hi d. - di and + hi 16. A man starts from a distance and begins to approach a convex lens that forms a real image of him on a screen. He gets closer and closer to the lens until his image disappears. As he nears the lens, his image a. Gets larger until he reaches the focal point. b. Gets larger until he reaches the lens. c. Is right-side up until he reaches the lens. d. Is right-side up until he reaches the focal point. 35. A 1.4-cm tall object is placed 7 cm from a converging lens that has a focal length of 12 cm. (8)Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of the image. 2F’ F’ b. Calculate the image distance. c. Calculate the image height. 17. A students investigating the relationship between the object distance and the real distance formed by a convex lens took the following data: a. From the data, determine the focal length of the lens. b. When the object is 60 cm from the lens, is the image formed larger, smaller, or the same size as the object? c. When the object is 30 cm from the lens, is the image right side up or inverted? F 2F 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 = 𝑑𝑠 𝑠 𝟏 𝒇 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 18. The graph shows the object distance vs. the image distance for convex lens. According to the graph, what is the focal length of the lens? 𝒉 𝒅 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 𝑆𝑝 𝑑𝑝 𝑆 𝟏 = 𝑑𝑠 𝒇 𝑠 𝟏 𝟏 𝒐 𝒊 =𝒅 +𝒅 𝒉 𝒅 𝑴 = 𝒉 𝒊 = − 𝒅𝒐𝒊 𝒐 n1sin θ1 = n2sin θ2 X10 Color 19. In order to create the illusion of partial invisibility in stage productions, an actor who is dressed entirely or partly in dark blue is illuminated with a red spotlight. The result is that parts of the performer will seem to “magically” disappear. This special effect works because a. Dark blue reflects red light to the audience. b. Dark blue absorbs red light but does not reflect any red light. c. Red light gives a dark blue shadow behind the performer. d. Dark blue light and red light form yellow light. 20. Two point light sources, green and red, shine onto a screen. A cyan filter is placed in between the lights and the screen. Using a ruler, show the light rays and label the colors formed. Explain what colors you see and why. Screen Red Source Green Source Cyan Filter