Post-Visit Activity #1 What is Your Water Footprint?
advertisement

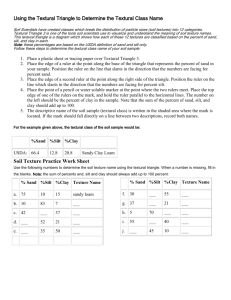
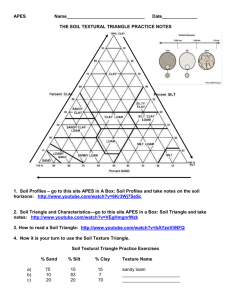
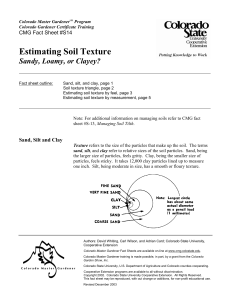
Post-Visit Activity #1 What is Your Water Footprint? NC Essential Standards: 3.E.2.1 Compare Earth’s saltwater and freshwater features (including oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ponds, streams, and glaciers). (using models or three dimensional diagrams) 3.G.1.3 Exemplify how people adapt to, change and protect the environment to meet their needs. 3C&G.2.2 Exemplify how citizens contribute to the well-being of the community’s natural environment. Materials needed: Internet connection Estimated time: Approximately one hour Ask students how much of the Earth’s surface is water (about 70%), and how much is land (about 30%). Explain that of all the water on Earth, 97% is saltwater. Two percent of the water on earth is frozen in glaciers and in polar icecaps. The remaining one percent is groundwater and surface water – aquifers, rivers, lakes, ponds and streams. Demonstrate what the percentages look like by drawing a pie chart or by using 100 of any type of item on hand – marbles, blocks, etc. How much of that water can we use? Thinking about the features of saltwater, glaciers, aquifers and rivers ask them which of these has water that is available for us to use. Explain that scientists estimate that .003 - .33% of water on earth is accessible to us. Why so little? Saltwater is very difficult to desalinate, glaciers are too far away, some surface and groundwater is too polluted to use and some groundwater is too deep to reach. Ask students what we use water for everyday. Drinking, cleaning and cooking should come up quickly. But what about the water used to grow the wheat or corn in the cereal they had for breakfast? Or to grow the cotton for the jeans they are wearing? Using the information on Cape Fear Public Utility Authority’s “What is your Water Footprint?” handout on the following page or by visiting the webpage listed on the handout, have students estimate how many gallons of water were used for the clothes they are wearing today, the food they will eat today and the paper they will use today. Visit www.gracelinks.org/about for more examples of how much water is needed to make various items. Ask students what they can do to reduce their water footprint, and why it’s important. Post-Visit Activity #2 Pollination NC Essential Standards: 3.L.2.1 Remember the function of the following structures as it relates to the survival of plants in their environments: Roots – absorb nutrients Stems – provide support Leaves – synthesize food Flowers – attract pollinators and produce seeds for reproduction Materials Needed: A journal or clipboard for each student Time: 30 minutes Pollinators are everywhere! Take students on a walk around the school grounds. Each student should have a journal or a clipboard to write and draw in. Use the following prompts and questions to guide your exploration. Look for flowers and have students draw one or two, showing the elements of a flower related to pollination. Notice differences in the shape, texture and orientation of stems and leaves. Look for pollinators. Do some flowers have more pollinators on them than others? How many pollinators can they find? Can they find any seeds? Have students write down how they think the flower was pollinated, using words like stamen, anther, egg and pollen. Post-Visit Activity #3 Soil Texture Triangle Name ______________________________________ Date ___________________________ Soil is made of up lots of particles that are divided into three categories based on their size. Soil particles are measured using millimeters, or mm. Some particles are so small, we can’t see them without a microscope! The types of particles help determine how well plants grow. These soil particles can be found in many different combinations, creating lots of different soil textures and types. Scientists have created a “soil texture triangle” to categorize and name these combinations. Using the soil texture triangle below, answer the following questions. 1) 2) 3) What type of soil is 65% silt, 10% sand and 30% clay? What type of soil is 80% silt, 50% sand and 20% clay? 1) What type of soil is 65% silt, 10% sand and 30% clay? What type of soils is 30% silt, 50% sand and 70% clay? 2) What type of soil is 80% silt, 50% sand and 20% clay? ____________ ____________ ______ ____________ ______ Bonus Question: People in a variety of jobs use the soil texture triangle. For instance, an engineer might use it to determine if a road can be built in a certain area. What other kinds of jobs do you think would use the soil texture triangle?