Gene Descriptions
advertisement

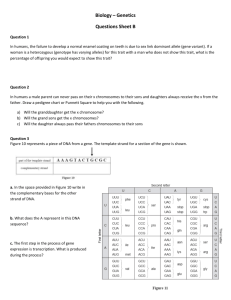
Vocab Chromosome Gene Allele Trait Gamete Haploid Diploid Homologous chromosomes Autosome Sex chromosome Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous Carrier Dominant Recessive Incompletely dominant Co-dominant X-linked Epistasis Polygenic Cross Test cross Linked Genes Crossing over Recombination X-inactivation Epigenetics Use a 6-sided die to determine some of your creature’s genotypes. Roll twice for each gene (one for each chromosome) and write the allele letters on your paper chromosomes BOLDLY! Leave unused genes blank. Genes B, R, T, W: B, R, T, W = 1, 2, 3 b, r, t, w = 4, 5, 6 Gene E E = 1, 2 eh = 3, 4 e = 5, 6 Gene L Lr = 1 Lg = 2,3 Ly = 4 Gene I IA 1, 2 IB 3, 4 i = 5, 6 Gene XE XE = 1, 2, 3 Xe = 4, 5, 6 Gene G: G = 1, 2, 3 g = 4, 5, 6 (If you roll gg, the creature dies before birth; pretend that didn’t happen and reroll) l = 5, 6 Gene Descriptions: Gene B codes for a protein that is a brown pigment in the iris (the colored part of the eye), Gene R codes for a protein that is a green pigment in the iris. Recessive alleles, (b) or (r), do not produce a functional protein. If both brown and green pigments are present, eyes will be colored hazel. If no pigment is present, eyes will be colored blue. Gene E codes for a protein that is required for cells to make colored pigments. This gene controls body color expression (3 possible alleles, each completely dominant over the next). E full color > eh “Himalayan” pattern (the protein only functions at colder temperatures: nose, ears, hands, feet) > e no color. Gene G codes for a protein growth factor: normal size (GG), dwarfism (Gg), lethal (gg) Gene I codes for proteins that are on the outside of red blood cells (your body will attack the proteins if it does not recognize them) IA/ IA or IA /i = “Blood type A” IA /IB = “Blood type AB” IB/IB or IB/i = “Blood type B” ii = “Blood type O” Gene L codes for a protein pigment on the body (4 possible alleles: red, blue, and yellow are equally dominant over white) Lr red = Lb blue = Ly yellow > l white Note: combinations of primary colors result in secondary colors (e.g. red + yellow = orange, etc.) Gene T codes for a protein pigment in the nails/claws: black (T_), colorless (tt) Gene W codes for the oxytocin receptor, which produces feelings of love and bonding when activated by oxytocin. The recessive allele (w) produces a dysfunctional protein. Homozygous recessive (ww) individuals are less dedicated to their mates than heterozygous (Ww) individuals. Gene SRY (“Sex-determining Region of the Y Chromosome) codes for a protein that triggers development of male gonads, which produce testosterone (a hormone that controls other male traits) Gene XE codes for a red photopigment used in the eye to distinguish between red and green. Without at least 1 copy of this gene, the creature can see yellows and blues, while greens and reds both appear brown. Chromosome Project: Step 0: Set up paper chromosomes -Cut them out, randomly select alleles, and label each of them on their backs. -Pick the sex of your creature. A female will have two of chromosome 1, two of chromosome 2, and two X chromosomes. A male will have one X chromosome and the Y chromosome instead of the second X chromosome. Put that leftover sex chromosome away. Your creature should have 6 chromosomes now. Note: We will define the vocab words as we go. Define them and use your paper chromosomes for examples.